In the past decade, deep-learning systems have proven remarkably successful at many artificial-intelligence tasks, but their applications tend to be narrow. A computer vision system trained to recognize cats and dogs, for instance, would need significant retraining to start recognizing sharks and sea turtles.
Meta-learning is a paradigm intended to turn machine learning systems into generalists. A meta-learning model is trained on a range of related tasks, but it learns not only how to perform those tasks but also how to learn to perform them. The idea is that it could then be adapted to new tasks with only a handful of labeled training examples, drastically reducing the need for labor-intensive data annotation.
At the (virtual) International Conference on Learning Representations, we will present an approach that improves performance on meta-learning tasks without increasing the data annotation requirements. The key idea is to adapt the meta-learning procedure so that it can leverage small sets of unlabeled data, in addition to the traditional labeled examples.

The intuition is that even without labels, these extra data still contain a lot of useful information. Suppose, for instance, that a meta-learning system trained on images of terrestrial animals (such as cats and dogs) is being adapted to recognize aquatic animals. Unlabeled images of aquatic animals (i.e., images that don’t indicate whether an animal is a shark or a sea turtle) still tell the model something about the learning task, such as the lighting conditions and background colors typical of underwater photos.
In experiments, we compared models trained through our approach to 16 different baselines on an object recognition meta-learning task. We found that our approach improved performance on one-shot learning, or learning a new object classification task from only a single labeled example, by 11% to 16%, depending on the architectures of the underlying neural networks.
Meta-learning
In conventional machine learning, a model is fed a body of labeled data and learns to correlate data features with the labels. Then it’s fed a separate body of test data and evaluated on how well it predicts the labels for that data. For evaluation purposes, the system designers have access to the test-data labels, but the model itself doesn’t.
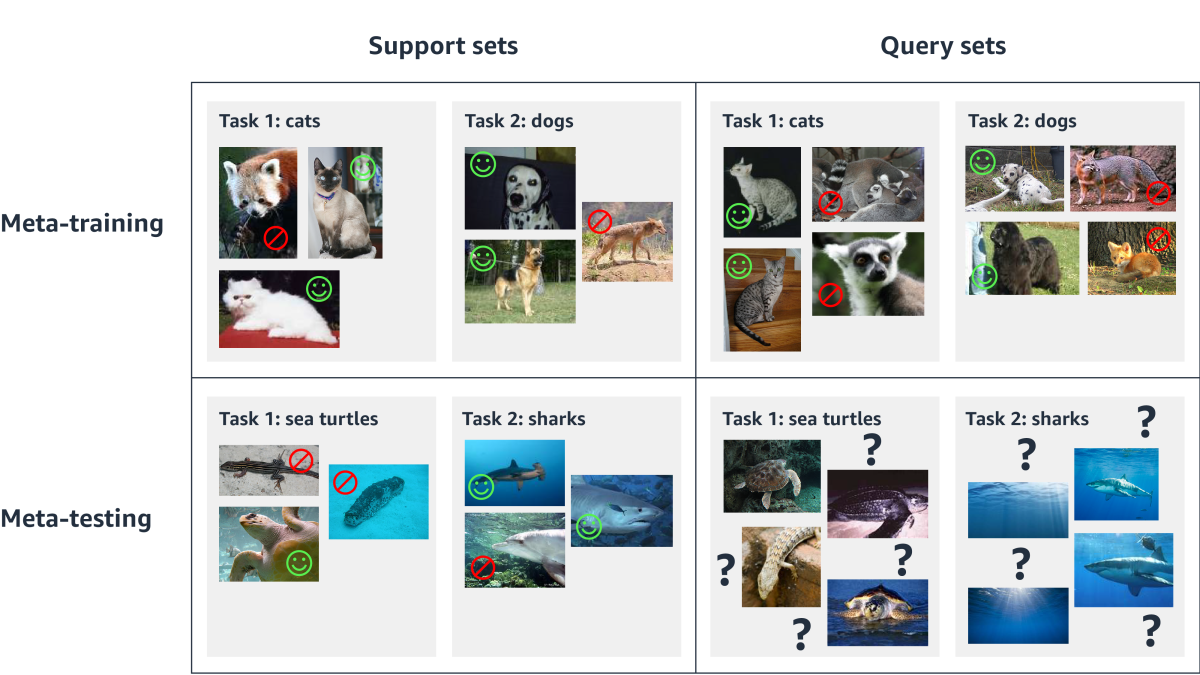
Meta-learning adds another layer of complexity. During meta-training — the analogue of conventional training — the model learns to perform a range of related tasks. Each task has its own sets of training data and test data, and the model sees both. That is, part of its meta-training is learning how particular ways of responding to training data tend to affect its performance on test data.
