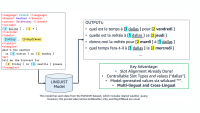
The documents used to train a large language model (LLM) are typically concatenated to form a single “superdocument”, which is then divided into sequences that match the model's context length. This improves training efficiency but often results in unnecessary truncations, where individual documents are broken up across successive sequences.
In paper we’re presenting at this year’s International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2024), titled “Fewer truncations improve language modeling”, we report an in-depth study of this common concatenation-chunking document-processing method. We found that it severely impairs the model's ability to understand contextual coherence and factual consistency. This not only affects the model's performance on downstream tasks but also increases the risk of hallucinations.
To address this issue, we propose best-fit packing, an innovative document-processing strategy that optimizes document combinations to eliminate unnecessary text truncations. In experiments, we compared a model trained using best-fit packing to one trained in the ordinary way on six downstream tasks: reading comprehension, natural-language inference, context following, summarization, commonsense and closed-book question answering, and program synthesis. We found that best-fit packing monotonically improves performance on an array of 22 sub-tasks, by as much as 15% (program synthesis) to 17% (context following). Importantly, best-fit packing also reduces closed-domain hallucination effectively by up to 58.3%.
Consequences of truncation
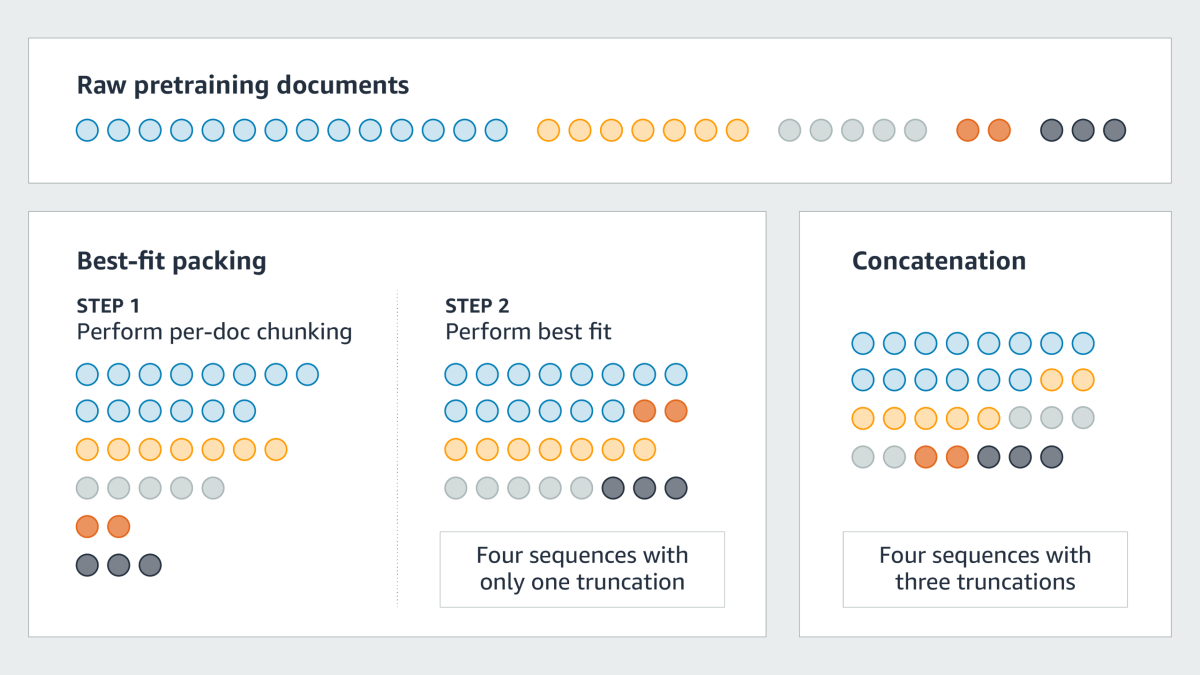
In the analysis reported in our paper, we identified several problems caused by document truncation, including undefined names, ungrounded content, and missing knowledge.
