Large language models (LLMs) have come to dominate the field of natural-language processing, so it’s no surprise that they also dominate the research that Amazon scientists are presenting at this year’s Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural-Language Processing (EMNLP). LLM training is the topic with the greatest number of Amazon papers, followed closely by strategies for mitigating misinformation in LLMs’ outputs — including but not limited to hallucinations. At the same time, a number of papers apply LLMs to topics of traditional interest at Amazon, such as speech, recommender systems, and information retrieval. (Papers marked with asterisks were accepted to Findings of EMNLP.)
AI agents
MARCO: Multi-agent real-time chat orchestration
Anubhav Shrimal, Shervin Malmasi, Kriti Biswas, Swarnalatha Raghuraman, Anish Nediyanchath, Yi Zhang, Promod Yenigalla
Code generation
CodeFort: Robust training for code generation models
Yuhao Zhang, Shiqi Wang, Haifeng Qian, Zijian Wang, Mingyue Shang, Linbo Liu, Sanjay Krishna Gouda, Baishakhi Ray, Murali Krishna Ramanathan, Xiaofei Ma, Anoop Deoras
Socratic human feedback (SoHF): Expert steering strategies for LLM code generation
Subramanian Chidambaram, Erran Li, Min Bai, Xiaopeng LI, Kaixiang Lin, Xiong Zhou, Alex C. Williams
