Most modern search applications, ad platforms, and recommender systems share a similar multitier information retrieval (IR) architecture with (at a minimum) a candidate selection or retrieval phase and a candidate ordering or ranking phase. Given a query and a context, the retrieval phase reduces the space of possible candidates from millions, sometimes billions, to (typically) hundreds or less. The ranking phase then fine-tunes the ordering of candidates to be presented to customers. This approach is both flexible and scalable.

At Amazon Music, we have previously improved our ranking of the top-k candidates by applying learning-to-rank (LTR) models, which learn from customer feedback or actions (clicks, likes, adding to favorites, playback, etc.). We combine input signals from the query, context, customer preferences, and candidate features to train the models.
However, these benefits apply only to the candidates selected during the retrieval phase. If the best candidate is not in the candidate set, it doesn’t matter how good our ranking model is; customers will not get what they want.
More recently, we have extended the learning-to-rank approach to include retrieval, in what we are calling learning-to-rank-and-retrieve (LTR&R). Where most existing retrieval models are static (deterministic), learning to retrieve is dynamic and leverages customer feedback.
Consequently, we advocate an approach to learning to retrieve that uses contextual multiarmed bandits, a form of reinforcement learning that optimizes the trade-off between exploring new retrieval strategies and exploiting known ones, in order to minimize “regret”.
In what follows, we review prior approaches to both retrieval and ranking and show how, for all of their success, they still have shortcomings that LTR&R helps address.
Candidate selection strategies
Structured search and query understanding
A common candidate retrieval strategy is full-text search, which indexes free-text documents as bags of words stored in an inverted index using term statistics to generate relevance scores (e.g., the BM25 ranking function). The inverted index maps words to documents containing those words.
Full-text search solves for many search use cases, especially when there is an expectation that the candidates for display (e.g., track titles or artist names) should bear a lexical similarity to the query.
We can extend full-text search in a couple of ways. One is to bias the results using some measure of entity quality. For example, we can take the popularity of a music track into account when computing a candidate score such that the more popular of two tracks with identical titles will be more likely to make it into the top page.
We can also extend full-text search by applying it in the context of structured data (often referred to as metadata). For instance, fields in a document might contain entity categories (e.g., product types or topics) or entity attributes (such as brand or color) that a more elaborate scoring function (e.g., Lucene scoring) could take into account.
Structured search (SS) can be effectively combined with query understanding (QU), which maps query tokens to entity categories, attributes, or combinations of the two, later used as retrieval constraints. These methods often use content understanding to extract metadata from free text in order to tag objects or entities with categories and attributes stored as fields, adding structure to the underlying text.
Neural retrieval models
More recently, inspired by advances in representation learning, transformers, and large language models for natural-language processing (NLP), search engineers and scientists have turned their attention to vector search (a.k.a. embedding-based retrieval). Vector search uses deep-learning models to produce dense (e.g., sentence-BERT) as well as sparse (e.g., SPLADE) vector representations, called embeddings, that capture the semantic content of queries, contexts, and entities. These models enable information retrieval through fast k-nearest-neighbor (k-NN) vector similarity searches using exact and approximate nearest-neighbor (ANN) algorithms.
Vector-and-hybrid (lexical + vector) search yields more relevant results than traditional approaches and runs faster on zero-shot IR models, according to the BEIR benchmark. In recommender systems, customer and session embeddings (as query/context) and entity embeddings are also used to personalize candidates in the retrieval stage. These documents can be further reranked by another LTR neural model in a multistage ranking architecture.
A memory index
Research suggests that users’ actions (e.g., query-click information) are the single most important field for retrieval, serving as a running memory of which entities have worked and which haven’t for a given query/context. In a cold-start scenario, we can even train a model that, when given an input document, generates questions that the document might answer (or, more broadly, queries for which the document might be relevant).
These predicted questions (or queries) and scores are then appended to the original documents, which are indexed as predicted query-entity (Q2E) scores. Once query-entailed user actions on entities are captured, these computed statistics can replace predicted values, becoming actual Q2E scores that update the memory index used in ranking. As newly encountered queries show up, resulting from hits on other strategies, additional Q2E pairs and corresponding scores will be generated.
Real-world complications
In his article “Throwing needles into haystacks”, Daniel Tunkelang writes,
If you’re interested in a particular song, artist, or genre, your interaction with a search engine should be pretty straightforward. If you can express a simple search intent using words that map directly to structured data, you should reasonably expect the search application to understand what you mean and retrieve results accordingly.
However, as we will show, when building a product that serves millions of customers who express themselves in ways that are particular to their experiences and locales, we cannot reasonably expect queries “to express a search intent using words that map directly to structured data.”

Let’s start by unpacking an example. Say we want to process the query “love” in a music search system. Even for a single domain (e.g., music/audio) there are many kinds of entities that could match this query, such as songs, artists, playlists, stations, and even podcasts. For each of these categories there could be hundreds and even thousands of possible candidates matching the keyword “love”. Beyond that, each category has different attributes that can also match the keyword (e.g., “love” maps to the genre “love songs”).
