Where a standard relational database stores data in linked tables, graph databases store data in graphs, where the edges represent relationships between data items. Graph databases are popular with customers for use cases like single-customer view, fraud detection, recommendations, and security, where you need to create relationships between data and quickly navigate these connections. Amazon Neptune is AWS’s graph database service, which is designed for scalability and availability and allows our customers to query billions of relationships in milliseconds.
In this blog post, we present joint work on a schema language for graph databases, which was carried out under the umbrella of the Linked Data Benchmarking Council (LDBC), a nonprofit organization that brings together leading organizations and academics from the graph database space. A schema is a way of defining the structure of a database — the data types permitted, the possible relationships between them, and the logical constraints upon them (such as uniqueness of entities).
This work is important to customers because it will allow them to describe and define the structures of their graphs in a way that is portable across vendors and makes building graph applications faster. We presented our work in a paper that won the best-industry-paper award at this year’s meeting of the Association for Computing Machinery's Special Interest Group on Management of Data (SIGMOD).
Labeled-property graphs
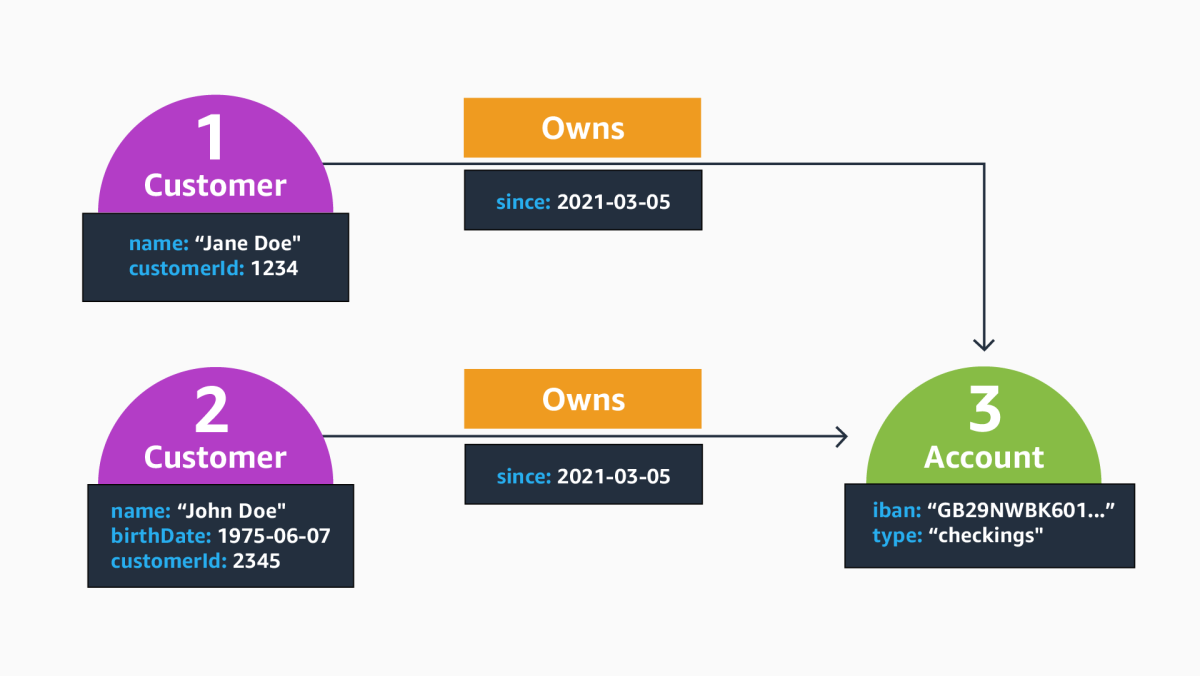
The labeled-property-graph (LPG) data model is a prominent choice for building graph applications. LPGs build upon three primitives to model graph-shaped data: nodes, edges, and properties. The figure below represents an excerpt from a labeled property graph in a financial-fraud scenario. Nodes are represented as green circles, edges are represented as directed arrows connecting nodes, and properties are enclosed in orange boxes.
The node with identifier 1, for instance, is labeled Customer and carries two properties, specifying the name with string value “Jane Doe” and a customerId. Both node 1 and 2 two are connected to node 3, which represents a shared account with a fixed iban number; the two edges are marked with the label Owns, which specifies the nature of the relationship. Just like vertices, edges can carry properties. In this example, the property since specifies 2021-03-05 as the start date of ownership.
Relational vs. graph schema
One property that differentiates graph databases from, for instance, relational databases — where the schema needs to be defined upfront and is often hard to change — is that graph databases do not require explicit schema definitions. To illustrate the difference, compare the graph data model from the figure above to a comparable relational-database schema, shown below, with the primary-key attributes underlined.
