Yesterday at the joint Language Intelligence @ Work and SEMANTiCS conference in Vienna, Austria, Amazon senior applied scientist Jack FitzGerald delivered a keynote talk on multilingual virtual assistants and the path toward a massively multilingual future. This is an edited version of his talk.
The evolution of human-computer interaction paradigms
In the past 50 years, computing technology has progressed from text-based terminal inputs, to graphical user interfaces, to predominantly web-based applications, through the mobile era, and finally into the era of a voice user interface and ambient computing.

Each of these paradigms has its own challenges with respect to multilingualism, whether it was the migration from ASCII to Unicode or proper character rendering on a website. However, I would argue that a voice AI system is the most difficult paradigm yet with respect to massive multilingualism.
The first reason is that the input space for voice interface commands is unbounded: the user can phrase each command in hundreds of different ways, all of which are valid. Another reason is that even within a single language, there can be many different dialects and accents.
Most important, the coupling between language and culture is inescapable. Whether it’s the level of formality used, preferred activities, or religious differences, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Instead, we must adapt the virtual assistant to understand cultural context and say only things that are appropriate for a given locale.
Voice AI systems today
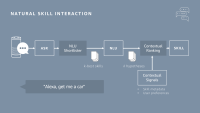
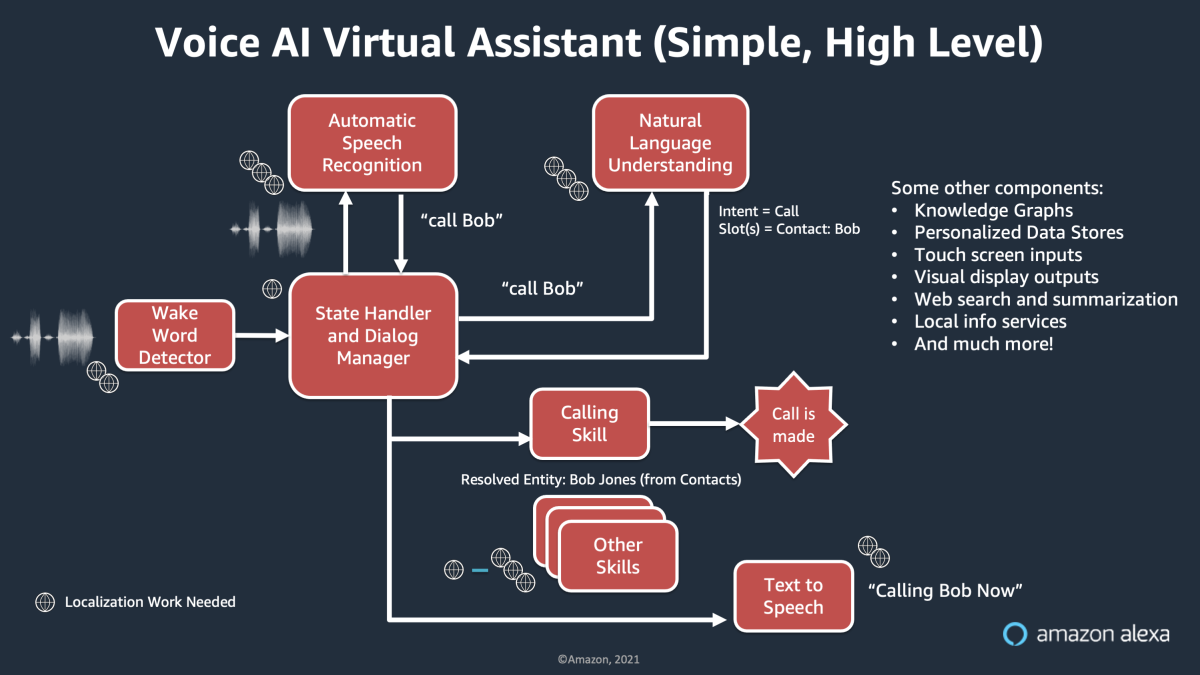
A typical voice AI system includes automatic-speech-recognition models, which convert raw audio into text; natural-language understanding models, which determine the user’s intent and recognize named entities; a central service for arbitration and dialogue management, which routes commands to the proper services or skills; and finally, a text-to-speech model, which issues the output. Additional tasks might include expansion of the underlying knowledge graph and semantic parsing, localization of touch screen content, or local information services.