Customers may also expect to see related entities in the search results (e.g., artists related to a song returned). So while in the customer’s mind there is surely a main search intent, expressed via a keyword, there could be many possible mappings or interpretations that should be considered. Each of these has a likelihood of being correct, which would generate series of underlying structured searches, first to identify the possible targeted entities and then to bring along related or derived content.
As we have discovered, the crafting and maintenance of such a system is inherently non-scalable.
There is also the problem of compounding errors due to incorrect query understanding and/or content understanding. Category and attribute assignment to queries and entities, which typically uses a combination of human tagging and ML classification models, could be wrong or even completely missing. Furthermore, assignment values may not be binary. For example, “Taylor Swift” is clearly considered a pop artist, but some of her songs are also categorized as country music, alternative/indie, or indie folk.
Given the centrality of interpretation in selecting candidate results, the ability to learn from interactions with customers is essential to successful retrieval. Search applications based on QU+SS and/or FT search, however, usually use static query plans that cannot incorporate feedback in the retrieval stage.
On the other hand, while deep models show enormous promise, they also require significant investment and seem unlikely to completely replace keyword-based retrieval methods in the foreseeable future.
Learning to retrieve
In a world with infinite resources and no latency constraints, we wouldn’t need a retrieval funnel, and we might prefer to rank all possible candidates. But we don’t live in such a world. The reality is that deciding the right balance between increasing precision, usually by exploiting what we already know works, and increasing recall, by exploring more sources and increasing the number of candidates retrieved, is critical for search, ad platforms, and recommender systems. This is especially true in very dynamic applications such as music search, where context matters and new entities, categories, and attributes get added all the time.
And while it would be terrific if we could identify the single candidate selection strategy that produces an optimal top page for every query/context, in practice this is not achievable. The optimal candidate selection strategy depends on the query/context, but we do not know that dependency a priori. We need to learn to retrieve.
One way to try to strike the right explore-exploit trade-off is to implement a multiarmed bandit (MAB) optimization, to learn a policy to select a subset of retrieval strategies (arms) that maximize the sum of stochastic rewards earned through a sequence of searches. That is, the policy should maximize the sum of the likelihoods that the expected results are present in the sets produced by such strategies, as later confirmed by user actions (such as clicking on a link).
The MAB approach uses reinforcement learning (RL) to draw more candidates from strategies that perform well while drawing fewer from underperforming strategies. In particular, for learning-to-retrieve, contextual multiarmed bandit algorithms are ideal, as they are designed to take the query/context features and action features (related to the candidate selection strategy) as input to maximize the reward while keeping healthy rate of exploration to minimize regret.
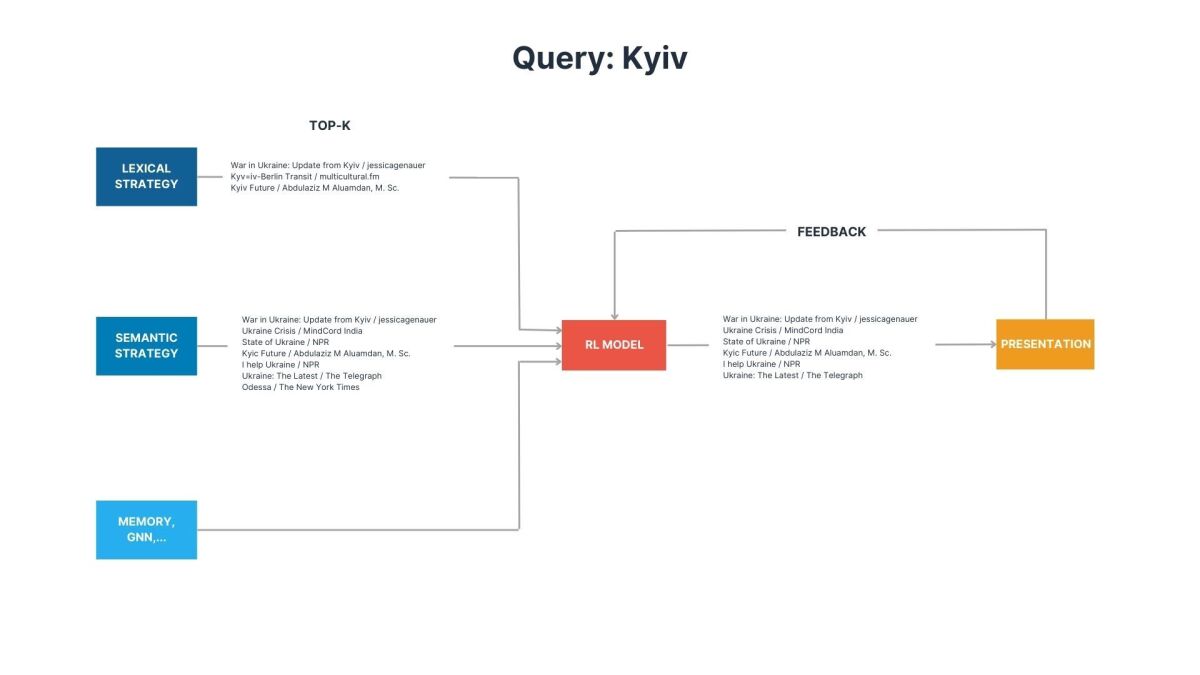
For example, we expect that embeddings based on language models (i.e., a semantic strategy) will perform better for topic search, while the lexical strategy will be more useful for direct entity search (a.k.a. spearfishing queries).
