Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is the core technology of autonomous mobile robots. It involves simultaneously building a map of the robot’s environment and finding the robot’s location within that map.
SLAM is computationally intensive, and deploying it on resource-constrained robots — such as consumer household robots — generally requires techniques for making computations more tractable.
One such technique is the use of low-precision floating-point arithmetic, or reducing the number of bits used to represent numbers with decimal points. The technique is popular in deep learning, where halving the number of bits (from the standard 32 to 16) can double computational efficiency with little effect on accuracy.
But applying low-precision arithmetic to SLAM is more complicated. Where deep-learning-based classification models are discrete-valued, SLAM involves solving a nonlinear optimization problem with continuous-valued functions, which require higher accuracy.
At Amazon, we’ve tackled this problem by designing a novel mixed-precision solver, which combines 64-bit (fp64), 32-bit (fp32), and 16-bit (fp16) precisions for nonlinear optimization problems in the SLAM algorithm. This innovation paves the way for faster and greener on-device navigation.
General framework
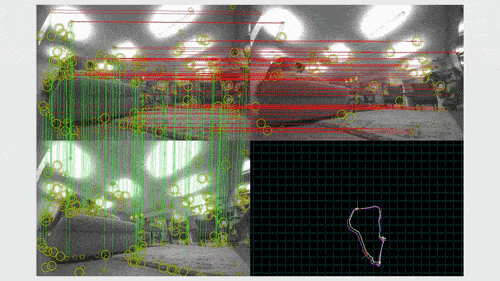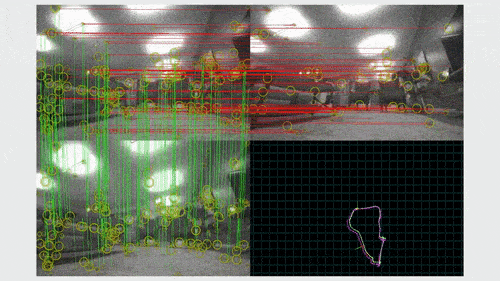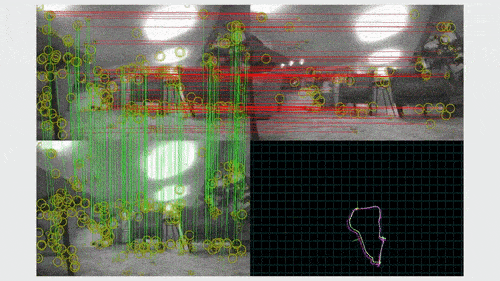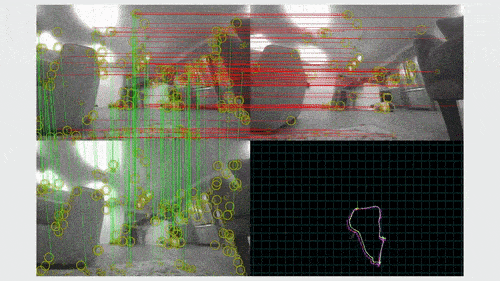
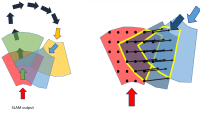
A SLAM algorithm has two key components: visual odometry and loop closure. Visual odometry gives real-time estimates of the robot’s pose, or its orientation and location on the map, based on the most recent observations. When the robot recognizes that it has arrived at a place that it previously visited, it closes the loop by globally correcting its map and its location estimate.
Both visual odometry and loop closure involve solving nonlinear optimization problems — bundle adjustment (BA) and pose graph optimization (PGO), respectively. To solve them efficiently, SLAM systems typically use approximate methods that recast them as sequences of linearized optimization problems. If the goal is to find the pose estimate x, then each linear problem minimizes the linearized error function, which is the sum of the current error function and its first-order correction. The first-order correction is the product of the Jacobian, which is the matrix of the function’s first-order derivatives, and the update to the pose estimation. The linear problems are typically solved through factorization, using either Cholesky or QR methods. The solution of each linearized optimization problem is the update for the current pose estimate.
