The risk that a quantum computer might break cryptographic standards widely used today has ignited numerous efforts to standardize quantum-resistant algorithms and introduce them into transport encryption protocols like TLS 1.3. The choice of post-quantum algorithm will naturally affect TLS 1.3’s performance. So far, studies of those effects have focused on the “handshake time” required for two parties to establish a quantum-resistant encrypted connection, known as the time to first byte.
Although these studies have been important in quantifying increases in handshake time, they do not provide a full picture of the effect of post-quantum cryptography on real-world TLS 1.3 connections, which often carry sizable amounts of data. At the 2024 Workshop on Measurements, Attacks, and Defenses for the Web (MADweb), we presented a paper advocating time to last byte (TTLB) as a metric for assessing the total impact of data-heavy, quantum-resistant algorithms such as ML-KEM and ML-DSA on real-world TLS 1.3 connections. Our paper shows that the new algorithms will have a much lower net effect on connections that transfer sizable amounts of data than they do on the TLS 1.3 handshake itself.
Post-quantum cryptography
TLS 1.3, the latest version of the transport layer security protocol, is used to negotiate and establish secure channels that encrypt and authenticate data passing between a client and a server. TLS 1.3 is used in numerous Web applications, including e-banking and streaming media.
Asymmetric cryptographic algorithms, such as the one used in TLS 1.3, depend for their security on the difficulty of the discrete-logarithm or integer factorization problems, which a cryptanalytically relevant quantum computer could solve efficiently. The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has been working on standardizing quantum-resistant algorithms and has selected ML-Key Encapsulation Mechanism (KEM) for key exchange. NIST has also selected ML-DSA for signatures, or cryptographic authentication.
As these algorithms have kilobyte-size public keys, ciphertexts, and signatures — versus the 50- to 400-byte sizes of the existing algorithms — they would inflate the amount of data exchanged in a TLS handshake. A number of works have compared handshake time using traditional TLS 1.3 key exchange and authentication to that using post-quantum (PQ) key exchange and authentication.
These comparisons were useful to quantify the overhead that each new algorithm introduces to the time to first byte, or completion of the handshake protocol. But they ignored the data transfer time over the secure connection that, together with the handshake time, constitutes the total delay before the application can start processing data. The total time from the start of the connection to the end of data transfer is, by contrast, the time to last byte (TTLB). How much TTLB slowdown is acceptable depends highly on the application.
Experiments
We designed our experiments to simulate various network conditions and measured the TTLB of classical and post-quantum algorithms in TLS 1.3 connections where the client makes a small request and the server responds with hundreds of kilobytes (KB) of data. We used Linux namespaces in a Ubuntu 22.04 virtual-machine instance. The namespaces were interconnected using virtual ethernet interfaces. To emulate the “network” between the namespaces, we used the Linux kernel’s netem utility, which can introduce variable network delays, bandwidth fluctuations, and packet loss between the client and server.