Let’s look at some of the operational considerations for supporting multiple languages in such models. One is the training data: they must be topically exhaustive, meaning that they cover the full spectrum of possible user utterances, and they must be culturally exhaustive — for instance, covering all of the holidays a user might celebrate. They must also remain up-to-date, and it’s not always easy to add something new to the model without regression on existing functionalities.
A second consideration is in-house testing. Though in many cases one can get away with synthetic or otherwise artificial data for model training, for testing it’s important to have realistic utterances. Those typically need to come from humans, and collecting them can be a major expense. It’s also useful to perform live, interactive testing, which requires people who can speak and understand each language that the system supports.
Finally, it’s important to have the ability to support users and process their feedback. In most cases, this again requires staff who understand each of the supported languages.
Ultimately, human-based processes are not very scalable if our goal is to support thousands of languages. Instead, we must turn to technology to the greatest extent possible.
Multilingual modeling today
One of the leading reasons for the current success of multilingual text models is self-supervision.
In traditional supervised learning, a model would be trained from scratch on the desired task. If we wanted a model that would classify the sentiment of a product review, for example, we would manually annotate a bunch of product reviews, and we would use that dataset to train the model.
Today, however, we make use of transfer learning, in which text models are pretrained on terabytes of text data that don’t require manual annotation. Instead, the training procedure leverages the structure inherent to the text itself.
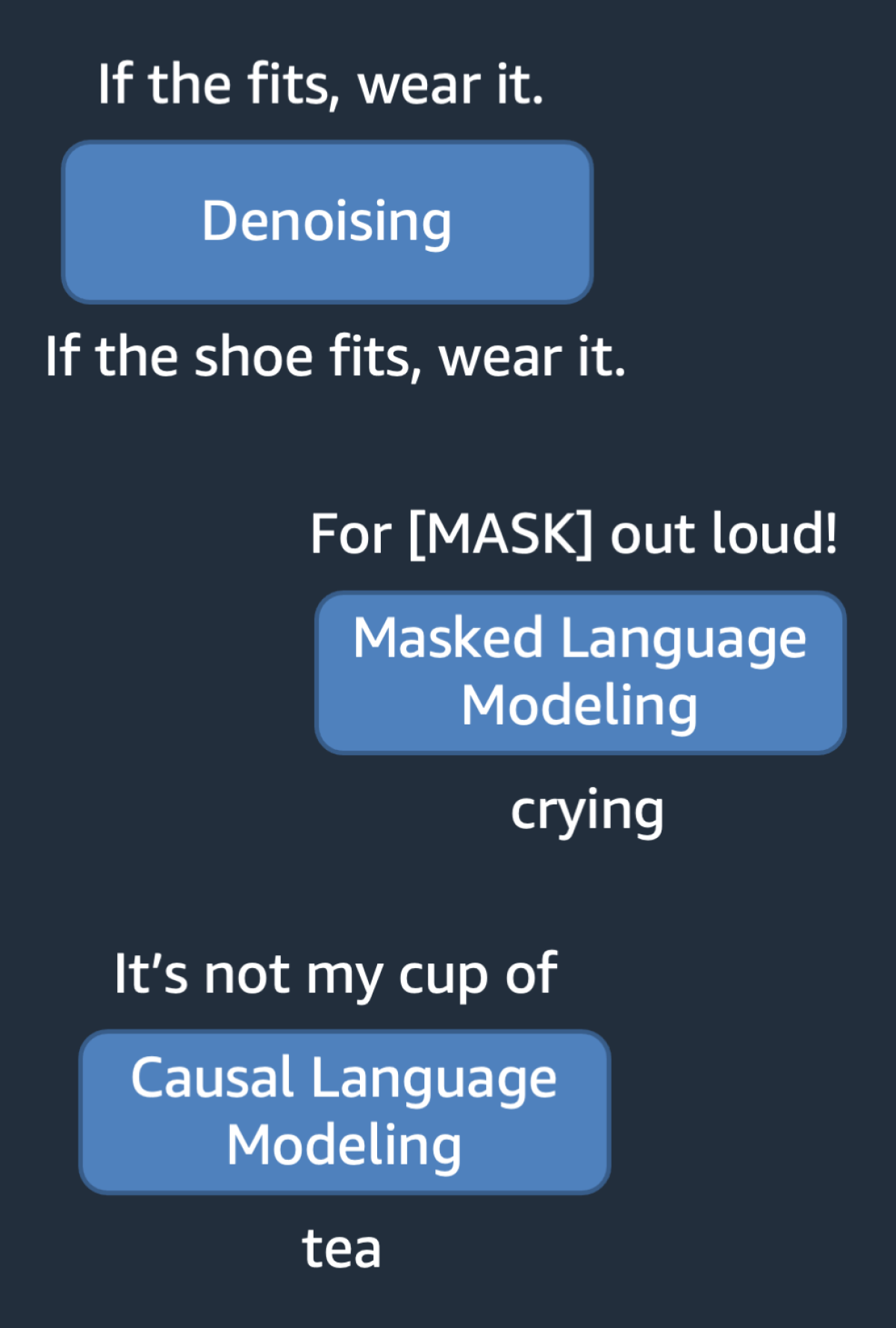
We’ll call this self-supervised pretraining With the masked-language-modeling training objective, for instance, the model is fed the input “for [MASK] out loud!”, and it must predict that “[MASK]” should be filled with the word “crying”. Other objectives, such as causal language modeling, span filling, deshuffling, and denoising can also be used.
