Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a technology that leverages the laws of quantum physics to securely share secret information between distant communicating parties. With QKD, quantum-mechanical properties ensure that if anyone tries to tamper with the secret-sharing process, the communicating parties will know. Keys established through QKD can then be used in traditional symmetric encryption or with other cryptographic technologies to secure communications.
“Record now, decrypt later" (RNDL) is a cybersecurity risk arising from advances in quantum computing. The term refers to the situation in which attackers record encrypted data today, even though they cannot decrypt it immediately. They store this data with the expectation that future quantum computers will be powerful enough to break the cryptographic algorithms currently securing it. Sensitive information such as financial records, healthcare data, or state secrets could be at risk, even years after it was transmitted.
Mitigating RNDL requires adopting quantum-resistant cryptographic methods, such as post-quantum cryptography (PQC) and/or quantum key distribution (QKD), to ensure confidentiality against future quantum advancements. AWS has invested in the migration to post-quantum cryptography to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of customer data.
Quantum communication is important enough that in 2022, three of its pioneers won the Nobel Prize for physics. However, misconceptions about QKD’s role still persist. One of them is that QKD lacks practical value because it “doesn’t solve the authentication problem”. This view can obscure the broad benefits that QKD brings to secure communications when integrated properly into existing systems.
QKD should be viewed as a complement to — rather than a replacement for — existing cybersecurity frameworks. Functionally, QKD solves the same problem solved by other key establishment protocols, including the well-known Diffie-Hellman (DH) method and the module-lattice-based key encapsulation mechanism (ML-KEM), the standard recently ratified by the FIPS — but it does it in a fundamentally different way. Like those methods, QKD depends on strong authentication to defend against threats such as man-in-the-middle attacks, where an attacker poses as one of the communicating parties.
In short, key exchange protocols and authentication mechanisms are different security primitives for solving distinct problems and must be integrated together in a secure communication system.
The challenge, then, is not to give QKD an authentication mechanism but to understand how it can be integrated with other established mechanisms to strengthen the overall security infrastructure. As quantum technologies continue to evolve, it’s important to shift the conversation from skepticism about authentication to consideration of how QKD can be thoughtfully and practically implemented to address today’s and tomorrow’s cybersecurity needs — such as the need to mitigating the “record now, decrypt later” (RNDL) attack (see sidebar).
Understanding the role of authentication in QKD
When discussing authentication in the context of QKD, we focus on the classical digital channel that the parties use to exchange information about their activities on the quantum channel. This isn’t about user authentication methods, such as logging in with passwords or biometrics, but rather about authenticating the communicating entities and the data exchanged. Entity authentication ensures that the parties are who they claim to be; data authentication guarantees that the information received is the same as what was sent by the claimed source. QKD protocols include a classical-communication component that uses both authentication methods to assure the overall security of the interaction.
Entity authentication
Entity authentication is the process by which one party (the "prover") asserts its identity, and another party (the "verifier") validates that assertion. This typically involves a registration step, in which the verifier obtains reliable identification information about the prover, as a prelude to any further authentication activity. The purpose of this step is to establish a “root of trust” or “trust anchor”, ensuring that the verifier has a trusted baseline for future authentications.
Several entity authentication methods are in common use, each based on a different type of trust anchor:
- Public-key-infrastructure (PKI) authentication: In this method, a prover’s certificate is issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA). The verifier relies on this CA, or the root CA in a certificate chain, to establish trust. The certificate acts as the trust anchor that links the prover’s identity to its public key.
- PGP-/GPG-based (web of trust) authentication: Here, trust is decentralized. A prover’s public key is trusted if it has been vouched for by one or more trusted third parties, such as a mutual acquaintance or a public-key directory. These third parties serve as the trust anchors.
- Pre-shared-key-based (PSK) authentication: In this case, both the prover and the verifier share a secret key that was exchanged via an offline or other secure out-of-band method. The trust anchor is the method of securely sharing this key a priori, such as a secure courier or another trusted channel.
These trust anchors form the technical backbones of all authentication systems. However, all entity authentication methods are based on a fundamental assumption: the prover is either the only party that holds the critical secret data (e.g., the prover’s private key in PKI or PGP) or the only other party that shares the secret with the verifier (PSK). If this assumption is broken — e.g., the prover's private key is stolen or compromised, or the PSK is leaked — the entire authentication process can fail.
Data authentication
Data authentication, also known as message authentication, ensures both the integrity and authenticity of the transmitted data. This means the data received by the verifier is exactly what the sender sent, and it came from a trusted source. As with entity authentication, the foundation of data authentication is the secure management of secret information shared by the communicating parties.