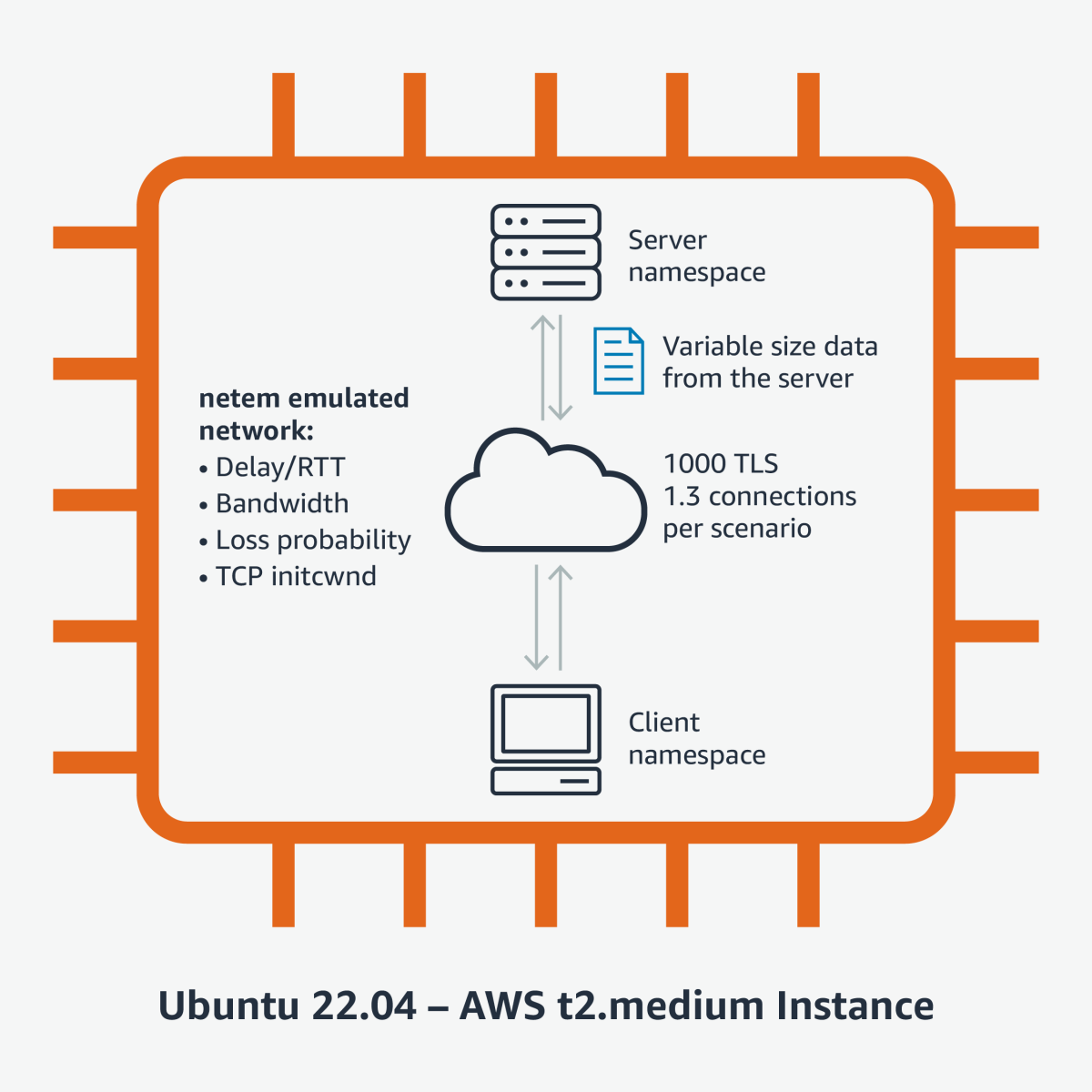
Our experiments had several configurable parameters that allowed us to compare the effect of the PQ algorithm on TTLB under stable, unstable, fast, and slow network conditions:
- TLS key exchange mechanism (classical ECDH or ECDH+ML-KEM post-quantum hybrid)
- TLS certificate chain size corresponding to classical RSA or ML-DSA certificates.
- TCP initial congestion window (initcwnd)
- Network delay between client and server, or round-trip time (RTT)
- Bandwidth between client and server
- Loss probability per packet
- Amount of data transferred from the server to the client
Results
The results of our testing are thoroughly analyzed in the paper. They essentially show that a few extra KB in the TLS 1.3 handshake due to the post-quantum public keys, ciphertexts, and signatures will not be noticeable in connections transferring hundreds of KB or more. Connections that transfer less than 10-20 KB of data will probably be more affected by the new data-heavy handshakes.
