The Federated Logic Conference (FLoC) is a superconference that, like the Olympics, happens every four years. FLoC draws together 12 distinct conferences on logic-related topics, most of which meet annually. The individual conferences have their own invited speakers, but FLoC as a whole has several plenary speakers as well.
At the last FLoC, in 2018, one of those plenary speakers was Byron Cook, who leads Amazon’s automated-reasoning group, and he was introduced by Daniel Kröning, then a professor of computer science at the University of Oxford
“What makes me so proud that Byron is here,” Kröning said, is “he’s now at Amazon, and he’s going to run the next Bell Labs, he’s going to run the next Microsoft Research, from within Amazon. My prediction is that — not 10 years but 16 years; remember, it’s multiples of four — 16 years from now you’ll be at a FLoC, and you’ll hear these stories about the great thing that Byron Cook built up at Amazon Web Services. And we’ll speak about it in the same tone as we’re now talking about Bell Labs and Microsoft Research.”
In the audience at the talk was Marijn Heule, a highly cited automated-reasoning researcher who was then at the University of Texas.
“I hadn't met Marijn, though I had heard about him from a couple other people and thought I should talk to him,” Cook says. “And then Marijn found me at the banquet after the talk and was like, ‘I want a job.’”

Heule is now an Amazon Scholar who divides his time between Amazon and his new appointment at Carnegie Mellon University. Kröning, too, has joined Amazon as a senior principal scientist, working closely with Cook’s group.
As 2022’s FLoC approached, Cook, Kröning, and Heule took some time to talk with Amazon Science about the current state of automated-reasoning research and its implications for Amazon customers.
Amazon Science: The conference name has the word “logic” in it. Does FLoC deal with other aspects of logic, or is logic coextensive with automated reasoning now?
Byron Cook: It’s about the intersection of logic and computer science. Automated reasoning is one dimension of that intersection.
Daniel Kröning: Traditionally, FLoC is split into two halves, with the first half more theoretical and the second half more applied.
Cook: One of the things about automated reasoning is you're on the bleeding edge of what is even computable. We're often working on intractable or undecidable problems. So people automating reasoning are really paying attention to both the applied and the theoretical.
AS: I know Marijn is concentrating on SAT solvers, and SAT is an intractable problem, right? It’s NP-complete?
Marijn Heule: Yes, but you can also use these techniques to solve problems that go beyond NP. For example, solvers for SAT modulo theories, called SMT. I even have a project with one student trying to solve the famous Collatz conjecture with these tools.
Kröning: SAT is now the inexpensive, easy-to-solve workhorse for really hard problems. People still have it in their heads that SAT equals NP hard, therefore difficult to solve or impossible to solve. But for us, it's the lowest entry point. On top of SAT, we build algorithms for solving problems that are way harder.
Cook: One of the tricks of the trade is abstraction, where you take a problem that's much, much bigger but represent it with something smaller, where classes of questions you might ask about the smaller problem imply that the answer also holds for the bigger problem. We also have techniques for refining the abstractions on demand when the abstraction is losing too much information to answer the question. Often we can represent these abstractions in tools for SAT.
Marijn’s work on the Collatz conjecture is a great example of this. He has done this amazing reduction of Collatz to a series of SAT questions, and he's tantalizingly close to solving it because he's got one decidable problem to go — and he's the world expert on solving those problems. [Laughs]
Heule: Tantalizingly close but also so far away, right? Because this problem might not be solvable even with a million cores.
Cook: But it's still decidable. And one of the thresholds is that NP, PSpace, all these things, they're actually decidable. There are questions that are undecidable — and we work on those, too. When a problem is undecidable, it means that your tool will sometimes fail to find an answer, and that's just fundamental: there are no extra computers you could use ever to solve that. The halting problem is a great example of that.
Heule: For these kinds of problems, you're asking the question “Is there a termination argument of this kind of shape?” And if there is one, you have your termination argument. If there is no termination argument of that shape, there could be one of another shape. So if the answer is SAT [satisfiable], then you're happy because you’ve solved the problem. If the answer is no, you try something else.
Cook: It's really, really exciting. In Amazon, we're building these increasingly powerful SAT solvers, using the power of the cloud and distributed systems. So there's no better place for Marijn to be than at Amazon.
AS: Daniel, could we talk a little bit about your research?
Kröning: What I'm looking at right now is reasoning about the cloud infrastructure that performs remote management of EC2 instances — how to secure that in a way that is provable. You also want to do that in a way that is economical.
Cook: One of the things that Daniel's focusing on is agents. We have pieces of software that run on other machines, like EC2 instances, agents for telemetry or for control, and you give them power to take action on your behalf on your machine. But you want to make sure that an adversary doesn't trick those agents into doing bad things.
