Editor’s note: This article is adapted from a keynote presentation Bharathan Balaji , an Amazon senior research scientist within the company’s Devices organization, delivered in June at the 17th International Conference on Intelligent Environments . It is further informed by the book "IP-Enabled Energy Management, A Proven Strategy for Administering Energy as a Service " and its author, Rob Aldrich, Amazon Web Services senior sustainability strategist.
Buildings generate about 28% of the global greenhouse gas emissions today. The United Nations Global Status Report projects that buildings need to be at least 30% more energy efficient to achieve Paris Agreement goals.
How can we achieve that 30% energy efficiency target?
The path to reducing our emissions by improving building energy efficiency can be paved with the framework of sense, act, and scale. We need to sense to ascertain efficiency gaps within buildings. We need solutions that act on the information to achieve energy savings. And finally, we need to scale solutions so they get implemented broadly. Here is how this proposed framework can help us achieve our goals.
Sense
For office buildings that are smart and connected, the data set is rich and has much of the granular, sustainability data needed to drive change. Electricity and gas meters tell us how much energy is being consumed by a building, occupancy sensors tell us the number of people in the building, and temperature sensors tell us how much energy we need to cool a room. Sensors are the source of our information and the key to unlocking energy efficiency gaps. Even simple dashboards with such data can motivate users to save energy.
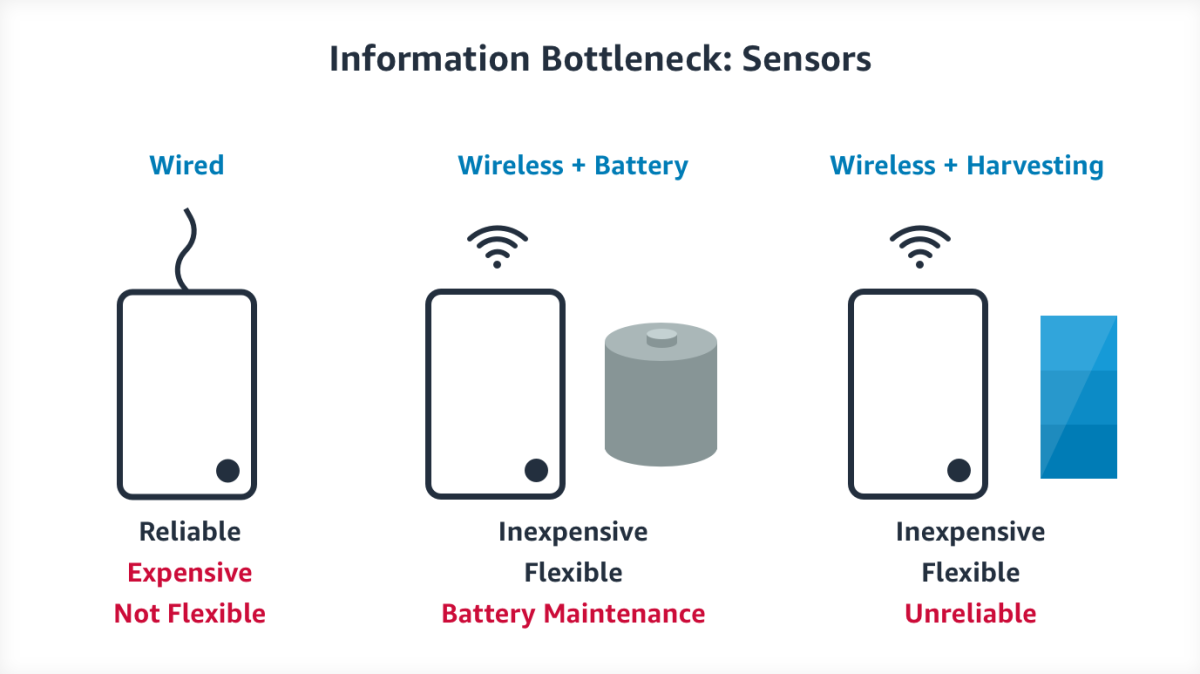
These types of sensors are abundant in modern buildings. However, many of them are wired sensors that are part of the building’s original design, and it is expensive to modify or install new sensors. Office buildings have a life of 50+ years, and sensor technology advances far more rapidly. Wireless sensors undoubtedly reduce communications costs, but they still need to be powered through wires, or use batteries that significantly increase maintenance costs at scale (imagine changing the batteries in every room of an office building).
New sensor options provide for ambient energy harvesting. These wireless sensors work by scavenging energy from the environment such as using ambient light, ventilation air flow, or hot water pipes. These sensors can minimize both energy and communications costs, but scavenged energy is insufficient to sense 24x7. We can improve reliability by predicting the environmental patterns and judiciously using the available energy.