Undefined names: In programming languages like Python, truncation may separate definitions of variables from their invocations, introducing syntax errors and causing some variables to be undefined. As a consequence, the model may learn misleading patterns and possibly hallucinate on downstream tasks.
Ungrounded content: Truncation damages data integrity. In the example below, for instance, a reference (“the earthquake on Monday morning”) is separated from its antecedent, resulting in unfaithful generation.
Missing knowledge: Truncation hinders knowledge acquisition. In the example below, the model cannot learn the location of the ICML conference because the conference name and location occur in different training sequences.
Best-fit packing
To address this issue, we propose optimizing the assignment of documents to training sequences so as to eliminate unnecessary truncations, while minimally increasing the number of sequences relative to concatenation. This is a variation of the well-known bin-packing problem, which is NP-hard in general, but we use a heuristic called the best-fit-decreasing (BFD) algorithm that tends to work well in practice. We thus call our method best-fit packing.
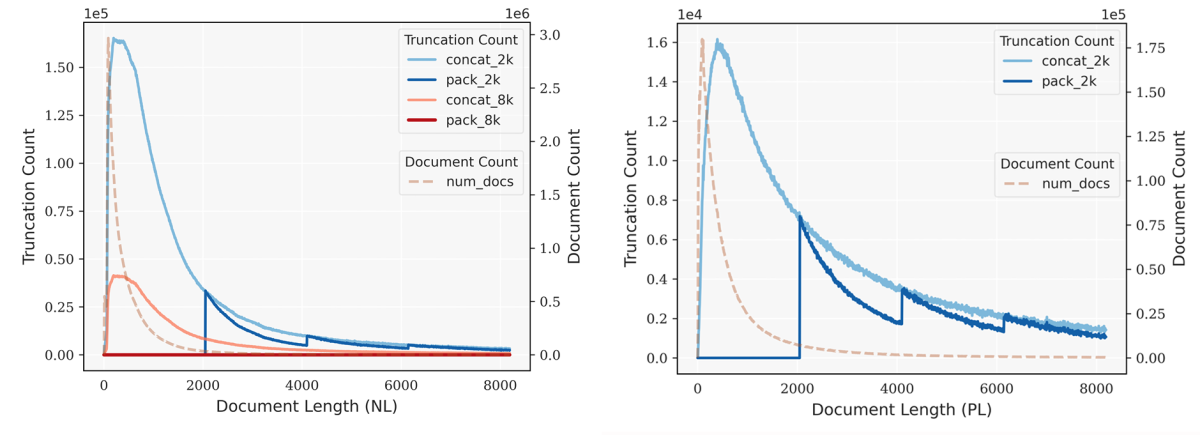
The normal implementation of BFD has quasi-linear time complexity, which is not efficient enough for LLM pretraining, which typically involves millions of documents. By taking advantage of the unique nature of pretraining data, however, we were able to optimize BFD so that it scales linearly with data size, ensuring its applicability to large-scale pretraining datasets. Further, we show that in practical applications, best-fit packing generates approximately the same number of training sequences as the traditional method, while significantly reducing data loss caused by truncation.
Curious to know how we achieve it? Let’s dive deep!
Best-fit packing — an example
Following the standard bin-packing nomenclature, we call each training sequence a “bin”, and each bin has a capacity equal to the LLM’s context size. The goal is to assign a combination of whole documents to each bin so as to minimize the wasted bin capacity.
First, we divide any document that’s larger than the LLM context into context-length chunks, plus a remainder. Then we sort the documents (and document fragments) from largest to smallest. Finally, we work our way down the sorted list, assigning each document to the bin whose available space is as close to the document size as possible.
To maximize efficiency, we use three data structures to manage the assignment of documents to bins: a binary tree and two tables. We can use this design because (1) the maximum bin size is the model’s context size, so the tree won’t be too deep, and (2) we do not need to distinguish bins with the same remaining capacity, which simplifies the the tree. Instead, we use the tables to map bin capacities to bins.