The most common approach to data authentication is symmetric cryptography, where both parties share a secret key. A keyed message authentication code (MAC), such as HMAC or GMAC, is used to compute a unique tag for the transmitted data. This tag allows the receiver to verify that the data hasn’t been altered during transit. The security of this method depends on the collision resistance of the chosen MAC algorithm — that is, the computational infeasibility of finding two or more plaintexts that could yield the same tag — and the confidentiality of the shared key. The authentication tag ensures data integrity, while the secret key guarantees the authenticity of the data origin.
An alternative method uses asymmetric cryptography with digital signatures. In this approach, the sender generates a signature using a private key and the data itself. The receiver, or anyone else, can verify the signature’s authenticity using the sender’s public key. This method provides data integrity through the signature algorithm, and it assures data origin authenticity as long as only the sender holds the private key. In this case, the public key serves as a verifiable link to the sender, ensuring that the signature is valid.
In both the symmetric and the asymmetric approaches, successful data authentication depends on effective entity authentication. Without knowing and trusting the identity of the sender, the verification of the data’s authenticity is compromised. Therefore, the strength of data authentication is closely tied to the integrity of the underlying entity authentication process.
Authentication in QKD
The first quantum cryptography protocol, known as BB84, was developed by Bennett and Brassard in 1984. It remains foundational to many modern QKD technologies, although notable advancements have been made since then.
QKD protocols are unique because they rely on the fundamental principles of quantum physics, which allow for “information-theoretic security.” This is distinct from the security provided by computational complexity. In the quantum model, any attempt to eavesdrop on the key exchange is detectable, providing a layer of security that classical cryptography cannot offer.
QKD relies on an authenticated classical communication channel to ensure the integrity of the data exchanged between parties, but it does not depend on the confidentiality of that classical channel. (This is why RNDL is not an effective attack against QKD). Authentication just guarantees that the entities establishing keys are legitimate, protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks.
Currently, several commercial QKD products are available, many of which implement the original BB84 protocol and its variants. These solutions offer secure key distribution in real-world applications, and they all pair with strong authentication processes to ensure the communication remains secure from start to finish. By integrating both technologies, organizations can build communication infrastructures capable of withstanding both classical and quantum threats.
Authentication in QKD bootstrap: A manageable issue
During the initial bootstrap phase of a QKD system, the authentic classical channel is established using traditional authentication methods based on PKI or PSK. As discussed earlier, all of these methods ultimately rely on the establishment of a trust anchor.
While confidentiality may need to be maintained for an extended period (sometimes decades), authentication is a real-time process. It verifies identity claims and checks data integrity in the moment. Compromising an authentication mechanism at some future point will not affect past verifications. Once an authentication process is successfully completed, the opportunity for an adversary to tamper with it has passed. That is, even if, in the future, a specific authentication mechanism used in QKD is broken by a new technology, QKD keys generated prior to that point are still safe to use, because no adversary can go back in time to compromise past QKD key generation.
This means that the reliance on traditional, non-QKD authentication methods presents an attack opportunity only during the bootstrap phase, which typically lasts just a few minutes. Given that this phase is so short compared to the overall life cycle of a QKD deployment, the potential risks posed by using authentication mechanisms are relatively minor.
Authentication after QKD bootstrap: Not a new issue
Once the bootstrap phase is complete, the QKD devices will have securely established shared keys. These keys can then be used for PSK-based authentication in future communications. In essence, QKD systems can maintain the authenticated classical communication channel by utilizing a small portion of the very keys they generate, ensuring continued secure communication beyond the initial setup phase.
It is important to note that if one of the QKD devices is compromised locally for whatever reason, the entire system’s security could be at risk. However, this is not a unique vulnerability introduced by QKD. Any cryptographic system faces similar challenges when the integrity of an endpoint is compromised. In this respect, QKD is no more susceptible to it than any other cryptographic system.
Overcoming key challenges to QKD’s role in cybersecurity
Up to now we have focused on clarifying the myths about authentication needs in QKD. Next we will discuss several other challenges in using QKD in practice.
Bridging the gap between QKD theory and implementation
While QKD protocols are theoretically secure, there remains a significant gap between theory and real-world implementations. Unlike traditional cryptographic methods, which rely on well-understood algorithms that can be thoroughly reviewed and certified, QKD systems depend on specialized hardware. This introduces complexity, as the process of reviewing and certifying QKD hardware is not yet mature.
In conventional cryptography, risks like side-channel attacks — which use runtime clues such as memory access patterns or data retrieval times to deduce secrets — are well understood and mitigated through certification processes. QKD systems are following a similar path. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has made a significant move by introducing the Common Criteria Protection Profile for QKD, the first international effort to create a standardized certification framework for these systems. ISO/IEC has also published standards on security requirements and test and evaluation methods for QKD. These represent crucial steps in building the same level of trust that traditional cryptography enjoys.