A recent paper in SenSys (coauthored by Bharathan, lead author of this article) showed that reinforcement-learning-based scheduling of energy harvesting sensors can detect 93% of events in a real-world deployment. While the small percentage of missed events make these sensors ineligible for use in essential services, we can use the data from these inexpensive sensors opportunistically to create a rich information layer that helps save energy.
This new, rich information layer can drive the return on investment (ROI) that has been lacking in many sensor installations. Energy and data managers can provide the missing link between top-end sustainability initiatives and the many different sensor options that exist in buildings. Furthermore, the cost of sensor architectures can be reduced by focusing only on the key data sources that support a given use case.
For this article we chose to focus primarily on building sustainability data: energy, occupancy, emissions, air and water. This focus helps enable an estimated ROI because you already have a use case that defines how you will act on the information available. The use case for sustainability is to reduce wasted energy while moving to low greenhouse gas (GhG) fuel sources. Informed by sensor data, the actions taken in support of these goals can be the mechanism by which savings are achieved.
Act
The traditional way to make buildings more energy efficient is to inspect the equipment, install sensors to measure baseline energy consumption, fix faults, upgrade equipment, and optimize equipment configuration. Heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems typically comprise the largest portion of building energy use, and many of the efficiency measures target HVAC improvements. These methods work, and can lead to more than 10% reductions in building energy use. The entire process is often referred to as building retrofitting through performance contracting.
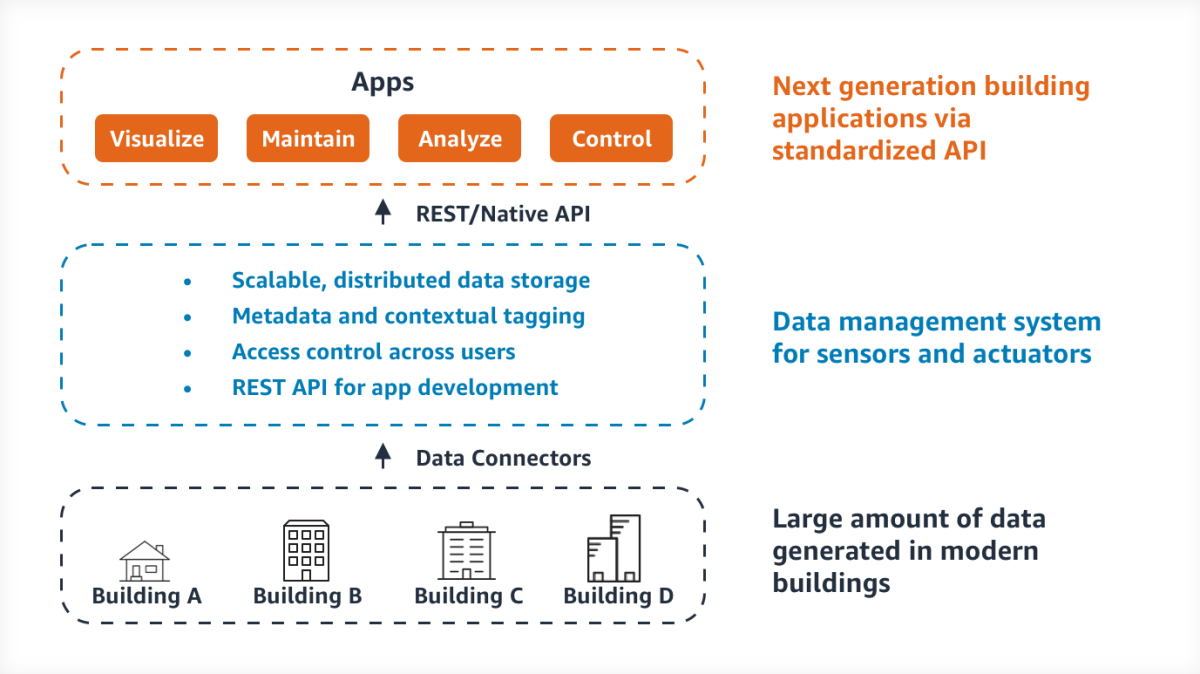
However, two issues with the above approach typically block adoption. First, there is an upfront cost to hire experts and upgrade equipment. The ROI can take years. Second, there is limited scope for innovation beyond the template followed during commissioning. Building innovation is stifled by vertically integrated systems and an inability to easily deploy third-party applications. One of the primary reasons for the explosive growth in the computing industry is a standard interface and ease of application installation. An analogous system for buildings will create new opportunities to save energy. The innovation opportunities with a standardized building information system is highlighted with three use cases below. It is easy to create such a system with current technologies; the figure below shows a high-level architecture.
