As an associate professor of electrical engineering and computer science at MIT, Tim Kraska researched instance-optimized database systems, or systems that can automatically adapt to new workloads with minimal human involvement.

Earlier this year, Amazon hired Kraska and his team to further develop this technology. Currently, Kraska is on leave from MIT, and as director of applied science for Amazon Web Services (AWS), he is helping establish Amazon’s new Learned Systems Group (LSG), which will focus on integrating machine learning (ML) into system design. The group’s first project is to bring instance optimization to AWS’s data warehousing service, Amazon Redshift. Kraska spoke with Amazon Science about the value of instance optimization and the attraction of doing research in an industrial setting.
- Q.
What is instance optimization?
A.If you develop a system from scratch for a particular use case, you are able to get orders of magnitude better performance, as you can tailor every system component to that use case. However, in most cases you don't want to do that, because it's a huge effort. In the case of databases, the saying is that it normally takes at least seven years to get the system so that it's usable and stable.
The idea of instance optimization is that, rather than build one system per use case, we build a system that self-adjusts — instance-optimizes itself — to a particular scenario to get as close as possible to a hand-tuned solution.
- Q.
How does it do that?
A.There are different ways to achieve the self-adjustment. With any system, you have a bunch of knobs and a bunch of design choices. If you take Redshift, you can tune the buffer size; you can create materialized views; you can create different types of sort orders. And database administrators can adjust these knobs and make design choices, based on their workloads, to get better performance.
The first form of self-adjustment is to make those decisions automatically. You have, let's say, a machine learning model that observes the workload and figures out how to adjust these knobs and what materialized views and sort keys to create. Redshift already does this, for example, with a feature called Automated Materialized Views, which accelerates query performance.
The next step is that in some cases it's possible to replace components through novel techniques that allow either more customization or tuning in ways that weren’t previously possible.
To give you an example, in the case of data layouts, current systems mainly support partitioning data by one attribute, which could be a composite key. The reason is that the developers of these systems always thought that someone has to eventually make these design choices manually. Thus, in the past, the tendency was to reduce the number of tuning parameters as much as possible.