The general procedure is to start with the current approximation of x, compute the error function and the Jacobian, solve a linear optimization problem, and update x accordingly, repeating the process until certain stopping criteria are met. At each iteration, the value of the error function is known as the residual, since it’s the residual error left over from the previous iteration.
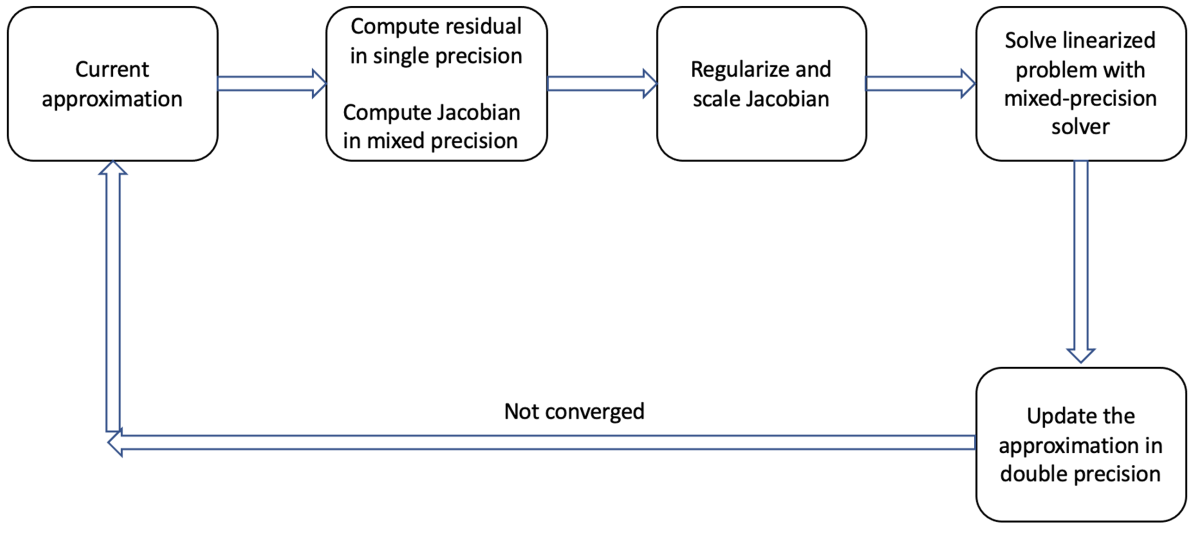
The most expensive computations in the nonlinear optimizations for both BA and PGO are the computation of the Jacobian (about 15% of the optimization time) and the solution of the linear problem (about 60%). Simply solving either problem at half-precision (fp16) from beginning to end will result in lower accuracy and sometimes numerical instability.
To mitigate these difficulties, we regularize and scale the matrices to avoid overflow and rank deficiency. The rank deficiency occurs when columns of the Jacobian are linearly dependent. Through careful experiments, we further identified the computations to be done at precision higher than fp16 and proposed a mixed-precision nonlinear optimization solver.
We found that, to match the accuracy of the solution in pure double-precision, the following two components have to be computed in precision higher than fp16:
- The residual must be evaluated in single or higher precision;
- The update of x, which is a six-degree position-angle update, must be done in double precision.
Although this general optimization framework applies to both BA and PGO, the details vary across the two applications, because of the different structures and properties of the matrices in the linear problems. We thus propose two mixed-precision solving strategies for the relevant linear systems.
Visual odometry
For visual odometry, people traditionally use filter-based methods, which can suffer from large linearization error. Nonlinear optimization-based methods have become more popular in recent years. These methods estimate the position and orientation of the robot by minimizing an error function, which is the difference between the re-projection of landmarks and their observation in the image frame. This procedure is called bundle adjustment because we are adjusting a bundle of light rays to match the projection with the observation.