Because the datasets required for self-supervised pretraining are unlabeled and monolingual, we can leverage troves of data, such as Common Crawl web scrapes, every Wikipedia page in existence, thousands of books and news articles, and more. Couple these large datasets with highly parallelizable architectures such as transformers, which can be trained on over a thousand GPUs with near linear scaling, and we can build models with tens or hundreds of billions of dense parameters. Such has been the focus for many people in the field for the past few years, including the Alexa Teacher Model team.
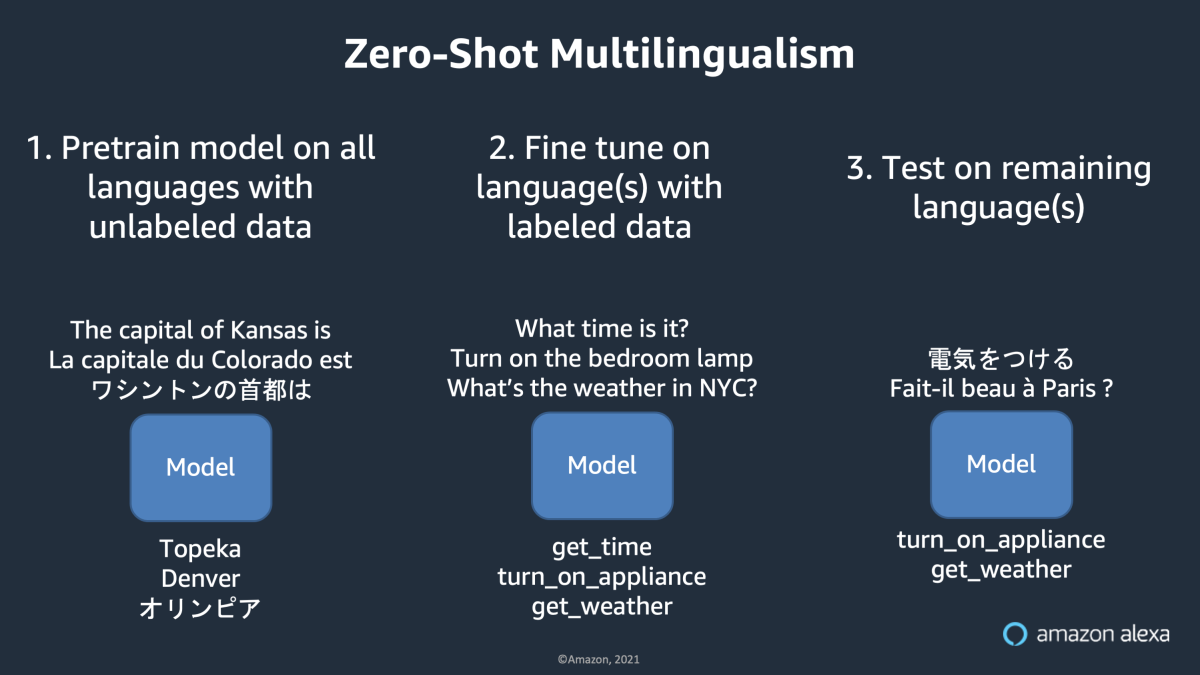
One incredible consequence of the transfer learning paradigm is called zero-shot learning. In the context of multilingual modeling, it works like this: the modeler begins by pretraining the model on some set of languages, using self-supervision. As an example, suppose that the modeler trains a model on English, French, and Japanese using every Wikipedia article in those three languages.
The next step is to adapt the model to a particular task using labeled data. Suppose that the modeler has a labeled dataset for intent classification, but only in English. The modeler can go ahead and fine-tune the model on the English data, then run it on the remaining languages.
