Since 2013, Amazon has held an annual internal conference, the Amazon Machine Learning Conference (AMLC), where machine learning practitioners from around the company come together to share their work, teach and learn new techniques, and discuss best practices.
At the third AMLC, in 2015, Guido Imbens, a professor of economics at the Stanford University Graduate School of Business, gave a popular tutorial on causality and machine learning. Nine years and one Nobel Prize for economics later, Imbens — now in his tenth year as an Amazon academic research consultant — was one of the keynote speakers at the 2024 AMLC, held in October.

In his talk, Imbens discussed causal inference, a mainstay of his research for more than 30 years and the topic that the Nobel committee highlighted in its prize citation. In particular, he considered so-called panel data, in which multiple units — say, products, customers, or geographic regions — and outcomes — say, sales or clicks — are observed at discrete points in time.
Over particular time spans, some units receive a treatment — say, a special product promotion or new environmental regulation — whose effects are reflected in the outcome measurements. Causal inference is the process of determining how much of the change in outcomes over time can be attributed to the treatment. This means adjusting for spurious correlations that result from general trends in the data, which can be inferred from trends among the untreated (control) units.
Imbens began by discussing the value of his work at Amazon. “I started working with people here at Amazon in 2014, and it's been a real pleasure and a real source of inspiration for my research, interacting with the people here and seeing what kind of problems they're working on, what kind of questions they have,” he said. “I've always found it very useful in my econometric, in my statistics, in my methodological research to talk to people who are using these methods in practice, who are actually working with these things on the ground. So it's been a real privilege for the last 10 years doing that with the people here at Amazon.”
Panel data
Then, with no further ado, he launched into the substance of his talk. Panel data, he explained, is generally represented by a pair of matrices, whose rows represents units and whose columns represent points in time. In one matrix, the entries represent measurements made on particular units at particular times; the other matrix takes only binary values, which represent whether a given unit was subject to treatment during the corresponding time span.
Ideally, for a given unit and a given time span, we would run an experiment in which the unit went untreated; then we would back time up and run the experiment again, with the treatment. But of course, time can’t be backed up. So instead, for each treated cell in the matrix, we estimate what the relevant measurement would have been if the treatment hadn’t been applied, and we base that estimate on the outcomes for other units and time periods.
For ease of explanation, Imbens said, he considered the case in which only one unit was treated, for only one time interval: “Once I have methods that work effectively for that case, the particular methods I'm going to suggest extend very naturally to the more-general assignment mechanism,” he said. “This is a very common setup.”
Control estimates
Imbens described five standard methods for estimating what would have been the outcome if a treated unit had been untreated during the same time period. The first method, which is very common in empirical work in economics, is known as known as difference of differences. It involves a regression analysis of all the untreated data up to the treatment period; the regression function can then be used to estimate the outcome for the treated unit if it hadn’t been treated.
The second method is called synthetic control, in which a control version of the treated unit is synthesized as a weighted average of the other control units.
“One of the canonical examples is one where he [Alberto Abadie, an Amazon Scholar, pioneer of synthetic control, and long-time collaborator of Imbens] is interested in estimating the effect of an anti-smoking regulation in California that went into effect in 1989,” Imbens explained. “So he tries to find the convex combination of the other states such that smoking rates for that convex combination match the actual smoking rates in California prior to 1989 — say, 40% Arizona, 30% Utah, 10% Washington and 20% New York. Once he has those weights, he then estimates the counterfactual smoking rate in California.”

The third method, which Imbens and a colleague had proposed in 2016, adds an intercept to the synthetic-control equation; that is, it specifies an output value for the function when all the unit measurements are zero.
The final two methods were variations on difference of differences that added another term to the function to be optimized: a low-rank matrix, which approximates the results of the outcomes matrix at a lower resolution. The first of these variations — the matrix completion method — simply adds the matrix, with a weighting factor, to the standard difference-of-differences function.
The second variation — synthetic difference of differences — weights the distances between the unit-time measurements and the regression curve according to the control units’ similarities to the unit that received the intervention.
“In the context of the smoking example,” Imbens said, “you assign more weight to units that are similar to California, that match California better. So rather than pretending that Delaware or Alaska is very similar to California — other than in their level — you only put weight on states that are very similar to California.”
Drawbacks
Having presented these five methods, Imbens went on to explain what he found wrong with them. The first problem, he said, is that they treat the outcome and treatment matrices as both row (units) and column (points in time) exchangeable. That is, the methods produce the same results whatever the ordering of rows and columns in the matrices.
“The unit exchangeability here seems very reasonable,” Imbens said. “We may have some other covariates, but in principle, there's nothing that distinguishes these units or suggests treating them in a way that's different from exchangeable.
“But for the time dimension, it's different. You would think that if we're trying to predict outcomes in 2020, having outcomes measured in 2019 is going to be much more useful than having outcomes measured in 1983. We think that there's going to be correlation over time that makes predictions based on values from 2019 much more likely to be accurate than predictions based on values from 1983.”
The second problem, Imbens said, is that while the methods work well in the special case he considered, where only a single unit-time pair is treated — and indeed, they work well under any conditions in which the treatment assignments have a clearly discernible structure — they struggle in cases where the treatment assignments are more random. That’s because, with random assignment, units drop in and out of the control group from one time period to the next, making accurate regression analysis difficult.