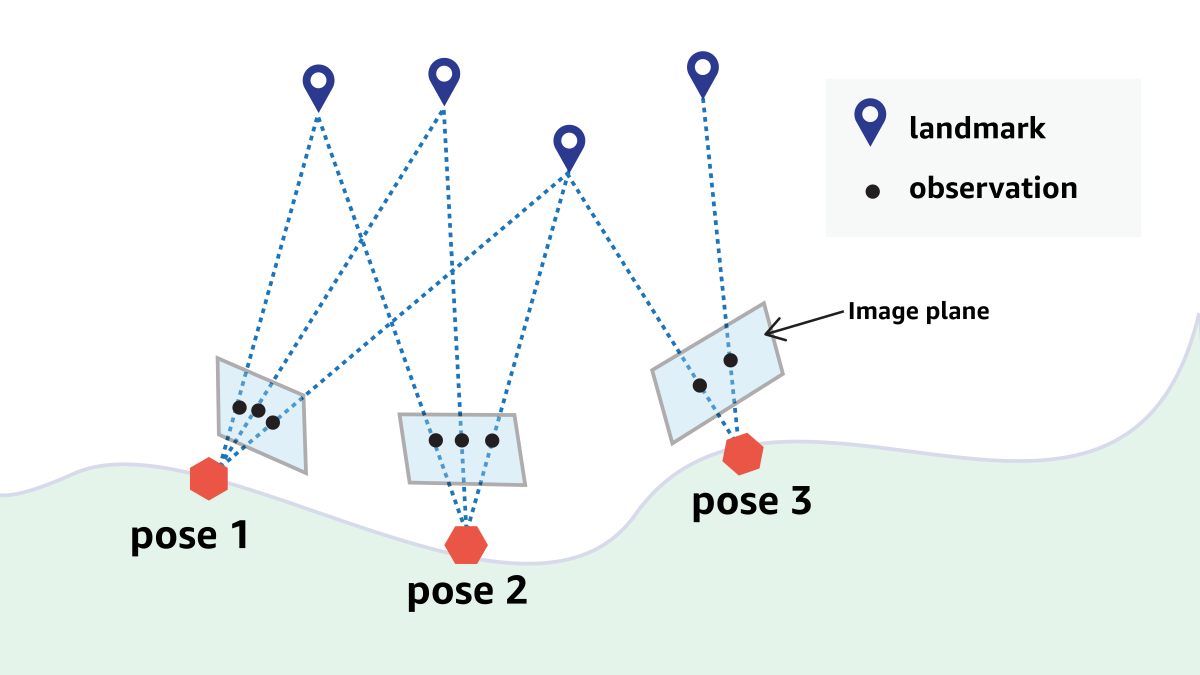
BA-based visual odometry operates over a sliding window that contains a fixed number of (key) frames. On average, a new key frame comes at 10Hz. The challenge is to solve the BA problem within a given time budget. One popular way to do this is to solve the normal equation that is the equivalent of the linearized optimization problem; this involves the approximation of the Hessian matrix, or the matrix of second-order derivatives of the residual.
The BA problem involves two sets of unknown state variables: one indicates the robot’s pose and the other indicates the landmark location. One way to reduce the computational burden of the BA problem is to marginalize the constraints between camera poses and landmarks and focus on the camera poses first. In the SLAM community, this procedure is known as Schur elimination or landmark marginalization.