Structured object language modeling (SoLM): Native structured objects generation conforming to complex schemas with self-supervised denoising
Amir Tavanaei, Kee Kiat Koo, Hayreddin Ceker, Shaobai Jiang, Qi Li, Julien Han, Karim Bouyarmane
Contrastive decoding
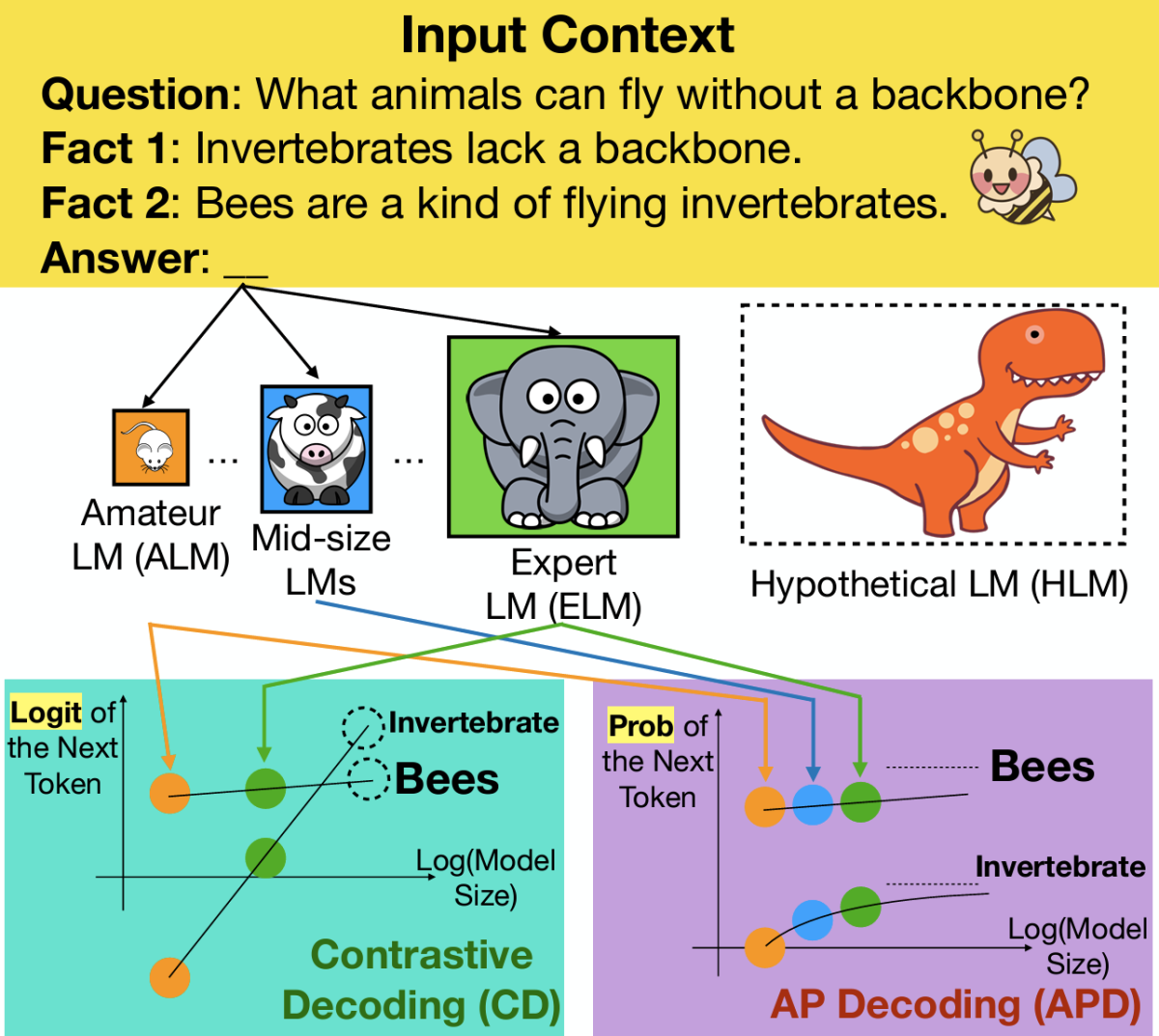
Explaining and improving contrastive decoding by extrapolating the probabilities of a huge and hypothetical LM
Haw-Shiuan Chang, Nanyun Peng, Mohit Bansal, Anil Ramakrishna, Tagyoung Chung
Data integration
ASTRA: Automatic schema matching using machine translation
Tarang Chugh, Deepak Zambre
Learning from natural language explanations for generalizable entity matching
Somin Wadhwa, Adit Krishnan, Runhui Wang, Byron C. Wallace, Chris (Luyang) Kong
Pretraining and finetuning language models on geospatial networks for accurate address matching
Saket Maheshwary, Arpan Paul, Saurabh Sohoney
Retrieval augmented spelling correction for e-commerce applications
Xuan Guo, Rohit Patki, Dante Everaert, Christopher Potts
Dataset distillation
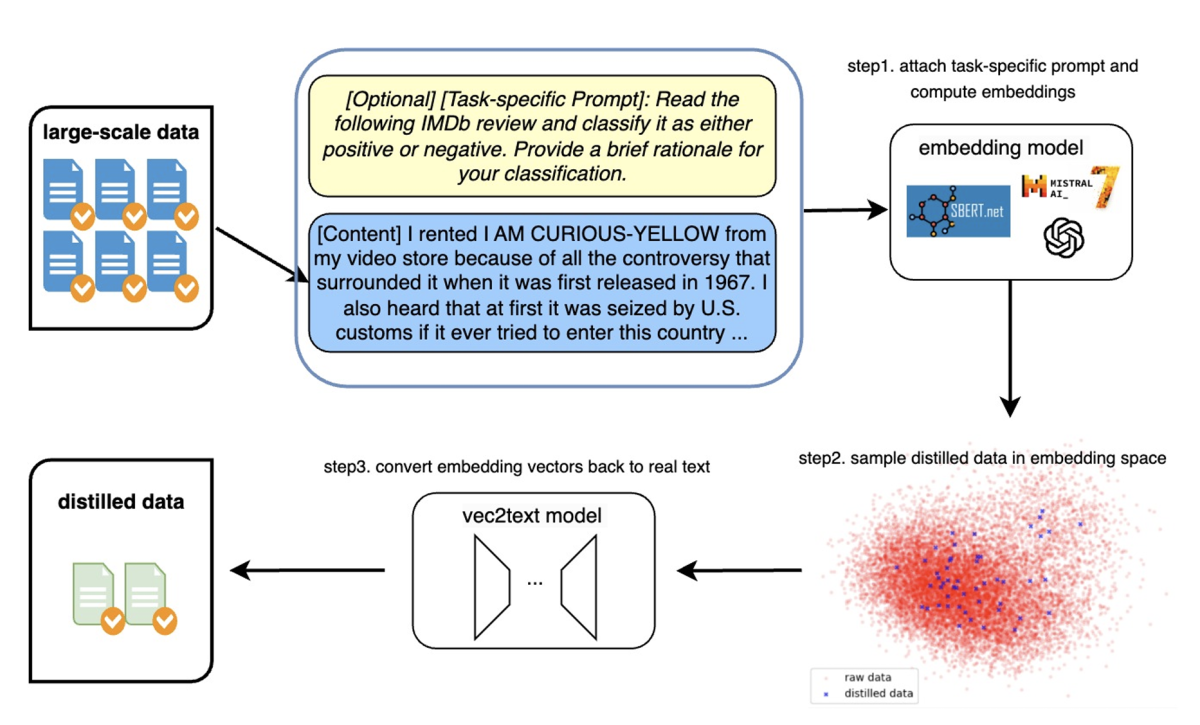
Textual dataset distillation via language model embedding
Yefan Tao, Chris (Luyang) Kong, Andrey Kan, Laurent Callot
Document understanding
DocKD: Knowledge distillation from LLMs for open-world document understanding models
Sungnyun Kim, Haofu Liao, Srikar Appalaraju, Peng Tang, Zhuowen Tu, Ravi Kumar Satzoda, R. Manmatha, Vijay Mahadevan, Stefano Soatto