Consider a simple example, in which the context size (the bin size) is eight. The binary tree has eight leaves, corresponding to the eight possibilities for available space in any given bin. (In a real LLM, the context size is on the order of thousands of tokens, so the tree would have thousands of leaves.)
Each parent node of the tree has an associated number, indicating the size of the largest available bin slot among its descendants. The number associated with the parent’s right child is always greater than or equal to the number associated with the left child.
Initially, the value of the rightmost node in each layer of the tree is eight, and all the other nodes have values of zero. This means that all the available bin slots have a capacity of eight.
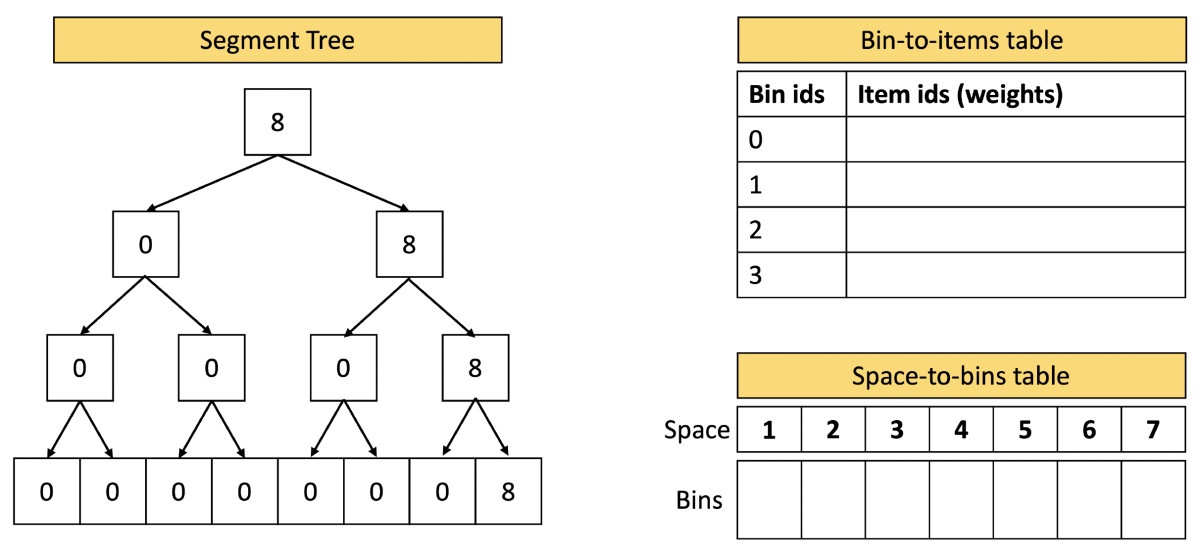
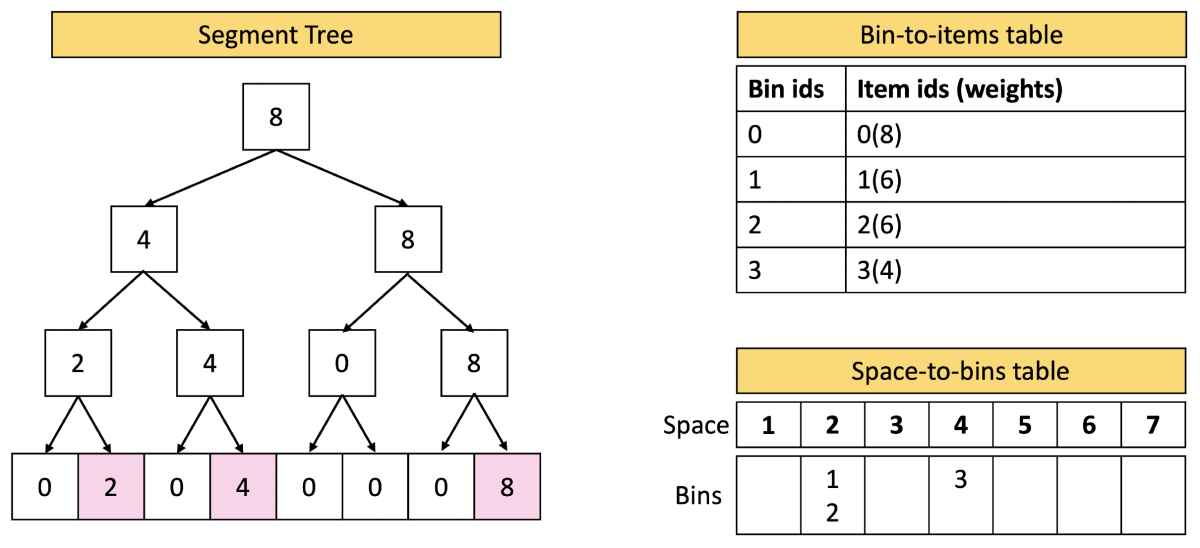
Now consider a later state, when four documents of size eight, six, six, and four have been packed. The two bins containing documents of size six have available