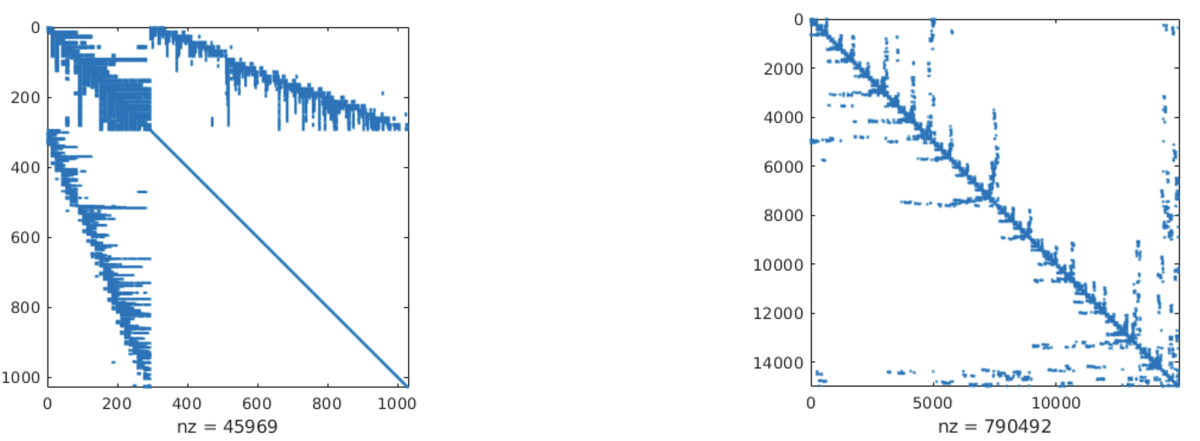
This marginalization step can greatly reduce the size of the linear system that needs to be solved. For a 50-frame BA problem, the Jacobian matrix is usually of the size 5,500 x 1,000, and the Hessian is of size 1,000 x 1,000. Decoupling constraints reduces the size of the linear system to 300 x 300, small enough to be solved with direct or iterative solvers. However, this strategy requires both the formulation of the Hessian matrix and a partial-elimination step, which are expensive to employ in practice.
Our mixed-precision linear solver, which mixes single and half-precision, is based on the conjugate gradient normal-equation residual (CGNR) method, which is an iterative method directly applied to the linear-optimization problem without explicit formulation of the Hessian.
As in the general framework, a naïve casting of all computations to half-precision will result in lower accuracy. In our experiments, we found that if we compute matrix-vector products in half-precision and all other operations in single precision, we will maintain the overall accuracy of the SLAM pipeline.
The matrix-vector products, which are the major computation in CGNR iterations, usually account for 83% of the computing cost, in terms of number of floating-point operations. That means that, if run on NVIDIA V100 GPUs, the mixed-precision solver could save at least 41% solving time compared to the single-precision linear solver.
Loop closure
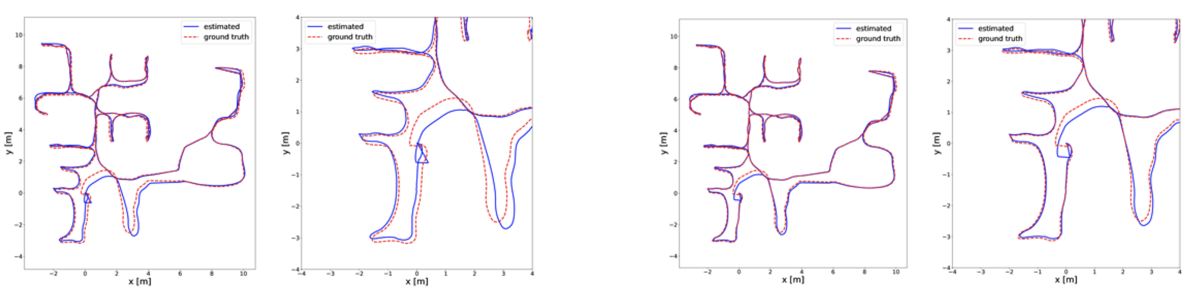
In the SLAM pipeline, the local pose estimates from VO usually exhibit large drift, especially in the long run. Loop closure corrects this drift.