A new estimator
So Imbens proposed a new estimator, one based on the matrix completion method, but with additional terms that apply two sets of weights to each control unit’s contribution to the regression analysis. The first weight reduces the contribution of a unit measurement according to its distance in time from the measurement of the treated unit — that is, it privileges more recent measurements.
The second weight reduces the contributions of control unit measurements according to their absolute distance from the measurement of the treated unit. There, the idea is to limit the influence of outliers in sparse datasets — that is, datasets that control units are constantly dropping in and out of.
Imbens then compared the performance of his new estimator to those of the other five, on nine existing datasets that had been chosen to test the accuracy of prior estimators. On eight of the nine datasets, Imbens’s estimator outperformed all five of its predecessors, sometimes by a large margin; on the ninth dataset, it finished a close second to the difference-of-differences approach — which, however, was the last-place finisher on several other datasets.
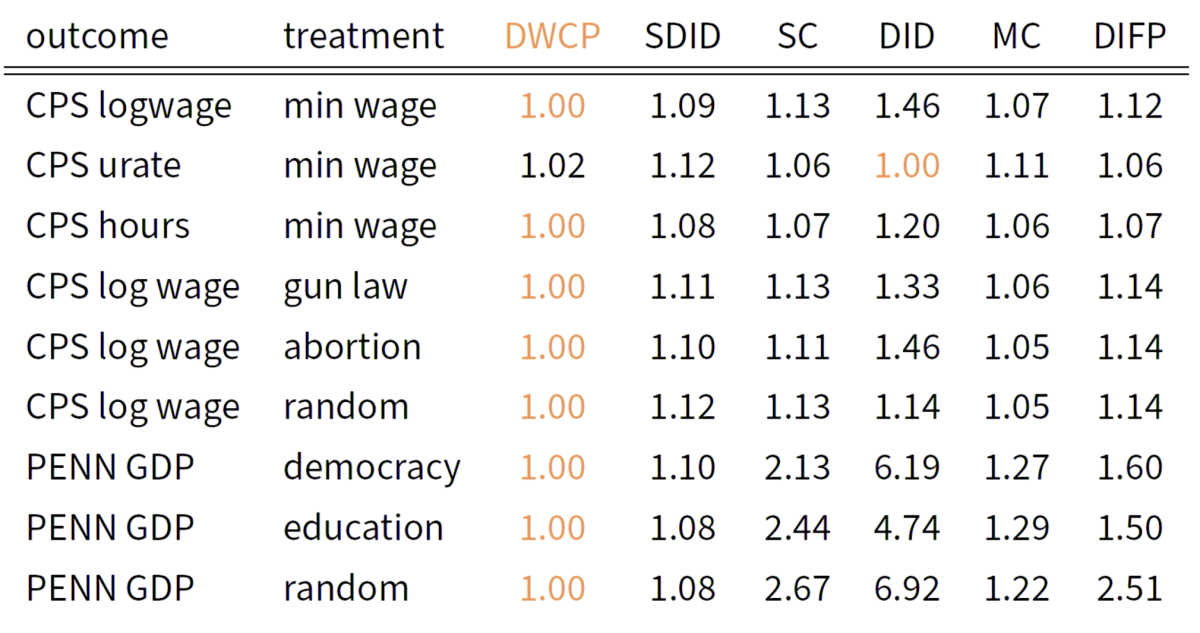
“I don't want to push this as a particular estimator that you should use in all settings,” Imbens explained. “I want to mainly show that even simple changes to existing classes of estimators can actually do substantially better than the previous estimators by incorporating the time dimension in a more uh more satisfactory way.”
For purposes of causal inference, however, the accuracy of an estimator is not the only consideration. The reliability of the estimator — its power, in the statistical sense — also depends on its variance, the degree to which its margin of error deviates from the mean in particular instances. The lower the variance, the more likely the estimator is to provide accurate estimates.
Variance of variance
For the rest of his talk, Imbens discussed methods of estimating the variance of counterfactual estimators. Here things get a little confusing, because the variance estimators themselves display variance. Imbens advocated the use of conditional variance estimators, which hold some variables fixed — in the case of panel data, unit, time, or both — and estimate the variance of the free variables. Counterintuitively, higher-variance variance estimators, Imbens said, offer more power.
“In general, you should prefer the conditional variance because it adapts more to the particular dataset you're analyzing,” Imbens explained. “It's going to give you more power to find the treatment effects. Whereas the marginal variance” — an alternative and widely used method for estimating variance — “has the lowest variance itself, and it's going to have the lowest power in general for detecting treatment effects.”
Imbens then presented some experimental results using synthetic panel data that indicated that, indeed, in cases where data is heteroskedastic — meaning that the variance of one variable increases with increasing values of the other — variance estimators that themselves use conditional variance have greater statistical power than other estimators.
“There's clearly more to be done, both in terms of estimation, despite all the work that's been done in the last couple of years in this area, and in terms of variance estimation,” Imbens concluded. “And where I think the future lies for these models is a combination of the outcome modeling by having something flexible in terms of both factor models as well as weights that ensure that you're doing the estimation only locally. And we need to do more on variance estimation, keeping in mind both power and validity, with some key role for modeling some of the heteroskedasticity.”