Occupancy-based control
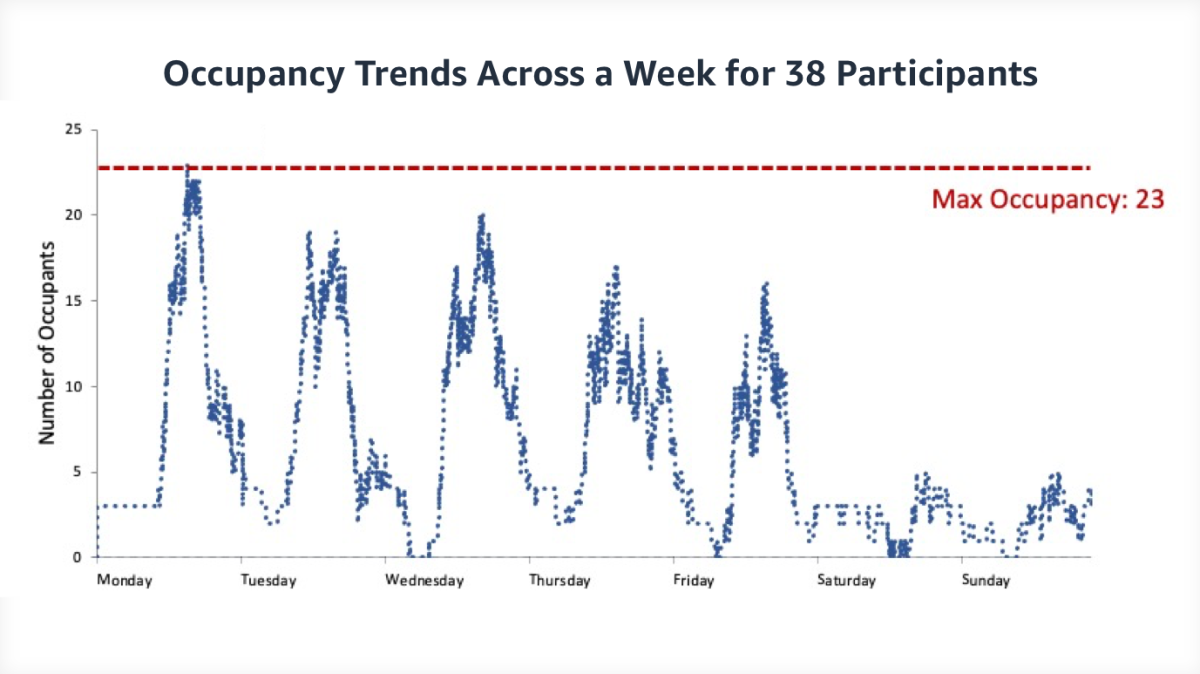
The idea is simple: if we shut off systems that aren’t required when people aren’t present, we save energy. However, detecting occupancy reliably in a privacy-preserving manner is challenging, and most buildings today keep the lights (and HVAC) on even when no one is present. A paper published in SenSys (coauthored by Bharathan) showed that it is possible to infer occupancy using WiFi data, building floor plans, and personnel office room assignments. Among the study participants, peak building occupancy was just 60% (see figure below), and occupancy-based control saved 18% of HVAC electricity use by controlling one-quarter of the building area. The proposed solution simply leverages existing building infrastructure and is inexpensive to deploy. This type of solution is possible only because the information across different systems is exchanged freely.
Fault detection
Fixing faults is core to building maintenance, but it is challenging to identify energy-wasting faults as they are difficult to notice, unlike a leak or an uncomfortable temperature. Typical building-fault detection relies on protocols established by experts, but these rules do not provide sufficient prioritization information, nor how much energy they waste.
Sophisticated fault detection algorithms have been published in literature, yet these are not deployed in practice because of vendor- locked systems. Using one year of building data, researchers (Bharathan was a coauthor) developed a simple machine learning algorithm that looks for rooms that do not follow typical temperature patterns. The algorithm identified 88 faults within the building’s HVAC system after an expert fixed all the faults found during an inspection. Many of these faults had existed for years, and resulted in estimated 410.3MWh/year savings. Again, the key component to this solution: easy access to building data.