Information retrieval
Evaluating D-MERIT of partial-annotation on information retrieval
Royi Rassin, Yaron Fairstein, Oren Kalinsky, Guy Kushilevitz, Nachshon Cohen, Alexander Libov, Yoav Goldberg
Identifying high consideration e-commerce search queries
Zhiyu Chen, Jason Choi, Besnik Fetahu, Shervin Malmasi
Learning when to retrieve, what to rewrite, and how to respond in conversational QA*
Nirmal Roy, Leonardo Ribeiro, Rexhina Blloshmi, Kevin Small
Natural-language understanding
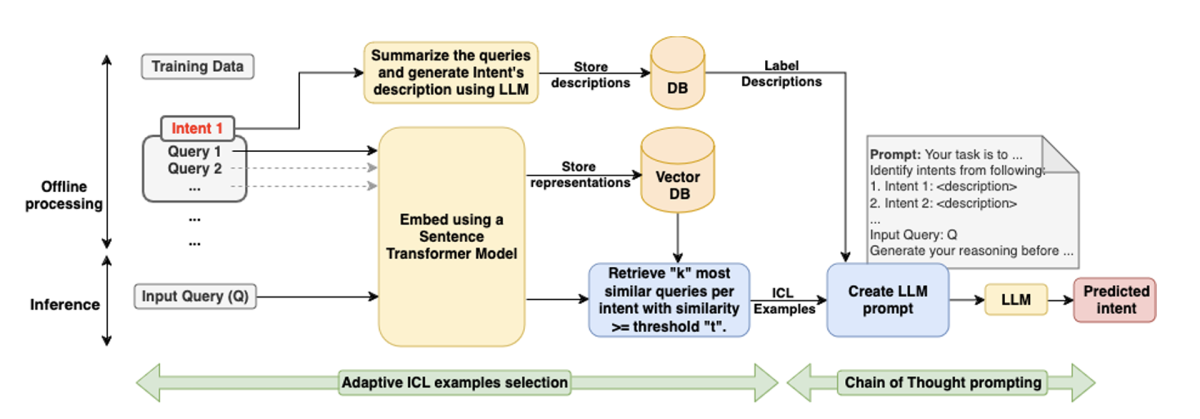
Intent detection in the age of LLMs
Gaurav Arora, Shreya Jain, Srujana Merugu
Predicting entity salience in extremely short documents
Ben Bullough, Harrison Lundberg, Chen Hu, Weihang Xiao
LLM evaluation
AXCEL: Automated eXplainable consistency evaluation using LLMs*
P Aditya Sreekar, Sahil Verma, Suransh Chopra, Sarik Ghazarian, Abhishek Persad, Narayanan Sadagopan
Precise model benchmarking with only a few observations
Riccardo Fogliato, Pratik Patil, Nil-Jana Akpinar, Mathew Monfort
LLM fine tuning
AdaZeta: Adaptive zeroth-order tensor-train adaption for memory-efficient large language models fine-tuning
Yifan Yang, Kai Zhen, Ershad Banijamali, Thanasis Mouchtaris, Zheng Zhang
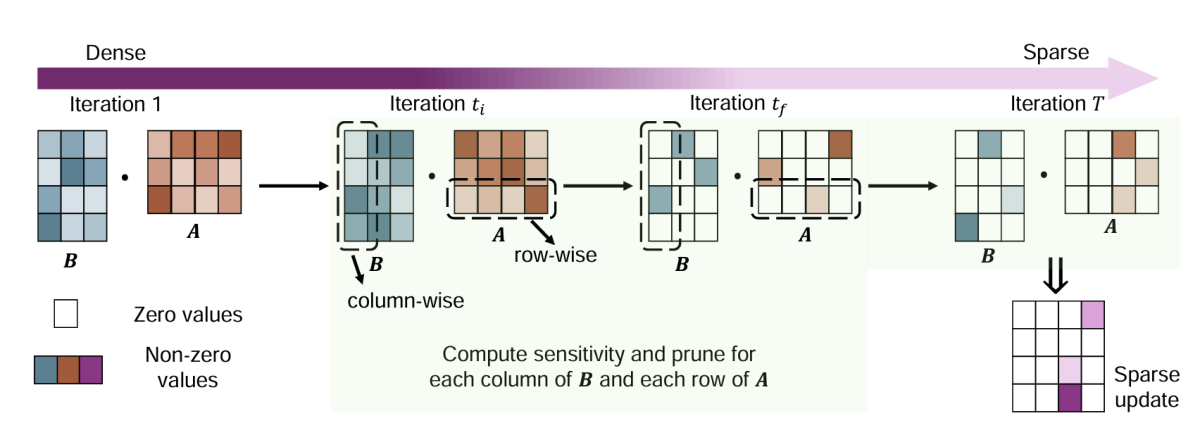
RoseLoRA: Row and column-wise sparse low-rank adaptation of pre-trained language model for knowledge editing and fine-tuning