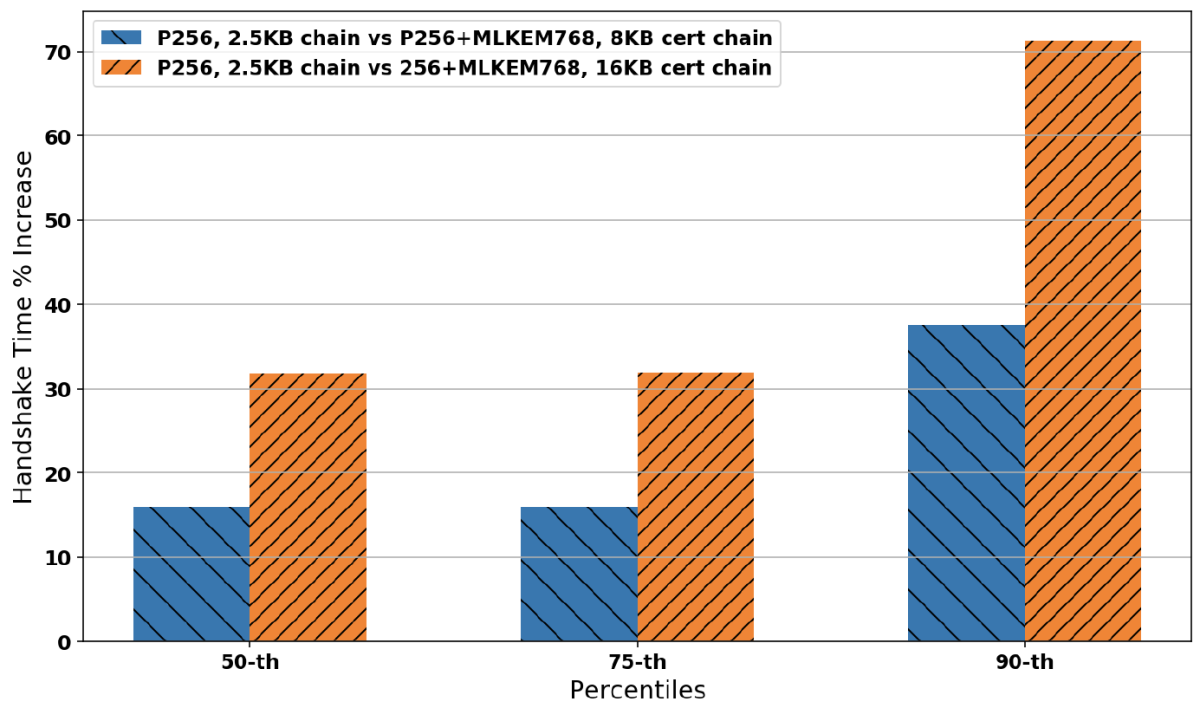
Figure 1 shows the percentage increase in the duration of the TLS 1.3 handshake for the 50th, 75th, and 90th percentiles of the aggregate datasets collected for 1Mbps bandwidth; 0%, 1%, 3%, and 10% loss probability; and 35-millisecond and 200-millisecond RTT. We can see that the ML-DSA size (16KB) certificate chain takes almost twice as much time as the 8KB chain. This means that if we manage to keep the volume of ML-DSA authentication data low, it would significantly benefit the speed of post-quantum handshakes in low-bandwidth connections.
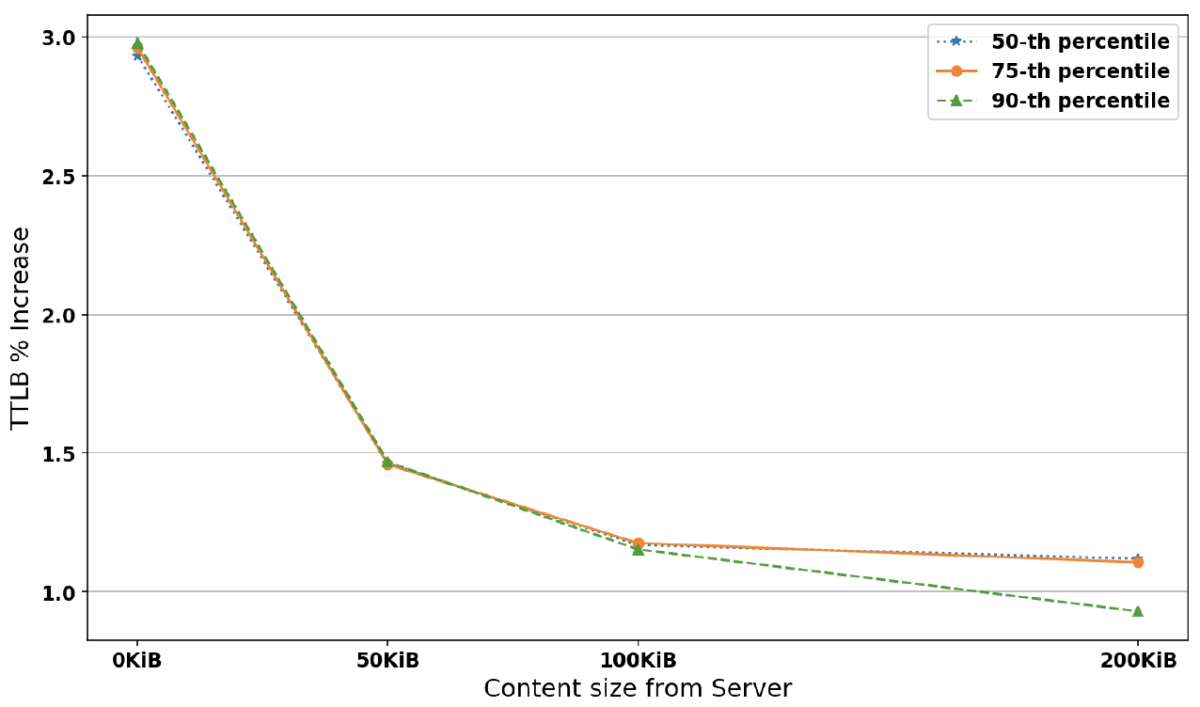
Figure 2 shows the percentage increase in the duration of the post-quantum handshake relative to the existing algorithm for all percentiles and different data sizes at 0% loss and 1Gbps bandwidth. We