Correct software
AS: I know that, commercially, formal methods have been used in hardware design and transportation systems for some time. But it seems that they’re really starting to make inroads in software development, too.
The storage team is able to write code that otherwise they might not want to deploy because they wouldn't be as confident about it, and they're deploying four times as fast. It was an investment in agility that's really paid off.
Cook: The thing we've seen is it's really by need. The storage team, for example, is able to be much more agile and be much more aggressive in the programs that they write because of the formal methods. They're able to write code that otherwise they might not want to deploy because they wouldn't be as confident about it, and they're deploying four times as fast. It was an investment in agility that's really paid off.
Kröning: There are actually a good number of stories wherein engineering teams didn't dare to roll out a particular feature or design revision or design variant that offers clear benefits — like being faster, using less power — because they just couldn't gain the confidence that it's actually right under all circumstances.
Heule: The interesting thing is that you even see this now in tools. Now we have produced proofs from the tools, and people start implementing features that they wouldn't dare have in the past because they were not clear that they were correct. So the solvers get faster and more complex because we now can check the results from the tools and to have confidence in their correctness.
Cook: Yeah, I wanted to double down on that point. There’s a distinction in automated reasoning between finding a proof and checking your proof, and the checking is actually relatively easy. It's an accounting thing. Whereas finding the proof is an incredibly creative activity, and the algorithms that find proofs are mind-blowing. But how do you know that the tool that found the proof is correct? Well, you produce an auditable artifact that you can check with the easy tool.
SAT in the cloud
AS: What are you all most excited about at this year’s FLoC?
Cook: The SAT conference is at FLoC, and there will be the SAT competition results, and one of the things I'm really excited about is the cloud track. Automated reasoning has really moved into the cloud, and the past couple years running the cloud track has really blown the doors off what's possible. I'm expecting that that will be true again this year.
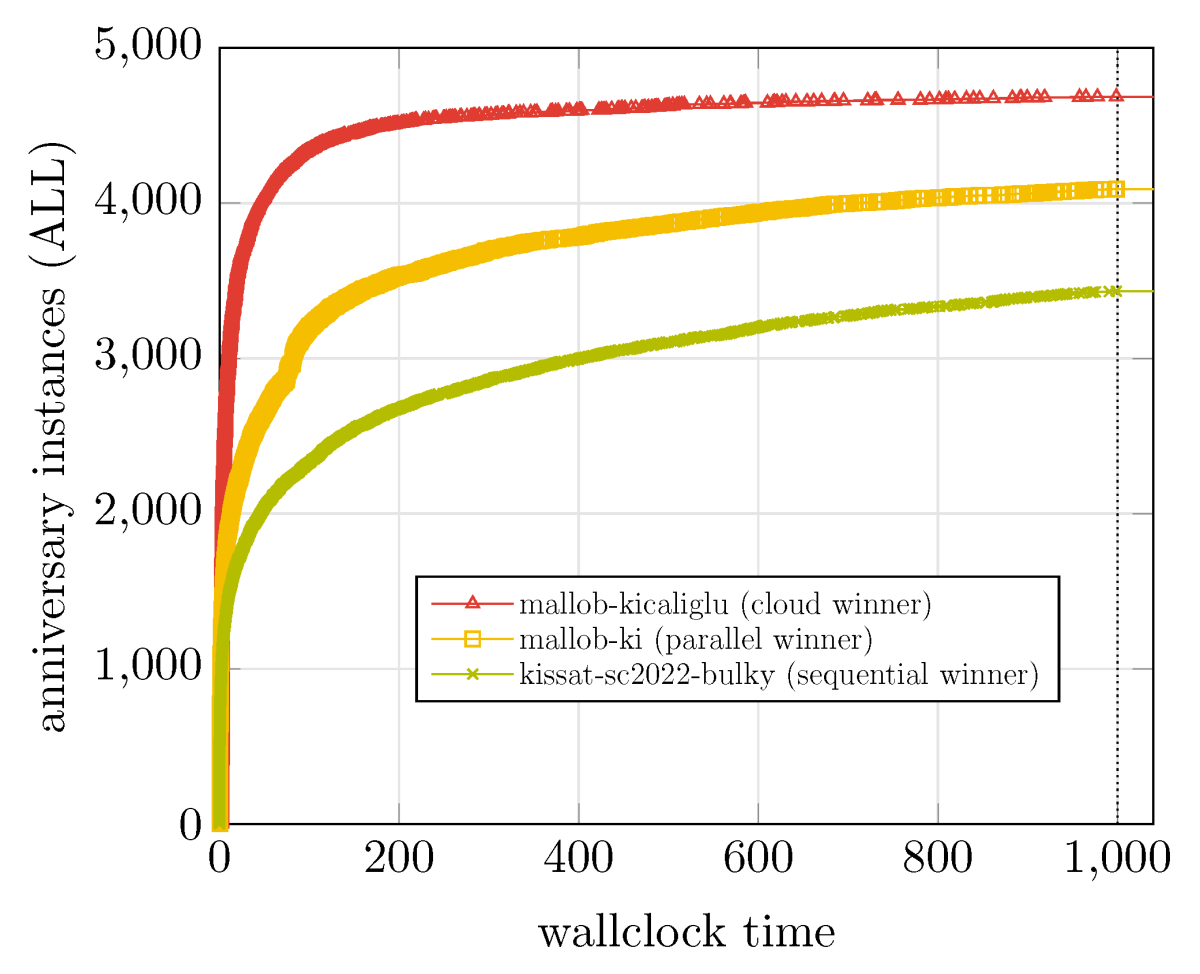
Heule: This is the first year that Amazon is running both the parallel track and the cloud track, and the cloud track was only possible because of Amazon. Before that, there was no way we had the resources to run a cloud track. In the cloud track, every solver-benchmark combination is run on 1,600 cores. And this year is extra special because it's 20 years of SAT, and we have a single anniversary track and all the competitions that were run in the past are in there. That is 5,355 problems, and all the solvers are running on this.