Despite the fact that the model was never trained to do intent classification with French or Japanese data, it can still classify intents in those languages, by leveraging what it learned about those languages during pretraining. Given that the acquisition of labeled data is often a bottleneck, this property of language models is highly valuable for language expansion. Of course, zero-shot learning is just the extreme end of a continuum: transfer learning helps even out performance when the labeled data in different languages is imbalanced.
The next step up the data efficiency ladder is performing tasks without any additional training or fine tuning, using only a couple of labeled records or none at all. This is possible through “in-context learning,” which was popularized in the GPT-3 paper.
To perform in-context learning, simply take a pretrained model and feed it the appropriate prompts. Think of a prompt is a hint to the model about the task it should perform. Suppose that we want the model to summarize a passage. We might prefix the passage with the word “Passage” and a colon and follow it with the word “Summary” and a colon. The model would then generate a summary of the passage.
This is the zero-shot in-context learning case, meaning that no fine-tuning is performed, and no labeled data are needed. To improve task performance, we can feed a few examples to the model before asking it to perform the task. Though this does require some labeled data, the amount is small, usually in the tens of examples only.
Our Alexa Teacher Model team recently trained and tested a 20-billion-parameter sequence-to-sequence model that was multilingual and showed nice performance for in-context learning. For example, we showed state-of-the-art performance on machine translation with in-context learning. The model can achieve competitive BLEU scores even for some low-resource languages, which is incredible given that no parallel data was used during pretraining, and no labeled data besides a single example was used at any step in the process.
We were particularly proud of the relatively small size of this model, which could compete with much larger models because it was trained on more data. (The Chinchilla model from OpenAI showed a similar result.) Though a large model trained on a smaller dataset and a smaller model trained on a larger dataset may use the same total compute at training time, the smaller model will require less compute and memory during inference, which is a key factor in real applications.
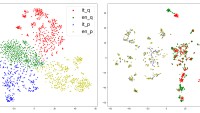
Given that models demonstrate multilingual understanding even without labeled data or parallel data, you may be wondering what’s happening inside of the model. Since the days of word2vec and earlier, we’ve represented characters, words, sentences, documents, and other inputs as vectors of floats, also known as embeddings, hidden states, and representations. Concepts cluster in certain areas of the representational space.
As humans, we can think only in three dimensions, whereas these representations are high-dimensional, but you can visualize this clustering in two or three dimensions as a reductive approximation. All the languages the model supports would cluster the concept of sitting in a chair in one region of the representational space; the concept of the ocean would inhabit a different cluster; and so forth.
Indeed, Pires et al. have shown that synonymous words across languages cluster together in the mBERT model. When examining 5,000 sentence pairs from the WMT16 dataset, they found that, given a sentence and its embedding in one language, the correct translation from another language is the closest embedding to the source embedding up to 75% of the time.
This manner of clustering can also be manipulated by changing the objective function. In their work on speech-to-text-modeling, Adams et al., from Johns Hopkins, were seeing undesirable clustering by language, rather than by phonemes, in the representational space. They were able to correct by adding training objectives around phoneme prediction and language identification.
The Alexa Teacher Model distillation pipeline
Once we have multilingual models, how do we adapt them to a real system? At the recent KDD conference, we presented a paper describing the Alexa Teacher Model pipeline, consisting of the following steps.
First, a multilingual model with billions of parameters is trained on up to a trillion tokens taken from Common Crawl web scrapes, Wikipedia articles, and more. Second, the models are further trained on in-domain, unlabeled data from a real system. Third, the model is distilled into smaller sizes that can be used in production. The final models can then be fine-tuned using labeled data and deployed.