can observe that although the slowdown is low (∼3%) at 0 kibibytes (KiB, or multiples of 1,024 bytes, the nearest power of 2 to 1,000) from the server (equivalent to the handshake), it drops even more (∼1%) as the data from the server increases. At the 90th percentile the slowdown is slightly lower.
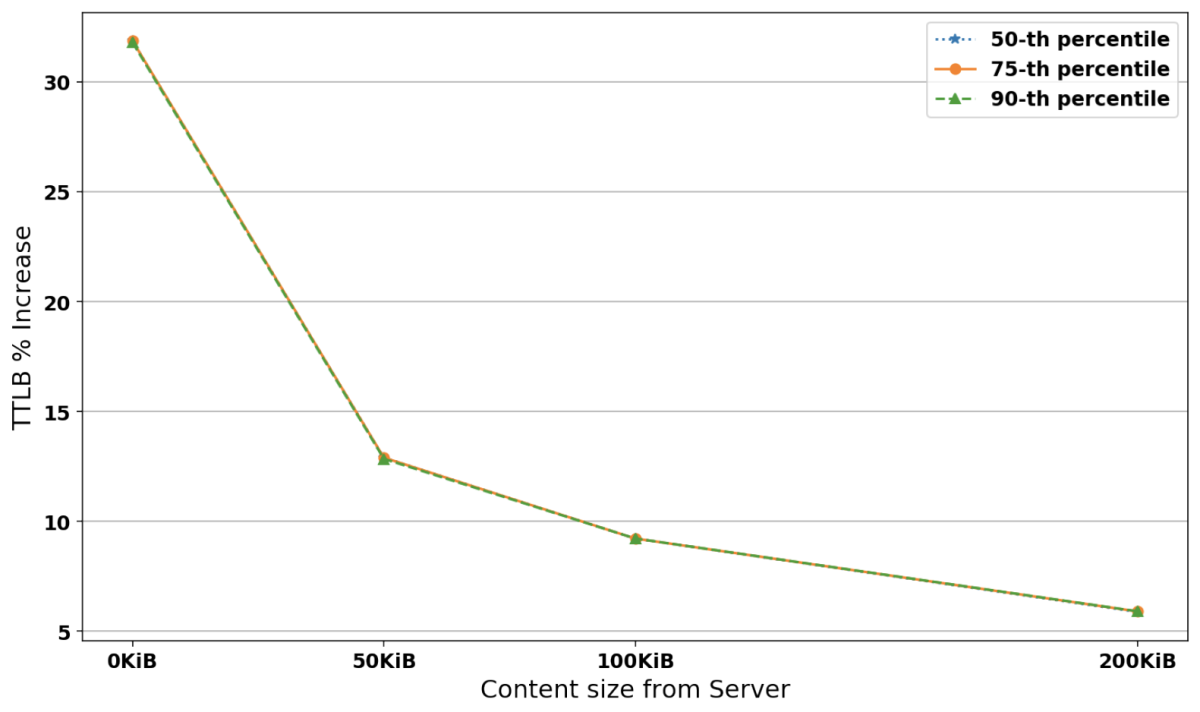
Figure 3 shows the percentage increase in the TTLB between existing and post-quantum TLS 1.3 connections carrying 0-200KiB of data from the server for each percentile at 1Mbps bandwidth, 200ms RTT, and 0% loss probability. We can see that increases for the three percentiles are almost identical. They start high (∼33%) at 0KiB from the server, but as the data size from the server increases, they drop to ∼6% because the handshake data size is amortized over the connection.