During meta-testing, it is again trained on a range of tasks. These are related to but not identical to the tasks it saw during meta-training — recognizing aquatic animals, for instance, as opposed to terrestrial animals. Again, for each task, the model sees both training data and test data. But whereas, during meta-training, the test data were labeled, during meta-testing, the labels are unknown and must be predicted.
The terminology can get a bit confusing, so meta-learning researchers typically refer to the meta-learning “training” sets as support sets and the meta-learning “test” sets as query sets. During meta-training, the learning algorithm has access to the labels for both the support sets and the query sets, and it uses them to produce a global model. During meta-testing, it has access only to the labels for the support sets, which it uses to adapt the global model to each of the new tasks.
Our approach has two key innovations. First, during meta-training, we do not learn a single global model. Instead, we train an auxiliary neural network to produce a local model for each task, based on the corresponding support set. Second and more important, during meta-training we also train a second auxiliary network to leverage the unlabeled data of the query sets. Then, during meta-testing, we can use the query sets to fine-tune the local models, improving performance.
Leveraging unlabeled data
A machine learning system is governed by a set of parameters, and in meta-learning, meta-training optimizes them for a particular family of tasks — such as recognizing animals. During meta-testing or operational deployment, the model uses a handful of training examples to optimize those parameters for a new task.
A particular set of parameter values defines a point in a multidimensional space, and adaptation to a new task can be thought of as searching the space for the point representing the optimal new settings.
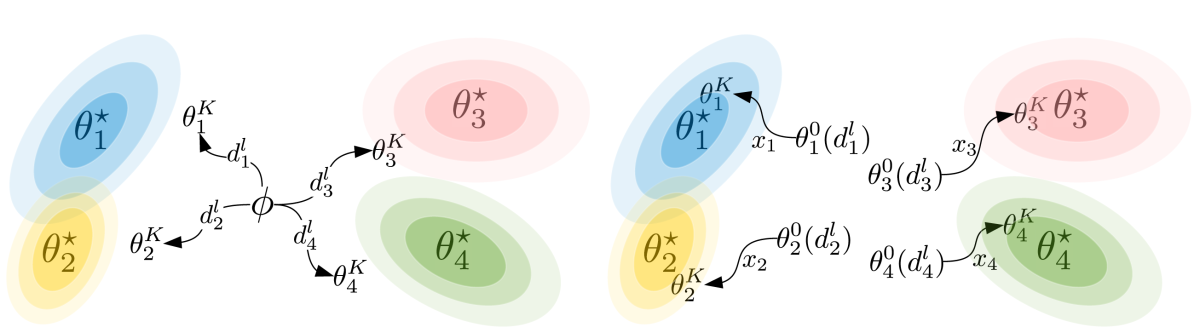
A traditional meta-learning system might begin its search at the point defined by the global model (φ in the figure above); this is the initialization step. Then, using the labeled data of the support set, it would work its way toward the settings that correspond to the new task; this is the adaptation step.
With our approach, by contrast, the initialization network selects a starting search location on the basis of the data in the support set (θ01(dl1) – θ04(dl4) in the figure above). Then it works its way toward the optimal settings using the unlabeled data of the query set (x1 – x4, above). More precisely, the second auxiliary neural network estimates the gradient implied by the query set data.
In the same way that the parameter settings of a machine learning model can be interpreted as a point in a representational space, so can the parameter settings and the resulting error rate on a particular data set. The multidimensional graph that results is like a topological map, with depressions that represent low error rates and peaks that represent high error rates. In this context, machine learning is a matter of identifying the slope of a depression — a gradient — and moving down it, toward a region of low error.
This is how many machine learning systems learn, but typically, they have the advantage of knowing, from training data labels, what the true error rate is for a given set of system parameters. In our case, because we’re relying on the unlabeled query set data, we can only guess at the true gradients.
That’s where the second auxiliary neural network comes in: it infers gradients from query set data. The system as a whole then uses the inferred gradients to fine-tune the initial parameter settings supplied by the first neural network.
The approach can be explained and justified through connections to two topics in theoretical machine learning, namely empirical Bayes and information bottleneck. These theoretical developments are beyond the scope of this blog post, but the interested reader can consult the full manuscript.
The associated software code has also been open-sourced as part of the Xfer repository.
Although our system beat all 16 baselines on the task of one-shot learning, there were several baseline systems that outperformed it on five-shot learning, or learning with five examples per new task. The approaches used by those baselines are complementary to our approach, and we believe that combining approaches could yield even lower error rates. Going forward, that’s one of several extensions of this work that we will be pursuing.

