This, of course, changes the moment you have automatic tuning techniques using machine learning, which can explore the space much more efficiently. And now maybe the opposite is true: providing more degrees of freedom and more knobs is a good thing, as they offer more potential for customization and, thus, better performance.
The third self-adjustment method is where you deeply embed machine learning models into a component of the system to give you much better performance than is currently possible.
Every database, for example, has a query optimizer that takes a SQL query and optimizes it to an execution plan, which describes how to actually run that query. This query optimizer is a complex piece of software, which requires very carefully tuned heuristics and cost models to figure out how best to do this translation. The state of the art now is that you treat this as a deep-learning problem. So we talk at that stage about learned components.

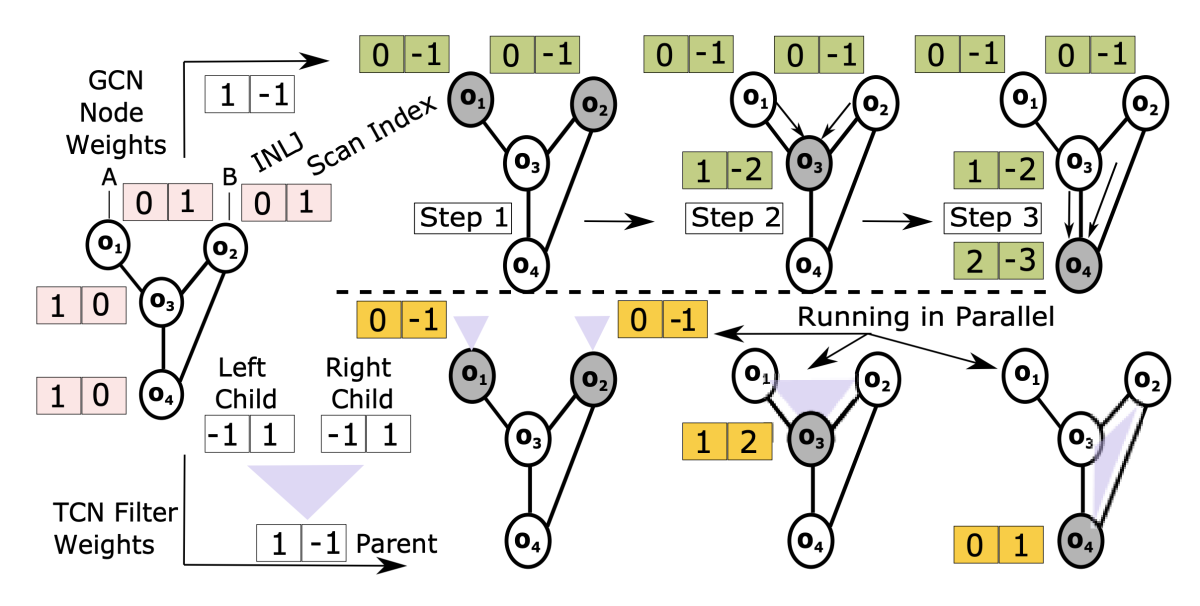
A comparison of two different approaches to learning to detect query patterns, using graph convolution networks (top) and tree convolution networks (bottom). From “LSched: A workload-aware learned query scheduler for analytical database systems”. The ultimate goal is to build a system out of learned components and to have everything tuned in a holistic way. There's a model monitoring the workload, watching the system, and making the right adjustments — potentially in ways no human is able to.
- Q.
Is it true that you developed an improved sorting algorithm? I thought that sorting was pretty much a solved problem.
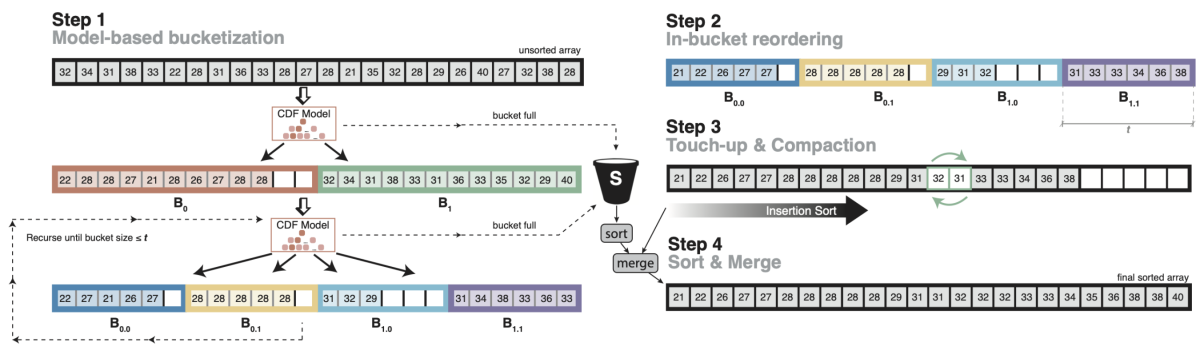
A.That's right. It's still surprising. The way it works is, you learn a model over the distribution of the data — the cumulative distribution function, or CDF, which tells you where an item falls into the probability mass. Let's assume that in an e-commerce database, you have a table with orders, each order has a date, and you want to sort the table by date. Now you can build the CDF over the date attribute, and then you can ask a question like “How many orders happened before January 1st, 2021?”, and it spits out the probability.
The nice thing about that is that, essentially, the CDF function allows you to ask, “Given an order date, where in the sorted order does it fit?” Assuming the model is perfect, it suddenly allows you to do sorting in O(n). [I.e., the sorting time is proportional to the number of items being sorted, n, not n2, nlogn, or the like.]

Recursively applying the cumulative distribution function (CDF) to sort items in an array in O(n) time. From “The case for a learned sorting algorithm”. Radix sort is also O(n), but it can be memory intensive, as the efficiency depends on the domain size — how many unique values there could possibly be. If your domain is one to a million, it might still be easily do-able in memory. If it's one to a billion, it already gets a little bit harder. If it's one to — pick your favorite power of ten — it eventually becomes impossible to do it in one pass.