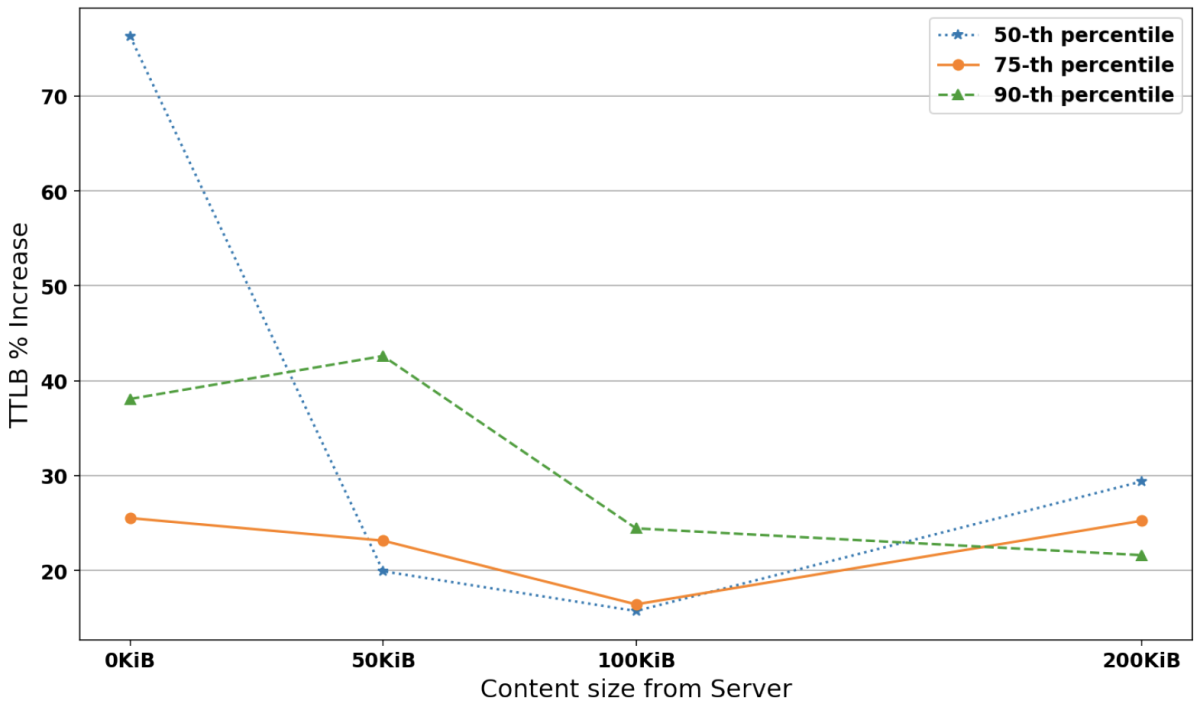
Figure 4 shows the percentage increase in TTLB between existing and post-quantum TLS 1.3 connections carrying 0-200 KiB of data from the server for each percentile at 1Mbps bandwidth, 200ms RTT, and 10% loss probability. It shows that at 10% loss, the TTLB increase settles between 20-30% for all percentiles. The same experiments for 35ms RTT produced similar results. Although a 20-30% increase may seem high, we note that re-running the experiments could sometimes lead to smaller or higher percentage increases because of the general network instability of the scenario. Also, bear in mind that TTLBs for the existing algorithm at 200KiB from the server, 200ms RTT, and 10% loss were 4,644ms, 7,093ms, and 10,178ms, whereas their post-quantum-connection equivalents were 6,010ms, 8,883ms, and 12,378ms. At 0% loss they were 2,364ms, 2,364ms, and 2,364ms. So, although the TTLBs for the post-quantum connections increased by 20-30% relative to the conventional connections, the conventional connections are already impaired (by 97-331%) due to network loss. An extra 20-30% is not likely to make much difference in an already highly degraded connection time.