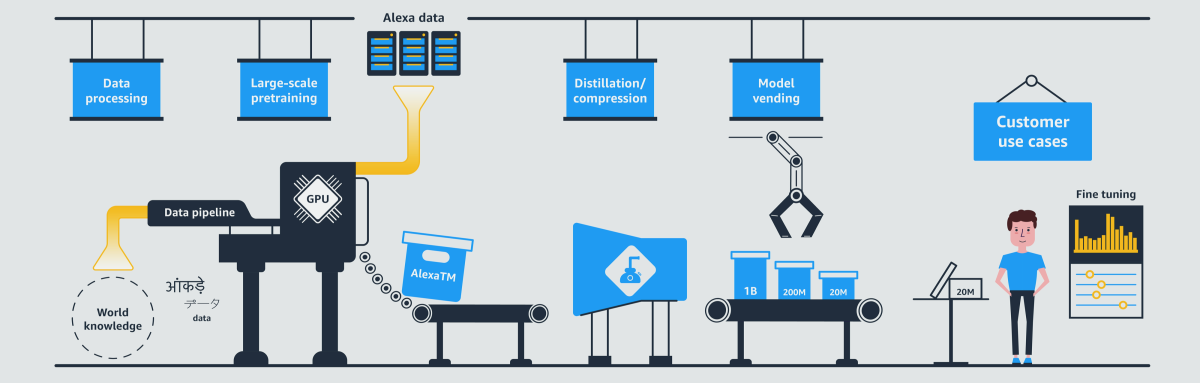
In tests, we found that our model was more accurate than a publicly available pretrained model fine-tuned on labeled data, and it significantly reduced customer dissatisfaction relative to a model trained by a smaller teacher model (85 million parameters, say, instead of billions). In short, we’ve verified that we can leverage the additional learning capacity of large, multilingual models for production systems requiring low latency and low memory consumption.
Scaling to 1,000 languages
I mentioned the fascinating ability of language models to learn joint representations of multiple languages without labeled or parallel data. This ability is crucial for us to scale to many languages. However, as we scale, we need test data that we can trust so that we can evaluate our progress.
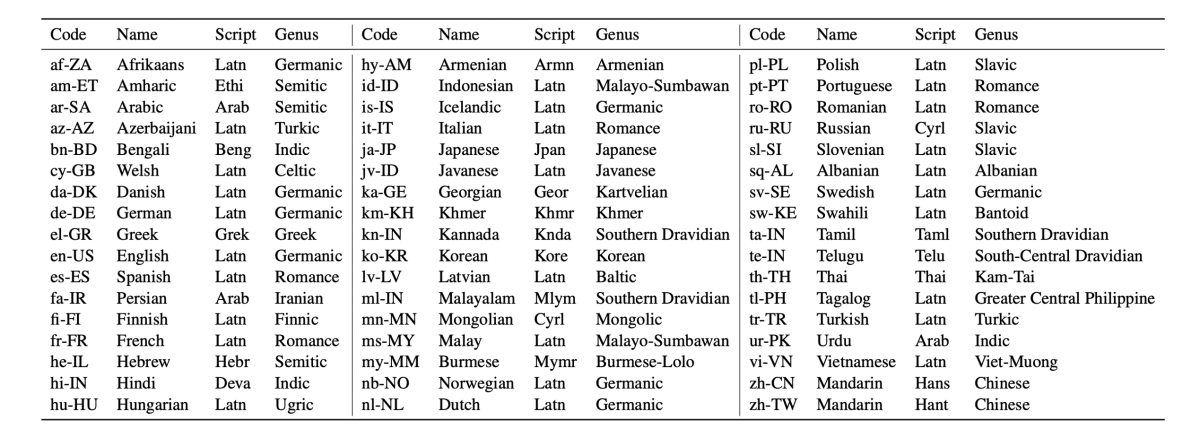
Toward this end, my team at Amazon recently released a new benchmark for multilingual natural-language understanding called MASSIVE, which is composed of one million labeled records spanning 51 languages, 18 domains, 60 intents, and 55 slots. All of the data were created by native speakers of the languages. We also released a GitHub repository with code that can be used as a baseline for creating multilingual NLU models, as well as leaderboards on eval.ai.
Now, you may retort that 51 languages is still a long ways from 1,000 languages. This is true, but we purposefully chose our languages in order to maximize typological diversity while staying within our budget. Our languages span 29 language genera, 14 language families, and 21 distinct scripts or alphabets. The diversity of the chosen languages allows a modeler to test technology that should scale to many more languages within each represented genus, family, and script.
That said, we certainly have some major gaps in language coverage, including across native North and South American languages, African languages, and Australian languages. Yet we are optimistic that our fellow researchers across the field will continue to produce new labeled benchmark datasets for the world’s thousands of low-resource languages.
Another difficulty with our current modeling approaches is that they rely on data sources such as web scrapes, encyclopedic articles, and news articles, which are highly skewed toward a small set of languages. Wang, Ruder, and Neubig recently presented some fascinating work leveraging bilingual lexicons — corpora consisting of word-level translations — to improve language model performance for low-resource languages. Lexicons cover a far greater portion of the world’s languages than our typical data sources for language modeling, making this an exciting approach.