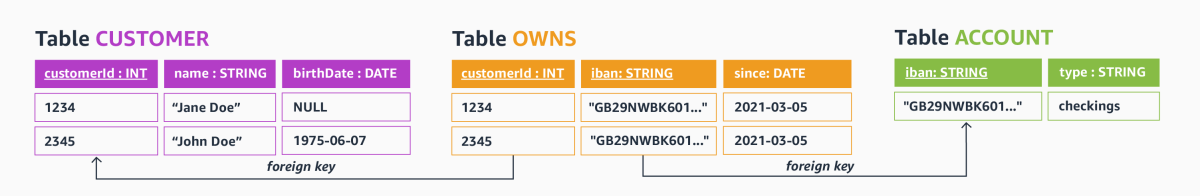
Schema-level information of the relational model — tables and attribute names — are represented as part of the data itself in graphs. Said otherwise, by inserting or changing graph elements such as node labels, edge labels, and property names, one can extend or change the schema implicitly, without having to run (oftentimes tedious) schema manipulations such as ALTER TABLE commands.
As an example, in a graph database one can simply add an edge with the previously unseen label Knows to connect the two nodes representing Jane Doe and John Doe or introduce nodes with new labels (such as FinancialTransaction) at any time. Such extensions would require table manipulations in our relational sample schema.
The absence of an explicit schema is a key differentiator that lowers the burden of getting started with data modeling and application building in graphs: following a pay-as-you-go paradigm, graph application developers who build new applications can start out with a small portion of the data and insert new node types, properties, and interconnecting edges as their applications evolve, without having to maintain explicit schemata.
Schemata evolution
While this contributes to the initial velocity of building graph applications, what we often see is that — throughout the life cycle of graph applications — it becomes desirable to shift from implicit to explicit schemata. Once the database has been seeded with an initial (and typically yet-to-be-refined) version of the graph data, there is a demand for what we call flexible-schema support.
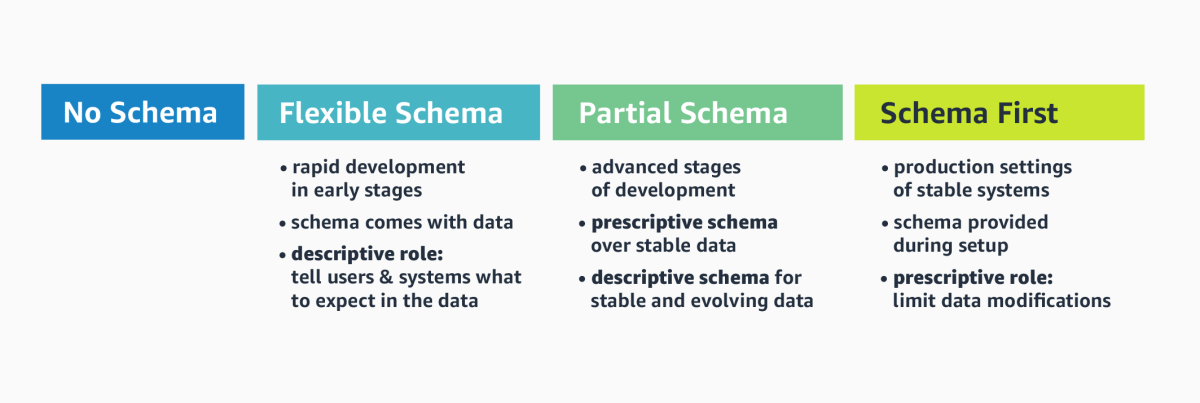
In that stage, the schema primarily plays a descriptive role: knowing the most important node/edge labels and their properties tells application developers what to expect in the data and guides them in writing queries. As the application life cycle progresses, the graph data model stabilizes, and developers may benefit from a more rigorous, prescriptive schema approach that strongly asserts shapes and logical invariants in the graph.
PG-Schema
Motivated by these requirements, our SIGMOD publication proposes a data definition language (DDL) called PG-Schema, which aims to expose the full breadth of schema flexibility to users. The figure below shows a visual representation of such a graph schema, as well as the corresponding syntactical representation, as it could be provided by a data architect or application developer to formally define the schema of our fraud graph example.