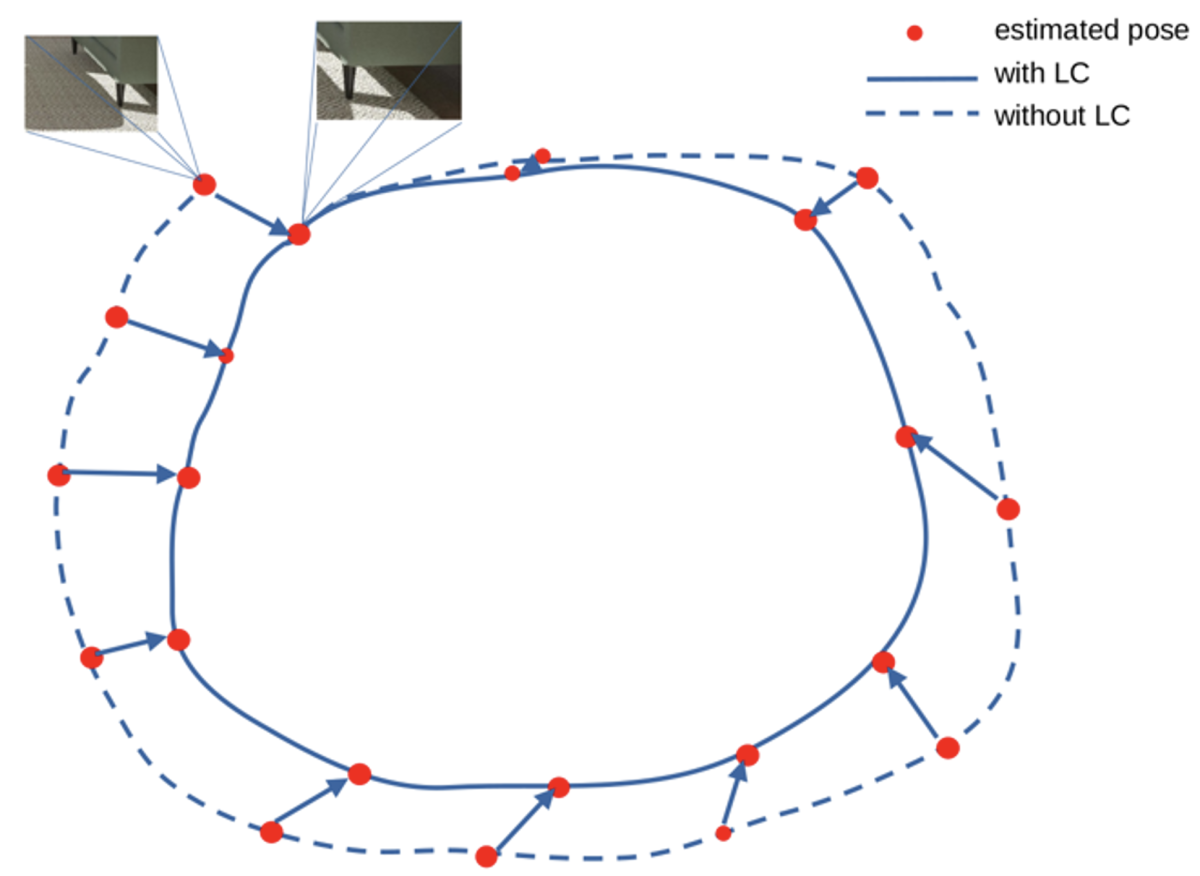
For a real-world mapping estimate, without LC correction, the average trajectory error could be at the order of 0.1 meter, which is not acceptable in practice. This error is reduced to 10-4 meters after applying LC corrections.
|
ATE w/o LC (m) |
ATE with LC (m) |
Max |
4.03E-01 |
5.83E-04 |
99% |
2.65E-01 |
5.71E-04 |
90% |
2.00E-01 |
5.57E-04 |
Mean |
9.72E-02 |
3.19E-04 |
The LC adjustment involves solving a global PGO problem. Like the BA problem, it is a nonlinear optimization problem and can be solved within the same mixed-precision framework. But the linear systems arising from PGO problems are much larger and sparser than those of the BA problem.