Software thermostat
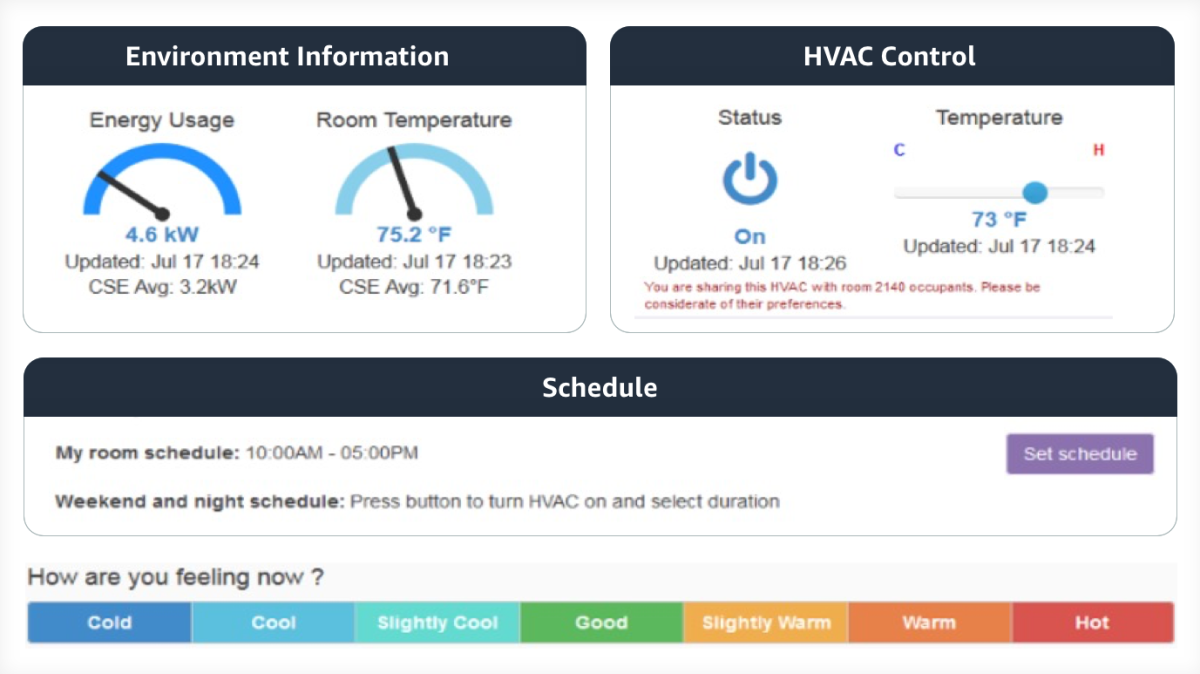
The thermostat is the only interface between building occupants and the energy-intensive HVAC system. And yet, in most buildings, occupants don’t know where the thermostat is or how to use it. The HVAC system’s primary function is to keep occupants comfortable so that they can be productive. But without thermostat feedback, occupants can end up being uncomfortable and waste energy.
With the building information system, researchers (Bharathan and collaborators) built a software version of the thermostat to address these concerns (screenshot below). The application was an instant hit and remains popular eight years after its launch. The resulting user study published in Ubicomp showed that users were frustrated with the old thermostat. In fact, one user actually taped a manila envelope on the vent to stop cold air from blowing. The software thermostat helped users precisely control their environment and send complaints if needed. The HVAC maintenance personnel were worried that the interface would lead to a flood of complaints that they weren’t staffed to handle. Usage data showed that most users were happy to use the application without giving any feedback. The few complaints received led to identification of major faults, such as a thermostat being blocked by a computer.
The three use cases above didn’t require additional sensor installations and simply leveraged existing information. With low-cost solutions, we can attract building owners to adopt solutions that save energy. But we need additional incentives within the building industry to create these low-cost solutions that can have large-scale impact.
These use cases demonstrate that sustainable design doesn’t stop at the brick and mortar of the building. It should carry through to how the energy, emissions, air, water and waste can be managed as systems across buildings. As companies worldwide embark on making their buildings more sustainable, it will be critical to have a data-driven measure of success. The sense and act steps allow each company to look at what is common in the data model today, get started, assess the value, and scale as needed using open-source tools.
Scale
Even when an attractive energy-saving solution is available, it is difficult to deploy the solution at scale. This is because each building is unique, from its infrastructure and how it is used, to the software used to manage daily operations, and how it changes over time. While the fundamental components of a building remain the same (e.g., rooms, smoke sensors, ventilation fans), each vendor treats them differently. When we try to deploy a solution to a building, the discrepancies between vendor representations become difficult to resolve automatically.