slots of size two (8 – 6), and the bin containing a document of size four has an available slot of size four (8 – 4). These sizes are represented by the numbers two and four at leaves two and four of the tree. Multiple bins remain empty, so leaf eight has a value of eight, too.
Note that the value two at leaf two indicates only that at least one bin slot of size two is available; it doesn’t indicate how many such slots there are or where they can be found. That information is contained in the tables.
Now consider a document of size three, which we wish to assign to a bin. To find the best available bin slot, simply go left at each node of the tree, unless going left leads to a node whose value is less than the document size, in which case, go right.
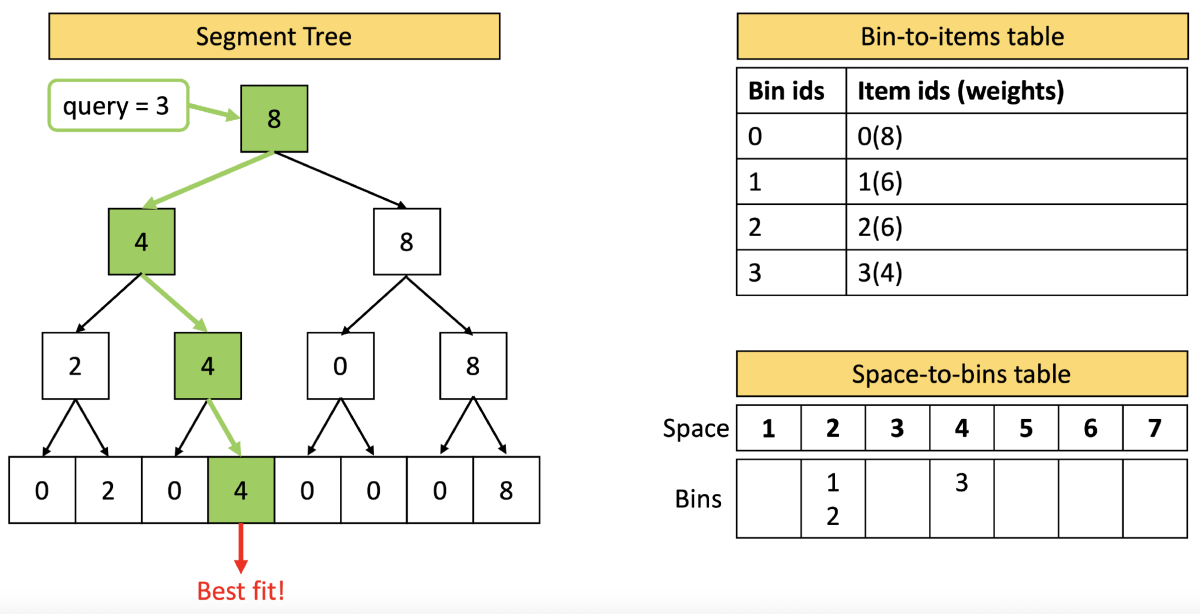
The best fit for a document of size three is a slot of size four, and in the “space-to-bins” table, we see that there is one bin — bin three — with a slot of that size. So there we place the document.