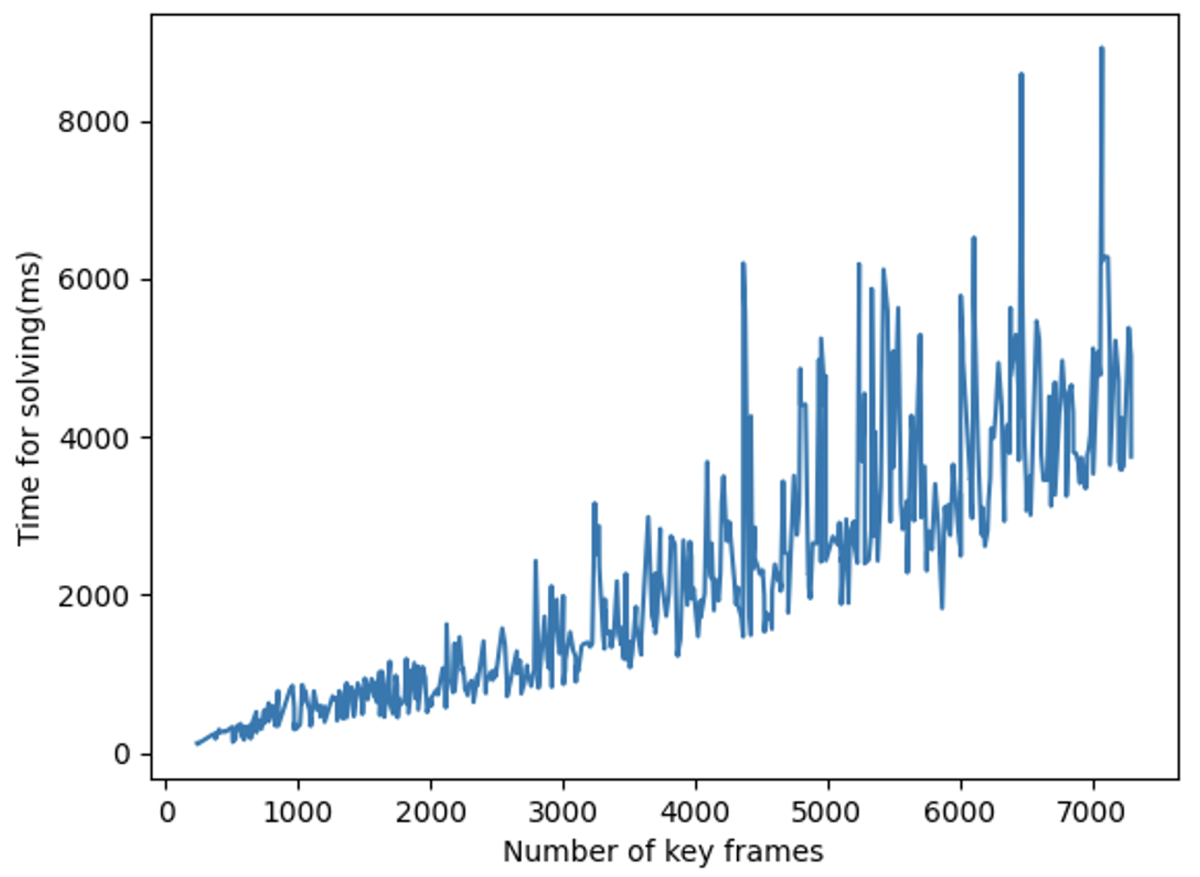
As more and more loops are closed, the problem size could grow from several hundreds of poses to several thousands of poses. If we measure the size of a matrix by the number of its rows, during loop closure, the size could grow from the order of 100 to the order of 10,000. Directly solving sparse matrices of this size in double precision is challenging, especially considering the time and computation constraints of on-device applications. For a real-world trajectory estimation, the solving time for the PGO problem could grow up to eight seconds with full CPU usage.
This results in a different strategy for designing a mixed-precision solver for PGO problems. Due to the sparsity of the Jacobian matrix, our mixed-precision method is still based on the iterative CGNR method. But to accelerate the convergence of the CGNR iterations, we apply a static incomplete Cholesky preconditioner in each iteration. Cholesky factorization decomposes a symmetric linear system into a product of two triangular matrices, meaning that all of their nonzero values are concentrated on one side of a diagonal across the matrix. This decomposition step is expensive, so we do it only once for the whole problem. The computational cost is mostly dominated by the application of the preconditioner, which involves solving two triangular systems. In our timing analysis, this step consumes around 50% of the computation in each linear solving.