Once the certification process is fully established, confidence in QKD’s hardware implementations will continue to grow, enabling the cybersecurity community to embrace QKD as a reliable, cutting-edge solution for secure communication. Until then, the focus remains on advancing the review and certification processes to ensure that these systems meet the highest security standards.
QKD deployment considerations
One of the key challenges in the practical deployment of QKD is securely transporting the keys generated by QKD devices to their intended users. While it’s accepted that QKD is a robust mechanism for distributing keys to the QKD devices themselves, it does not cover the secure delivery of keys from the QKD device to the end user (or key consumer).
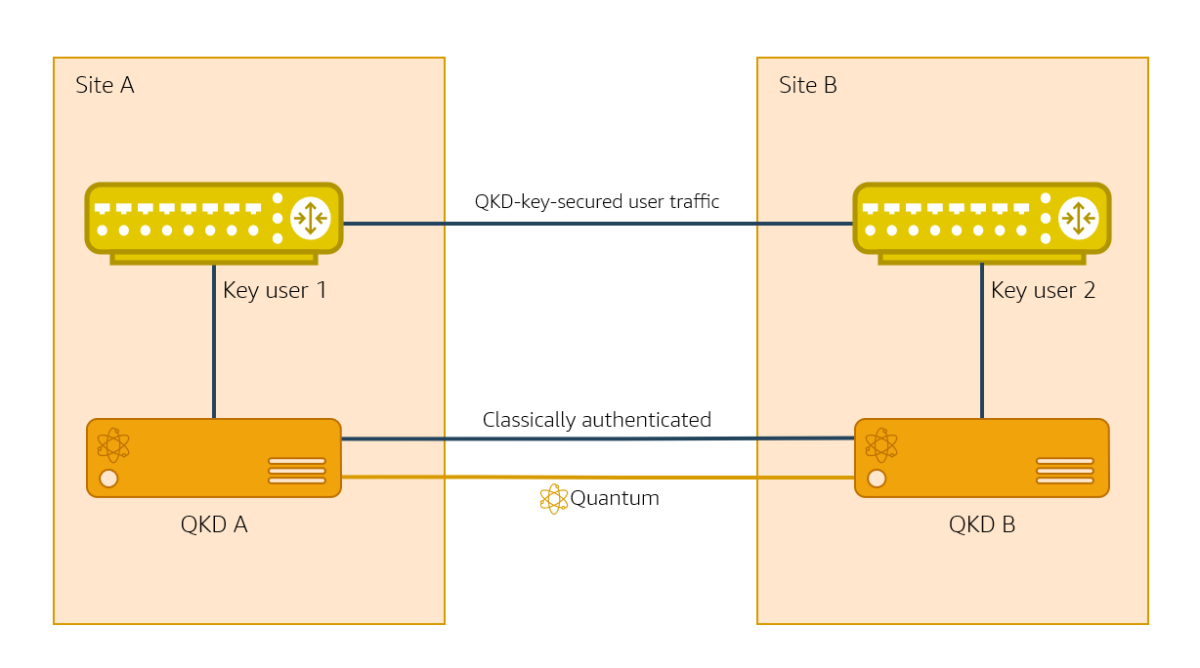
This issue arises whether the QKD system is deployed within a large intranet or a small local-area network. In both cases, the keys must be transported over a non-QKD system. The standard deployment requirement is that the key delivery from the QKD system to the key consumer occurs “within the same secure site”, and the definition of a “secure site” is up to the system operator.
The best practice is to make the boundary of the secure site as small as is practical. One extreme option is to remove the need for transporting keys over classical networks entirely, by putting the QKD device and the key user’s computing hardware in the same physical unit. This eliminates the need for traditional network protocols for key transport and realizes the full security benefits of QKD without external dependency. In cases where the extreme option is infeasible or impractical, the secure site should cover only the local QKD system and the intended key consumers.
Conclusion
QKD-generated keys will remain secure even when quantum computers emerge, and communications using these keys are not vulnerable to RNDL attacks. For QKD to reach its full potential, however, the community must collaborate closely with the broader cybersecurity ecosystem, particularly in areas like cryptography and governance, risk, and compliance (GRC). By integrating the insights and frameworks established in these fields, QKD can overcome its current challenges in trust and implementation.
This collective effort is essential to ensure that QKD becomes a reliable and integral part of secure communication systems. As these collaborations deepen, QKD will be well-positioned to enhance existing security frameworks, paving the way for its adoption across industries and applications.