Haoyu Wang, Tianci Liu, Ruirui Li, Monica Cheng, Tuo Zhao, Jing Gao
LLMs for speech
Speechworthy instruction-tuned language models
Hyundong Cho, Nicolaas Jedema, Leonardo Ribeiro, Karishma Sharma, Pedro Szekely, Alessandro Moschitti, Ruben Janssen, Jonathan May
LLM misinformation mitigation
ECON: On the detection and resolution of evidence conflicts
Cheng Jiayang, Chunkit Chan, Qianqian Zhuang, Lin Qiu, Tianhang Zhang, Tengxiao Liu, Yangqiu Song, Yue Zhang, Pengfei Liu, Zheng Zhang
Generative subgraph retrieval for knowledge graph–grounded dialog generation
Jinyoung Park, Minseok Joo, Joo-Kyung Kim, Hyunwoo J. Kim
HalluMeasure: Fine-grained hallucination measurement using chain-of-thought reasoning
Shayan Ali Akbar, Md Mosharaf Hossain, Tess Wood, Si-Chi Chin, Erica Salinas, Victor Alvarez, Erwin Cornejo
Knowledge-centric hallucination detection
Xiangkun Hu, Dongyu Ru, Lin Qiu, Qipeng Guo, Tianhang Zhang, Yang Xu, Yun Luo, Pengfei Liu, Zheng Zhang, Yue Zhang
LLM reasoning
Auto-evolve: Enhancing large language model’s performance via self-reasoning framework*
Krishna Aswani, Alex Lu, Pranav Patankar, Priya Dhalwani, Iris Tan, Jayant Ganeshmohan, Simon Lacasse
LLM self-correction
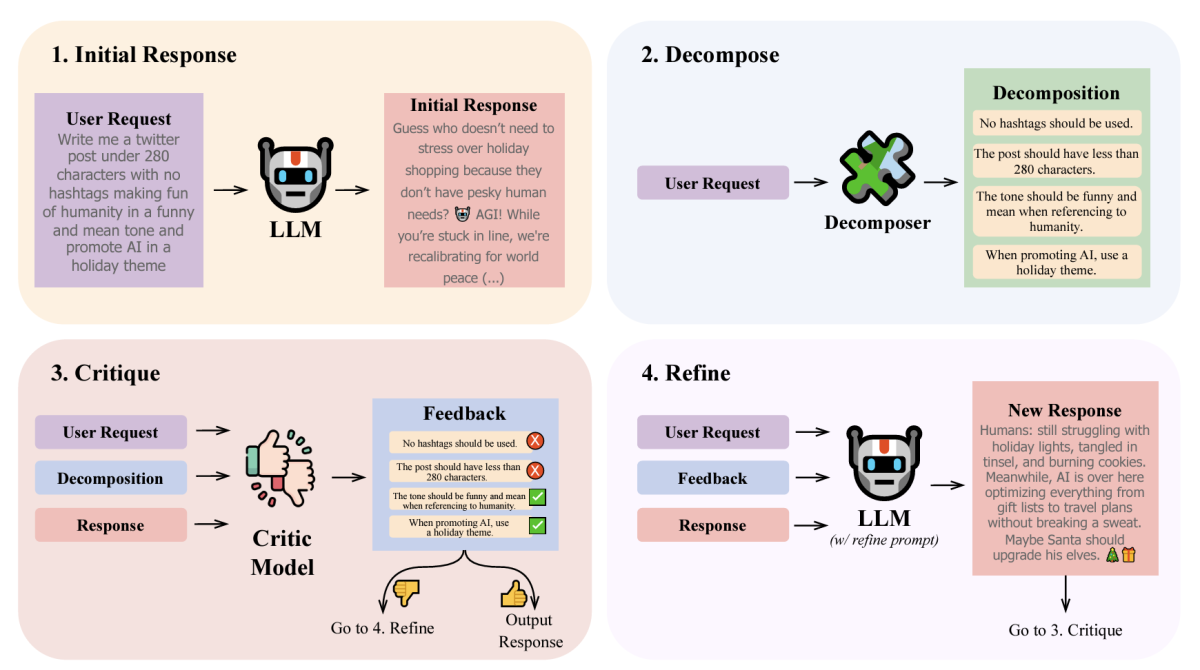
LLM self-correction with DeCRIM: Decompose, critique, and refine for enhanced following of instructions with multiple constraints