Cook: Wow.
Heule: I'm also excited to see the results. We have seen in the last year and the year before that the cloud solver can, say, solve in 100 seconds as much as the sequential solvers can do in 5,000 seconds. The user doesn't have to wait for four hours but just for four minutes
Cook: And that raises all boats because, as we mentioned earlier, everything is reduced to SAT. If the SAT solvers go from one hour to one minute, that's really game changing. That means a whole other set of things you can do.
What has been clear for a while but continues to be true is there's some sort of Moore's-law thing happening with SAT. You fix the same hardware, the same benchmarks, and then run all the tools from the past 20 years, and you see every year they're getting dramatically better. What's also really amazing is that in many ways the tools are getting simpler.
LH: Are the simplicity and efficiency two sides of the same coin? Understanding the problems better helps you find a simpler solution, which is more efficient?
Cook: Yeah, but it’s also the point that Marijn made that because the tools produce auditable proofs that you can check independently, you can do aggressive things that we were scared to do before. Often, aggressive is much simpler.
Heule: It's also the case that we now understand there are different kinds of problems, and they need different kinds of heuristics. Solvers are combining different heuristics and have phases: “Let's first try this. Let's also try that.” And the code involved in changing the heuristics is very small. It's just changing a couple of parameters. But if you notice, okay, this set of heuristics works well for this problem, then you kind of focus more on that.
Cook: One of the things a SAT solver does is make decisions fast. It just makes a bunch of choices, and those choices won't work out, and then it spends some time to learn lessons why. And then it has a very efficient internal database for managing what has been learned, what not to do in the future. And that prunes the search space a lot.
One of the really exciting things that's happening in the cloud is that you have, say, 1,000 SAT solvers all running on the same problem, and they're learning different things and can share that information amongst them. So by adding 5,000 more solvers, if you can make the communication and the lookup efficient between them, you're really off to the races.
The other thing that's quite neat about that is the point that Marijn is making: it's becoming increasingly clear that there are these fundamental building blocks, and for different kinds of problems, you would want to use one kind of Lego brick versus a different kind of Lego brick. And the cloud allows you to run them all but then to share the information between them.

Heule: We have an Amazon paper at FLoC with some very cool ideas. If you run things in the cloud, you sometimes have a limited time window where you have to solve them, and otherwise it stops. You started with a certain problem, the solver did some modifications, and now we have a different problem. Initially we just tested, Okay, can we stop the solver and then store the modified problem somewhere and continue later, in case we need more time than we allocated initially? And then we can continue solving it.
But the interesting thing is that if you give the modified problem to another solver, and you give it, say, a couple of minutes, and then it stores the modified problem, and you give it to another solver, it actually really speeds things up. It turns out to solve the most instances from everything that we tried.
AS: Do you do that in a principled way, or do you just pick a new solver randomly?
Heule: The thing that turned out to work really well is to take two top-tier solvers and just Ping-Pong the problem among them. This functionality of storing and continuing search requires some work, so that implementing it in, say, a dozen solvers would require quite some work. But it would be a very interesting experiment.
AS: I’m sure our readers would love to know the result of that experiment!
Well, thank you all very much for your time. Does anyone have any last thoughts?
Cook: I think I speak for the thousands of others who are attending FLoC: we are ready to having our minds blown, just as we did in 2018. Many of the tools and theories presented by our scientific colleagues at this year’s FLoC will challenge our current assumptions or spark that next big insight in our brains. We will also get to catch up with old friends that we’ve known for around 20 years and meet new ones. I’m particularly excited to meet the new generation of scientists who have entered the field, to see the world afresh through their eyes. This is such an amazing time to be in the field of automated reasoning.