Researchers, missionaries, and businesspeople have been created fundamental linguistic resources for decades, from Bible translations to the Unimorph corpus. The Unimorph datasets are used for the SIGMORPHON shared task, in which a model must predict the correct formulation of word given that word’s root and certain morphological transformations, such as part of speech, tense, and person. We must find more ways to leverage such resources when creating massively multilingual voice AI systems.
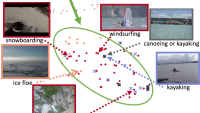
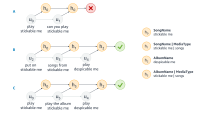
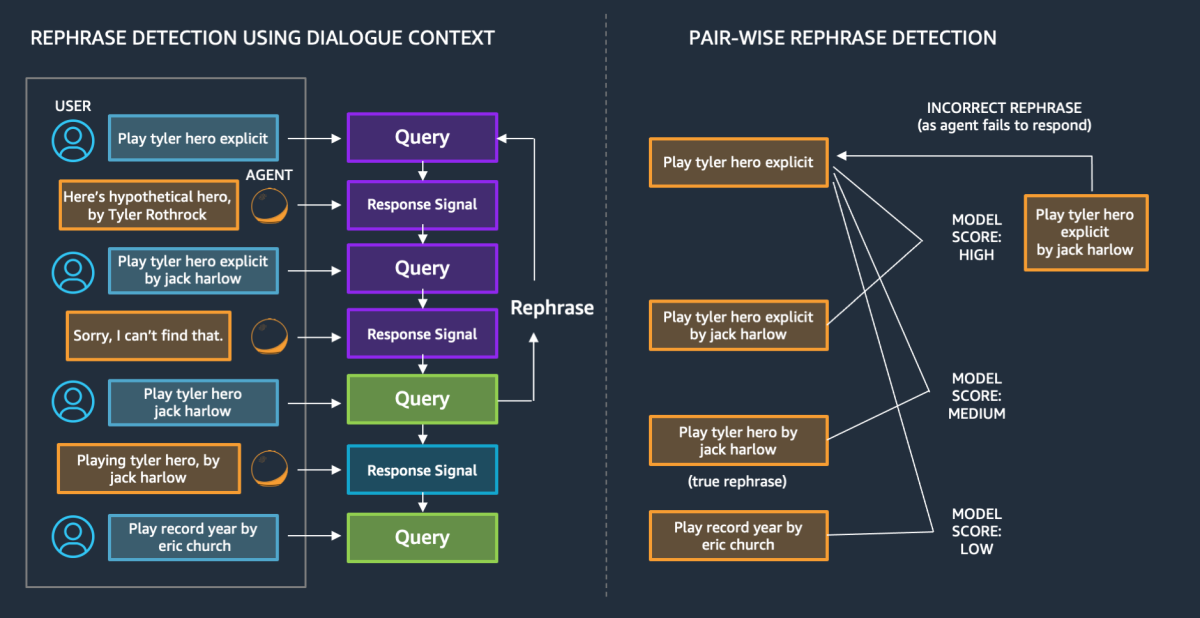
As a final technique for scaling to many more languages, we can consider what we in Alexa call “self-learning.” Some of my Alexa colleagues published a paper showing that we can mine past utterances to improve overall system performance. For example, if a user rephrases a request as part of a multiturn interaction, as shown on the left in the figure below, or if different users provide variations for the same desired goal, as shown on the right, then we can make soft assumptions that the different formulations are synonymous.
All of these cases can be statistically aggregated to form new training sets to update the system, without the need to manually annotate utterances. In a multilingual system, such technology is particularly valuable after the initial launch of a language, both to improve performance generally and to adapt to changes in the lexicon.
The road ahead
I hope that you share my wonder at the current state of the art — the scale of language-model training, the magic of zero-shot learning, and the distillation of knowledge into compact models that can run in latency-sensitive systems. All of this is incredible, but we’ve only scratched the surface of supporting the world’s 7,000 languages.
To move into the next era of massive multilingualism, we must build new and increasingly powerful models that can take advantage of low-cost data, particularly unlabeled monolingual data. We must also build models that can leverage existing and upcoming linguistic resources, such as bilingual lexicons and morphological-transformation databases. And finally, we must expand available language resources across more languages and domains, including more unlabeled monolingual corpora, more parallel resources, and more realistic, labeled, task-specific datasets.
Increased multilingualism is a win for all people everywhere. Each language provides a unique perspective on the world in which we live. A rich plurality of perspectives leads to a deeper understanding of our fellow people and of all creation.
Keep building.