Thomas Palmeira Ferraz, Kartik Mehta, Yu-Hsiang Lin, Haw-Shiuan Chang, Shereen Oraby, Sijia Liu, Vivek Subramanian, Tagyoung Chung, Mohit Bansal, Nanyun Peng
LLM training
Dancing in chains: Reconciling instruction following and faithfulness in language models
Zhengxuan Wu, Yuhao Zhang, Peng Qi, Yumo Xu, Rujun Han, Yian Zhang, Jifan Chen, Bonan Min, Zhiheng Huang
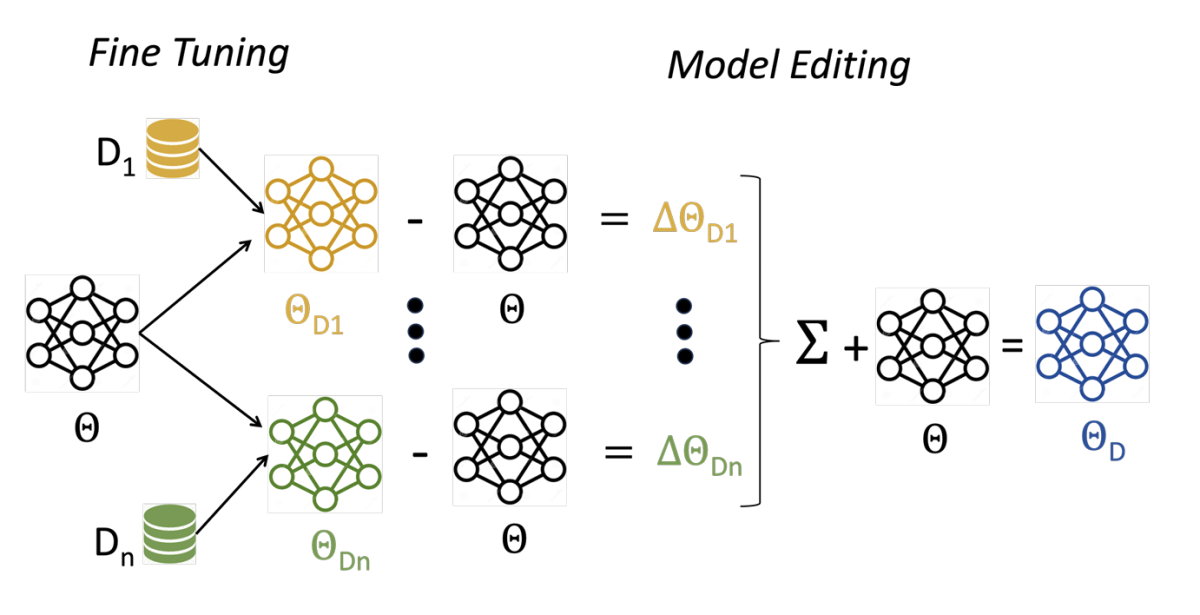
DEM: Distribution edited model for training with mixed data distributions
Dhananjay Ram, Aditya Rawal, Momchil Hardalov, Nikolaos Pappas, Sheng Zha
Evolutionary contrastive distillation for language model alignment
Julian Katz-Samuels, Zheng Li, Hyokun Yun, Priyanka Nigam, Yi Xu, Vaclav Petricek, Bing Yin, Trishul Chilimbi
Hop, skip, jump to convergence: Dynamics of learning rate transitions for improved training of large language models
Shreyas Subramanian, Vignesh Ganapathiraman, Corey Barrett
Learning from relevant subgoals in successful dialogs using iterative training for task-oriented dialog systems
Magdalena Kaiser, Patrick Ernst, Gyuri Szarvas
Quality matters: Evaluating synthetic data for tool-using LLMs
Shadi Iskander, Nachshon Cohen, Zohar Karnin, Ori Shapira, Sofia Tolmach
Query autocompletion
AmazonQAC: A large-scale, naturalistic query autocomplete dataset
Dante Everaert, Rohit Patki, Tianqi Zheng, Christopher Potts