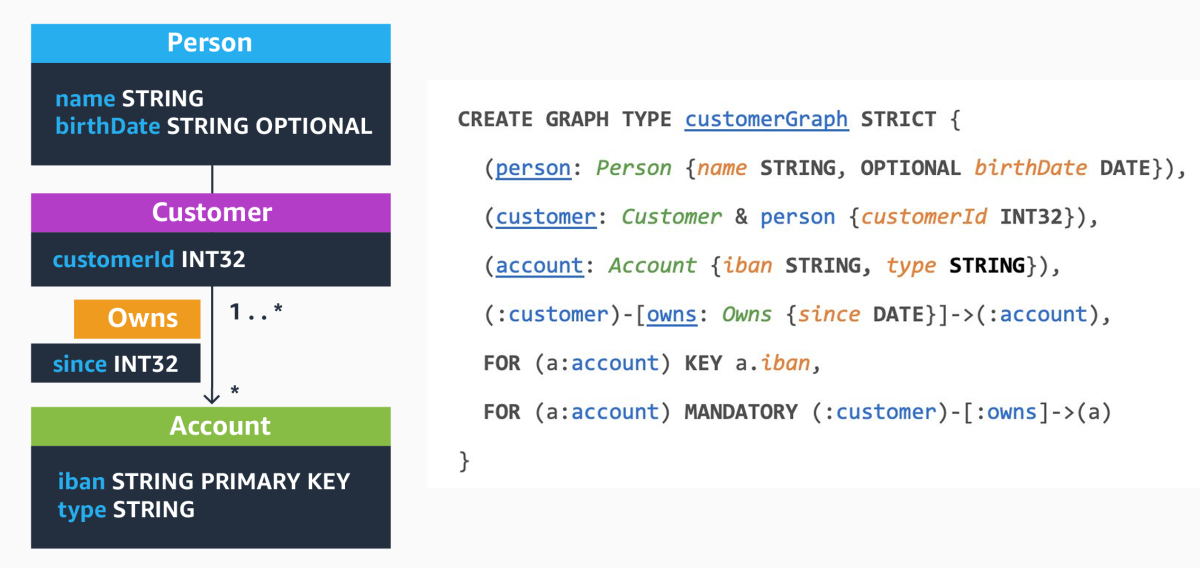
In this example, the overall schema is composed of the six elements enclosed in the top-level GRAPH TYPE definition:
- The first three lines of the GRAPH TYPE definition introduce so-called node types: person, customer, and account; they describe structural constraints on the nodes in the graph data. The customer node type, for instance, tells us that there can be nodes with label Customer, which carry a property customerId and are derived from a more general person node type. Concretely, this means that nodes with the label Customer inherit the properties name and birthDate defined in node type person. Note that properties also specify a data type (such as string, date, or numerical values) and may be marked as optional.
- Edge types build upon node types and specify the type and structure of edges that connect nodes. Our example defines a single edge type connecting nodes of node type customer with nodes of type account. Informally speaking, this tells us that Customer-labeled nodes in our data graph can be connected to Account-labeled nodes via an edge labeled Owns, which is annotated with a property since, pointing to a date value.
- The last two lines specify additional constraints that go beyond the mere structure of our graph. The KEY constraint demands that the value of the iban property uniquely identifies an account, i.e., no two Account-labeled nodes can share the same IBAN number. This can be thought of as the equivalent of primary keys in relational databases, which enforce the uniqueness of one or more attributes within the scope of a given table. The second constraint enforces that every account has at least one owner, which is reminiscent of a foreign-key constraint in relational databases.
Also note the keyword STRICT in the graph type definition: it enforces that all elements in the graph obey one of the types defined in the graph type body, and that all constraints are satisfied. Concretely, it implies that our graph can contain onlyPerson-, Customer-, and Account-labeled nodes with the respective sets of properties that the only possible edge type is between customers and accounts with label Owns and that the key and foreign constraints must be satisfied. Hence, the STRICT keyword can be understood as a mechanism to implement the schema-first paradigm, as it is maximally prescriptive and strongly constrains the graph structure.
To account for flexible- and partial-schema use cases, PG-Schema offers a LOOSE keyword as an alternative to STRICT, which comes with a more relaxed interpretation: graph types that are defined as LOOSE allow for node and edge types that are not explicitly listed in the graph type definition. Mechanisms similar to STRICT vs. LOOSE keywords at graph type level can be found at different levels of the language.
For instance, keywords such as OPEN (vs. the implicit default, CLOSED) can be used to either partially or fully specify the set of properties that can be carried by vertices with a given vertex label (e.g., expressing that a Person-labeled node must have a name but may have an arbitrary set of other (unknown) properties, without requiring enumeration of the entire set). The flexibility arising from these mechanisms makes it easy to define partial schemata that can be adjusted and refined incrementally, to capture the schema evolution requirements sketched above.
Not only does PG-Schema provide a concrete proposal for a graph schema and constraint language, but it also aims to raise awareness of the importance of a standardized approach to graph schemata. The concepts and ideas in the paper were codeveloped by major companies and academics in the graph space, and there are ongoing initiatives within the LDBC that aim toward a standardization of these concepts.
In particular, the LDBC has close ties with the ISO committee that is currently in the process of standardizing a new graph query language (GQL). As some GQL ISO committee members are coauthors of the PG-Schema paper, there has been a continuous bilateral exchange, and it is anticipated that future versions of the GQL standard will include a rich DDL, which may pick up concepts and ideas presented in the paper.