The model-based approach tries to overcome that in a clever way. You know roughly where items land, so you can place them into their approximate position and use insertion sort to correct for model errors. It’s a trick we used for indexes, but it turns out that you can use the same thing for sorting.
- Q.
For you, what was the appeal of doing research in the industrial setting?
A.One of the reasons we are so attracted to working for Amazon is access to information about real-world workloads. Instance optimization is all about self-adjusting to the workload and the data. And it's extremely hard to test it in academia.
There are a few benchmark datasets, but internally, they often use random-number generators to create the data and to determine when and what types of queries are issued against the system.
We fundamentally have to rethink how we build systems. ... Whenever a developer has to make a trade-off between two techniques or defines a constant, the developer should think about if this constant or trade-off shouldn’t be automatically tuned.
Tim KraskaBecause of this randomness, first of all, there are no interesting usage patterns — say, when are the dashboarding queries running, versus the batch jobs for loading the data. All that is gone. Even worse, the data itself doesn’t contain any interesting patterns, which either makes it too hard, because everything is random, or too easy, because everything is random.
For example, when we tested our learned query optimizer on a very common data-warehousing benchmark, we found that we barely got any improvements, whereas for real-world workloads, we saw big improvements.
We dug in a little bit, and it turns out that for common benchmarks, like TPC-H, every single database vendor makes sure that the query plans are close to perfect. They manually overfit the system to the benchmark. And this translates in no way to any real-world customer. No customer really runs queries exactly like the benchmark. Nobody does.
Working with Redshift’s amazing development team and having access to real-world information provides a huge advantage here. It allows us not only to evaluate if our previous techniques actually work in practice, but it also helps us to focus on developing new techniques, which actually make a big difference to users by providing better performance or improved ease of use.
- Q.
So the collaboration with the Redshift team is going well?
A.It has been great and, in many ways, exceeded our expectations. When we joined, we certainly had some anxiety about how we would be working with the Redshift team, how much we would still be able to publish, and so on. For example, I know many researchers in industry labs who struggle to get access to data or have actual impact on the product.
None of these turned out to be a real concern. Not only did we define our own research agenda, but we are also already deeply involved with many exciting projects and have a whole list of exciting things we want to publish about.
- Q.
Do you still collaborate with MIT?
A.Yes, and it is very much encouraged. Amazon recently created a Science Hub at MIT, and as part of the hub, AWS is also sponsoring DSAIL, a lab focused on ML-for-systems research. This allows us to work very closely with researchers at MIT.
- Q.
Some of the techniques you’ve discussed, such as sorting, have a wide range of uses. Will the Learned Systems Group work with groups other than Redshift?
A.We decided to focus on Redshift first as we had already a lot of experience with instance optimization for analytical systems, but we’ve already started to talk to other teams and eventually plan to apply the ideas more broadly.
I believe that we fundamentally have to rethink how we build systems and system components. For example, whenever a developer has to make a trade-off between two techniques or defines a constant, the developer should think about if this constant or trade-off shouldn’t be automatically tuned. In many cases, the developer would probably approach the design of the component completely differently if she knows that the component is expected to self-adjust to the workload and data.
This is true not only for data management systems but across the entire software stack. For example, there has been work on improving network packet classification using learned indexes, spark scheduling algorithms using reinforcement learning, and video compression using deep-learning techniques to provide a better experience when bandwidth is limited. All these techniques will eventually impact the customer experience in the form of performance, reduced cost, or ease of use.
For good reason, we already see a lot of adaptation of ML to improve systems at Amazon. Redshift, for example, offers multiple ML-based features — like Automated Materialized Views or automatic workload management. With the Learned Systems Group, we hope to accelerate that trend, with fully instance-optimized systems that self-adjust to workloads and data in ways no traditional system can. And that will provide better performance, cost, and ease of use for AWS customers.