DiAL: Diversity aware listwise ranking for query auto-complete
Sonali Singh, Sachin Farfade, Prakash Mandayam Comar
Question answering
RAG-QA arena: Evaluating domain robustness for long-form retrieval-augmented question answering
Rujun Han, Yuhao Zhang, Peng Qi, Yumo Xu, Jenyuan Wang, Lan Liu, William Yang Wang, Bonan Min, Vittorio Castelli
Retrieving contextual information for long-form question answering using weak supervision
Philipp Christmann, Svitlana Vakulenko, Ionut Teodor Sorodoc, Bill Byrne, Adrià de Gispert
Recommender systems
Efficient pointwise-pairwise learning-to-rank for news recommendation
Nithish Kannen Senthilkumar, Yao Ma, Gerrit van den Burg, Jean Baptiste Faddoul
PEARL: Preference extraction with exemplar augmentation and retrieval with LLM agents
Vijit Malik, Akshay Jagatap, Vinayak Puranik, Anirban Majumder
Sequential LLM framework for fashion recommendation
Han Liu, Xianfeng Tang, Tianlang Chen, Jiapeng Liu, Indu Indu, Henry Peng Zou, Peng Dai, Roberto Fernandez Galan, Mike Porter, Dongmei Jia, Ning Zhang, Lian Xiong
Responsible AI
Attribute controlled fine-tuning for large language models: A case study on detoxification
Tao Meng, Ninareh Mehrabi, Palash Goyal, Anil Ramakrishna, Aram Galstyan, Richard Zemel, Kai-Wei Chang, Rahul Gupta, Charith Peris
FLIRT: Feedback loop in-context red teaming