Query/context features may include query information, such as language, type of query, QU slotting and intent classification, query length, etc.; demographic and profile information about your user; information about the current time, such as day of the week, weekend or not, morning or afternoon, holiday season or not, etc.; and historical (aggregate) data of user behavior, such as what genres of music this user has listened to the most.
Action features may include relevance/similarity scores; historical query-strategy performance and number of results; types of entities retrieved, e.g., newly added, popular, personalized, etc.; and information about the underlying retrieval source, e.g., lexical matching, text/graph embeddings, memory, etc.
The model learns a generalization based on these features and the combination of retrieval strategies that maximizes the reward. Finally, we use the union of results produced by the selected strategies to produce a single candidate list that bubbles up to the ranking layer.
Summary
In conclusion, using query understanding (when available) and structured search is a good place to start when building search systems. By adding learning-to-rank, you can start to reap the benefits of factoring in customer feedback and improving the system’s quality. However, this is not sufficient to address the hard problems we observe in real-life applications like music search.
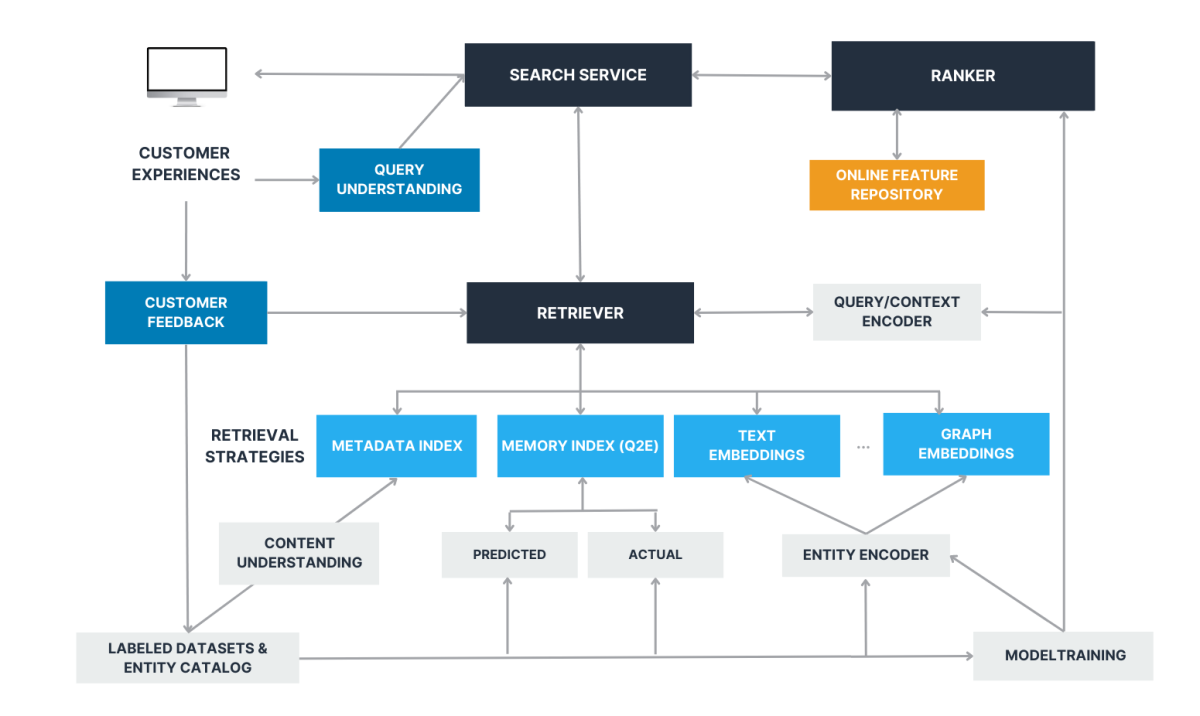
As an extension to the common retrieval-and-ranking phases present in the multitier IR architectures used in most search, ads, and recommender systems, we propose a generic learning-to-rank-and-retrieve (LTR&R) system architecture that comprises multiple candidate generators based on different retrieval strategies. Some produce well-known, exploitable results, like those based on our memory index, while others focus more on exploration, producing novel, riskier, or more-unexpected results that can increase the diversity of the feedback and provide counterfactual data.
This feedback cannot be collected by the static (i.e., fully deterministic) retrieval-and-ranking systems used nowadays. We also suggest using ML, and in particular RL, to optimize the selection of the subset of retrieval strategies and the number of candidates drawn from them, to maximize the likelihood of finding the expected result in such sets.
By incorporating customer feedback and using ML for LTR&R we can (1) simplify the search systems and (2) bubble up the best possible candidates for our customers. LTR&R is a promising path to solving both precision-oriented search and broad and ambiguous queries that require more recall and exploration.
Acknowledgments: Chris Chow, Adam Tang, Geetha Aluri, and Boris Lerner