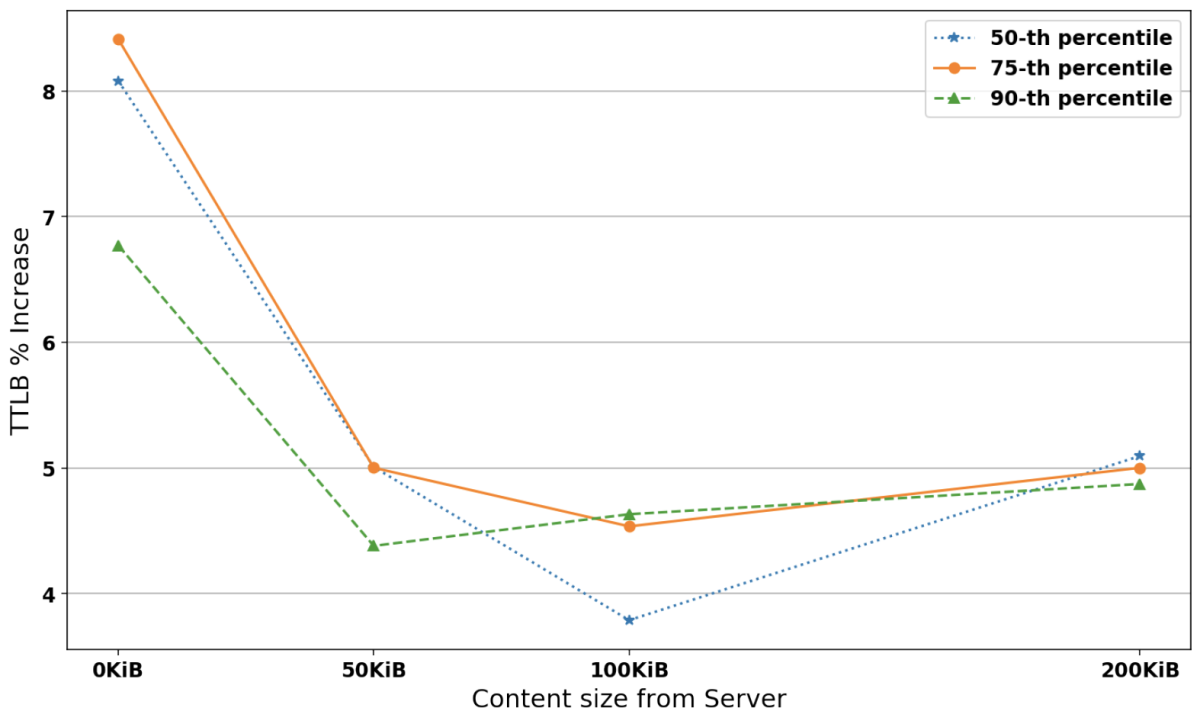
Figure 5 shows the percentage increase in TTLB between existing and post-quantum TLS 1.3 connections for 0% loss probability and 0-200KiB data sizes transferred from the server. To model a highly volatile RTT, we used a Pareto-normal distribution with a mean of 35ms and 35/4ms jitter. We can see that the increase in post-quantum connection TTLB starts high at 0KiB server data and drops to 4-5%. As with previous experiments, the percentages were more volatile the higher the loss probabilities, but overall, the results show that even under “volatile network conditions” the TTLB drops to acceptable levels as the amount of transferred data increases.