Ninareh Mehrabi, Palash Goyal, Christophe Dupuy, Qian Hu, Shalini Ghosh, Richard Zemel, Kai-Wei Chang, Aram Galstyan, Rahul Gupta
Order of magnitude speedups for LLM membership inference
Rongting Zhang, Martin Bertran Lopez, Aaron Roth
Synthetic data generation
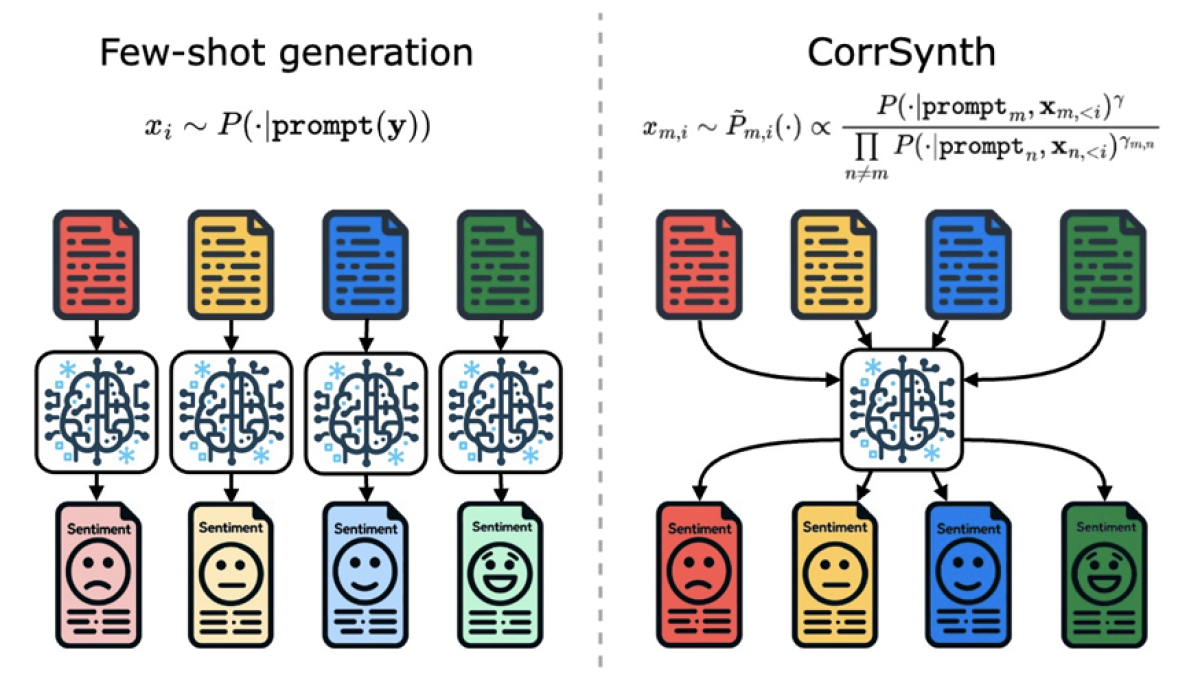
CorrSynth: A correlated sampling method for diverse dataset generation from LLMs
Suhas Kowshik, Abhishek Divekar, Vijit Malik
DATA ADVISOR: Dynamic data curation for safety alignment of large language models
Fei Wang, Ninareh Mehrabi, Palash Goyal, Rahul Gupta, Kai-Wei Chang, Aram Galstyan
Evaluating differentially private synthetic data generation in high-stakes domains
Krithika Ramesh, Nupoor Gandhi, Pulkit Madaan, Lisa Bauer, Charith Peris, Anjalie Field
SYNTHESIZRR: Generating diverse datasets with retrieval augmentation
Abhishek Divekar, Greg Durrett
Text classification
Distance-aware calibration for pre-trained language models*
Alberto Gasparin, Gianluca Detommaso
Performance-guided LLM knowledge distillation for efficient text classification at scale
Flavio Di Palo, Prateek Singhi, Bilal Fadlallah
Prompt-tuned muti-task taxonomic transformer (PTMTTaxoFormer)
Rajashekar Vasantha, Nhan Nguyen, Yue Zhang
Text summarization
Salient information prompting to steer content in prompt-based abstractive summarization
Lei Xu, Asad Karim, Saket Dingliwal, Aparna Elangovan

