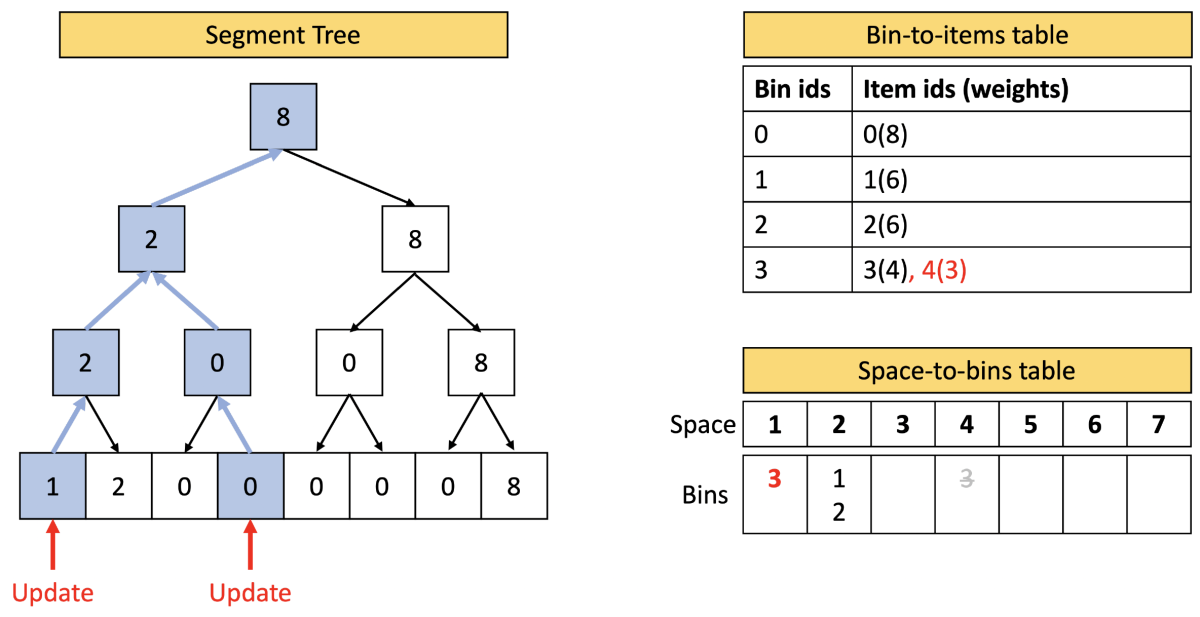
Finally, we update all three data structures to reflect the new placement:
Results
To evaluate the effect of bin-packing on downstream tasks, we pretrained models of 7 billion and 13 billion parameters with context lengths of 2,000 and 8,000 on text and code using both best-fit packing and concatenation. We then tested both sets of models on our six downstream tasks. On average, across multiple datasets, context lengths, and metrics, best-fit packing offered better performance on all six tasks. The biggest gains came in reading comprehension (+4.7%), natural-language inference (+9.3%), context following (+16.8%), and program synthesis (+15.0%).
We also found that best-fit packing helped prevent closed-domain hallucination, particularly in program synthesis tasks, where it reduced "undefined name" errors by up to 58.3%, indicating a more complete understanding of program structure and logic.
Additionally, models trained with best-fit packing were better at following instructions, such as adhering to length constraints. And best-fit packing helped the model acquire “tail knowledge” that is truncation sensitive due to scarcity in training data. Indeed, this result suggests a possible reason for why LLMs struggle to learn long-tail knowledge.
While the experiments conducted in our paper primarily focused on LLM pretraining, best-fit packing is broadly applicable to fine tuning as well. Determining the benefits it can offer during fine tuning is an intriguing topic for future study.