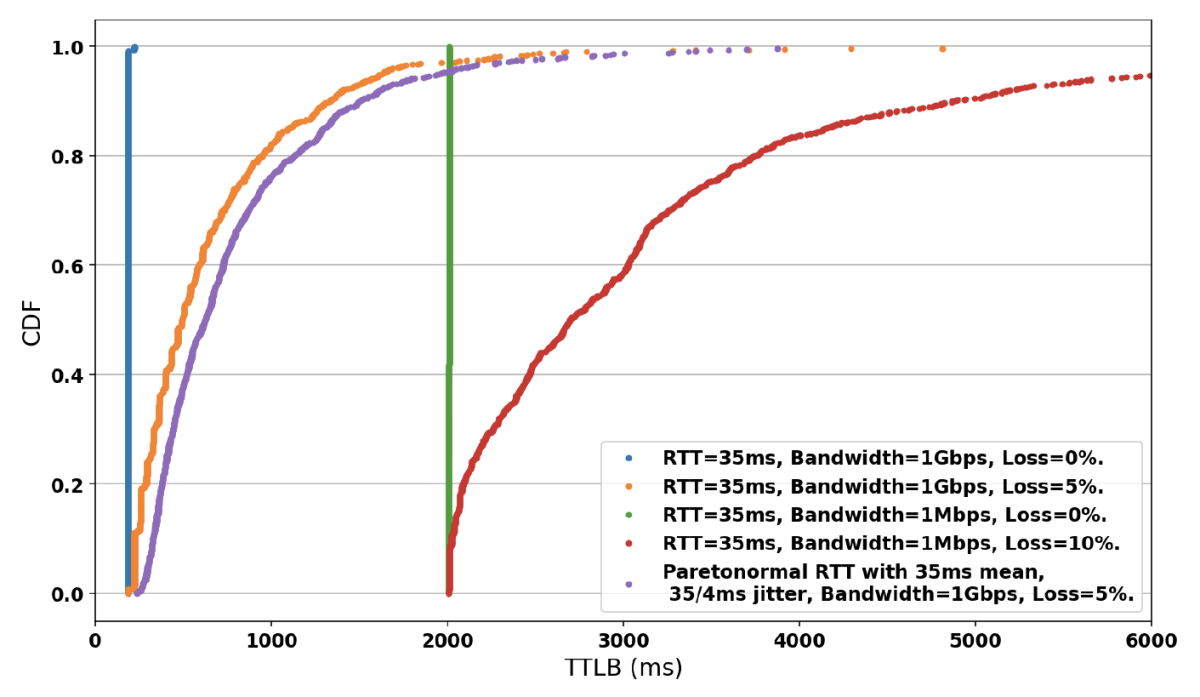
To confirm the volatility under unstable network conditions, we used the TTLB cumulative distribution function (CDF) for post-quantum TLS 1.3 connections transferring 200KiB from the server (figure 6). We observe that under all types of volatile conditions (1Gbps and 5% loss, 1Mbps and 10% loss, Pareto-normal distributed network delay), the TTLB increases very early in the experimental measurement sample, which demonstrates that the total connection times are highly volatile. We made the same observation with TLS 1.3 handshake times under unstable network conditions.
Conclusion
This work demonstrated that the practical effect of data-heavy, post-quantum algorithms on TLS 1.3 connections is lower than their effect on the handshake itself. Low-loss, low- or high-bandwidth connections will see little impact from post-quantum handshakes when transferring sizable amounts of data. We also showed that although the effects of PQ handshakes could vary under unstable conditions with higher loss rates or high-variability delays, they stay within certain limits and drop as the total amount of transferred data increases. Additionally, we saw that unstable connections inherently provide poor completion times; a small latency increase due to post-quantum handshakes would not render them less usable than before. This does not mean that trimming the amount of handshake data is undesirable, especially if little application data is sent relative to the size of the handshake messages.
For more details, please see our paper.