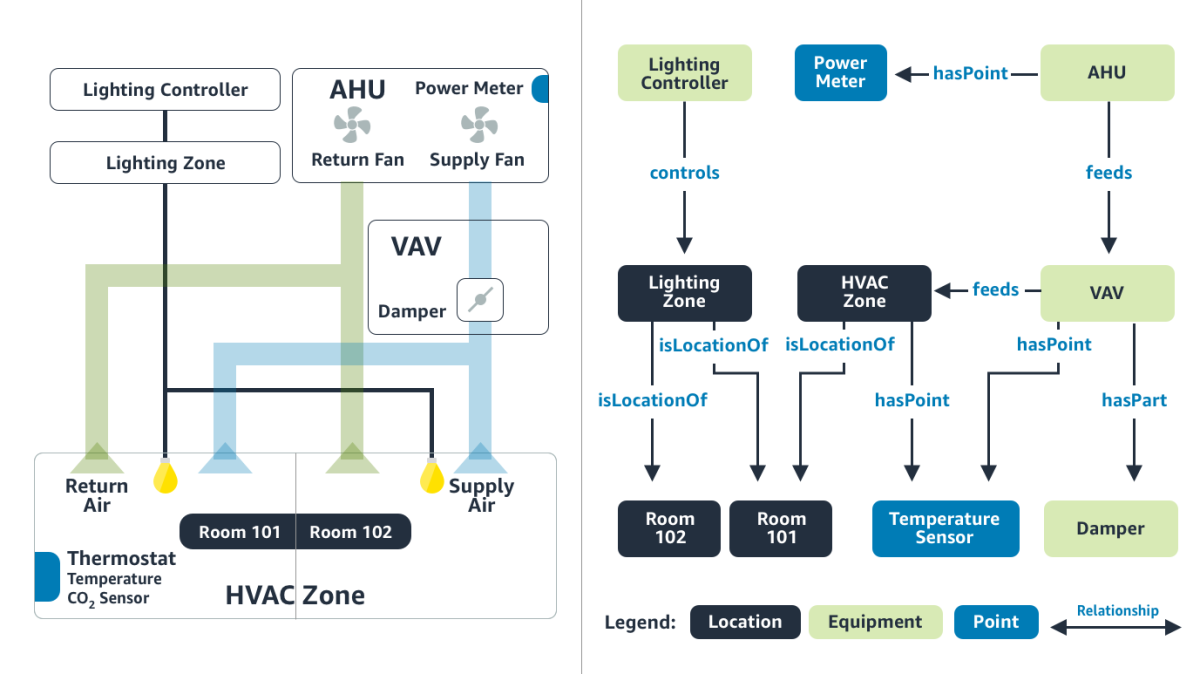
In the computing industry, on other hand, it is easy for us to install an application without worrying about the manufacturer or provider because of the use of specifications (e.g., standard protocols for WiFi) and programming interfaces (e.g., Android OS for the phone). Researchers (including Bharathan) created such a standard interface for buildings with the Brick schema, where the building components and their connections to each other are represented through a knowledge graph. The figure below shows a Brick representation of a toy building with two rooms and a few sensors. Brick is now an industry consortium with growing demand, and is in the process of being integrated into building standards.
Given a standard representation such as Brick, we still have the task of representing the existing building in this new format, which can take manual effort and be slow to deploy. Using machine-learning techniques in natural language processing, we can automate this translation and minimize manual effort. The algorithm’s performance improves as more buildings are mapped to Brick and it learns from representation patterns across buildings.
With the sense, act and scale framework, we envision a day when it will be as easy to configure a building as it is our phones today. We can improve the information available to building managers by using low-cost sensors, use the available information to develop innovations that save energy, and deploy the solution to many buildings with use of a knowledge graph.
Getting started
We are seeing early success in using the sense, act, scale approach in our AWS Sustainability Services practice to optimize how buildings report their sustainability data through the cloud. It solves several problems by providing a simple framework to plan how our top-level sustainability strategy can be supported by specific building-optimization steps, underpinned by a semi-standardized data model.
The lack of standardization across building management systems has resulted in difficulties in accessing the data. Now that those data acquisition problems are being solved through advances in IoT and API, it opens up new opportunities to expose, analyze and report data that was previously difficult or costly to acquire. With new advances like the Brick schema, we are making advances in how we can manage building assets at scale, just like servers, laptops and phones.
We are starting to see the potential to move the world from a building management systems approach; one building, one manager to a building systems management approach; many buildings, one manager. Energy efficiency gains of 30% or more are more feasible when we automate energy-control policies across all buildings at the push of a button.


