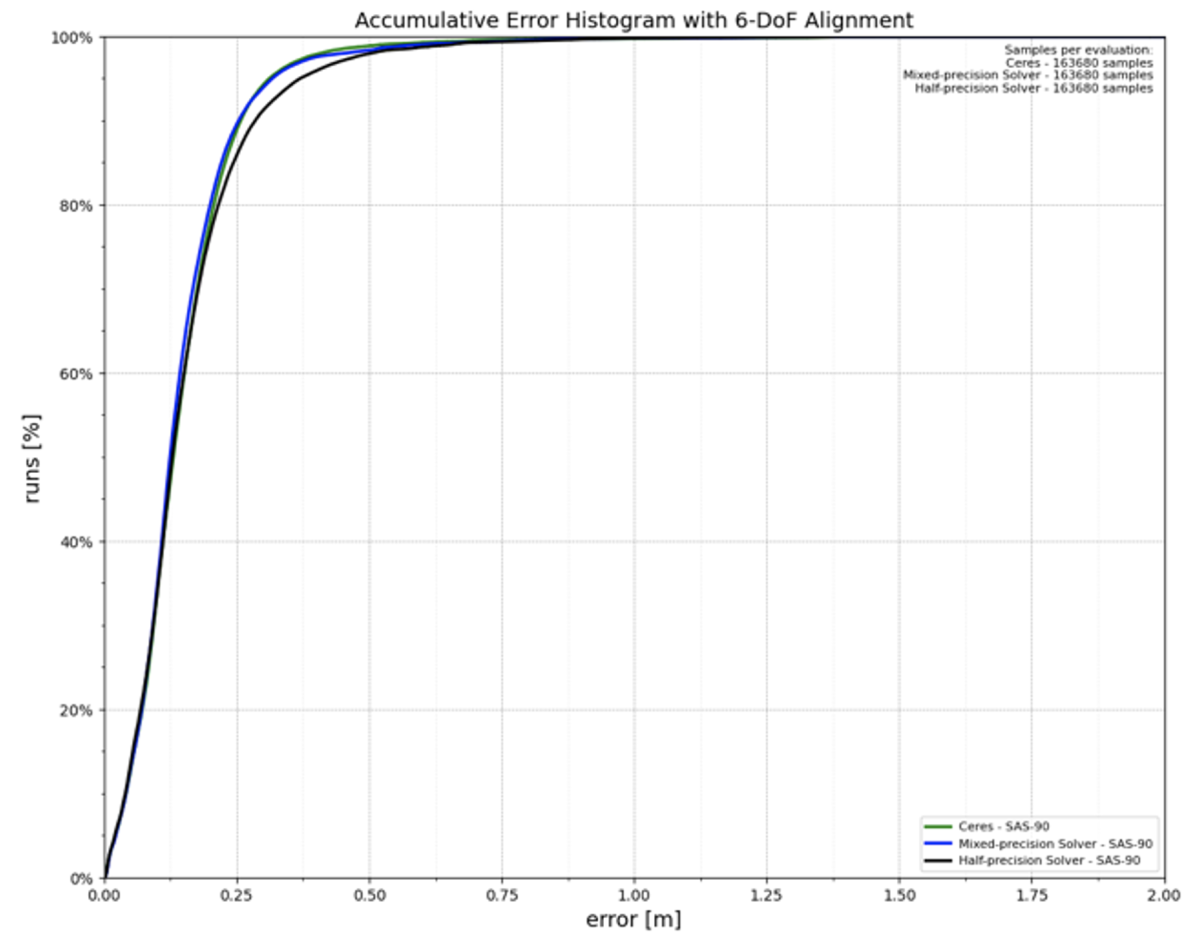
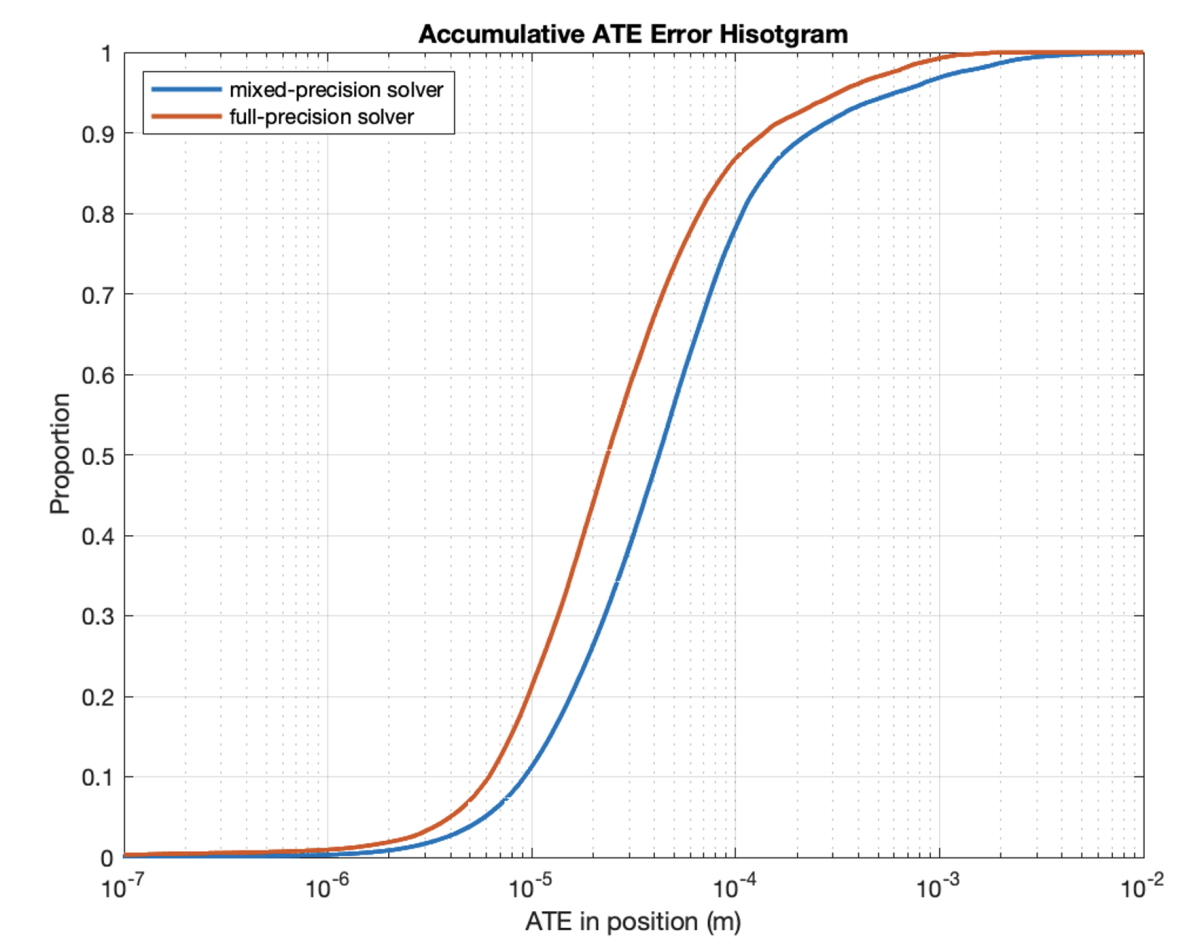
To accelerate the optimization, instead of computing matrix-vector products in half-precision, we solve the triangular system in half-precision, keeping all other operations in single precision. With this mixed-precision solver, we could almost match the accuracy of the full-precision solver while reducing computing time by 26% on average.
Our results across both the VO and LC applications show that because of the high-efficiency and low-energy nature of half-precision arithmetic, mixed-precision solvers could make on-device SLAM faster and greener.
Acknowledgments
The following contributed equally to this work: Tong Qin, applied scientist, Amazon Hardware; Sankalp Dayal, applied-science manager, Hardware; Joydeep Biswas, software development engineer, Amazon Devices; Varada Gopalakrishnan, vice president and distinguished engineer, Hardware; Adam Fineberg, senior principal engineer, Devices; Rahul Bakshi, senior manager of software, machine learning, and mobility, Hardware.