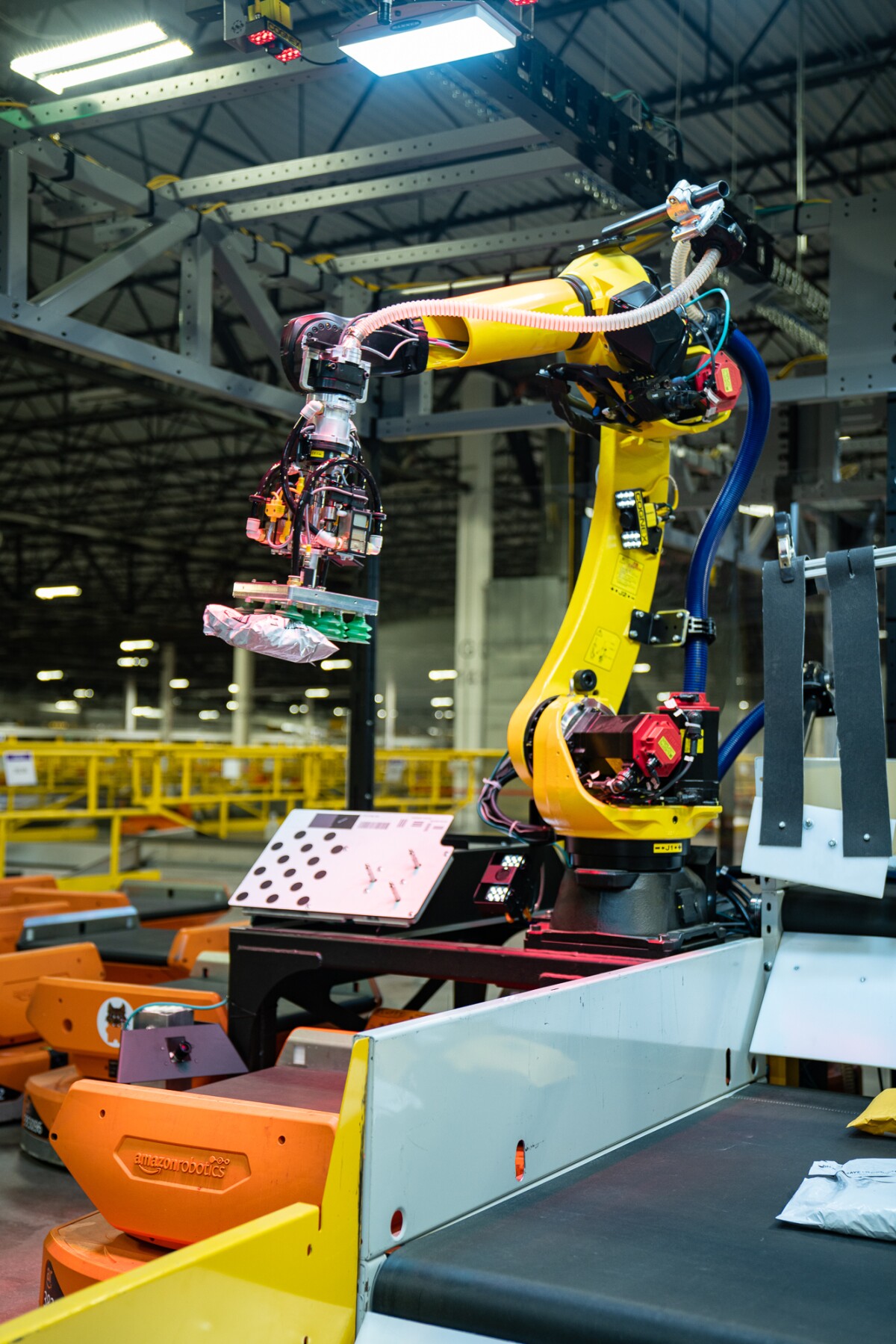
Inside an Amazon fulfillment center, as packages roll down a conveyor, the Robin robotic arm goes to work. It dips, picks up a package, scans its, and places it on a small drive robot that routes it to the correct loading dock. By the time the drive has dropped off its package, Robin has loaded several more delivery robots.
While Robin looks a lot like other robotic arms used in industry, its vision system enables it to see and react to the world in an entirely different way.
“Most robotic arms work in a controlled environment,” explained Charles Swan, a senior manager of software development at Amazon Robotics & AI. “If they weld vehicle frames, for example, they expect the parts to be in a fixed location and follow a pre-scripted set of motions. They do not really perceive their environment.
“Robin deals with a world where things are changing all around it. It understands what objects are there — different sized boxes, soft packages, envelopes on top of other envelopes — and decides which one it wants and grabs it. It does all these things without a human scripting each move that it makes. What Robin does is not unusual in research. But it is unusual in production.”
Yet, thanks to machine learning, Robin and its advanced perception system are moving rapidly into production. When Swan began working with the robot in 2021, Amazon was operating only a couple dozen units at its fulfillment centers. Today, Swan’s team is significantly scaling that perception system.
To reach that goal, Amazon Robotics researchers are exploring ways for Robin to achieve unparalleled levels of production accuracy. Because Amazon is so focused on improving the customer experience through timely deliveries, even 99.9% accuracy doesn’t meet the mark for robotics researchers.
Training day
Over the past five years, machine learning has significantly advanced the ability of robots to see, understand, and reason about their environment.
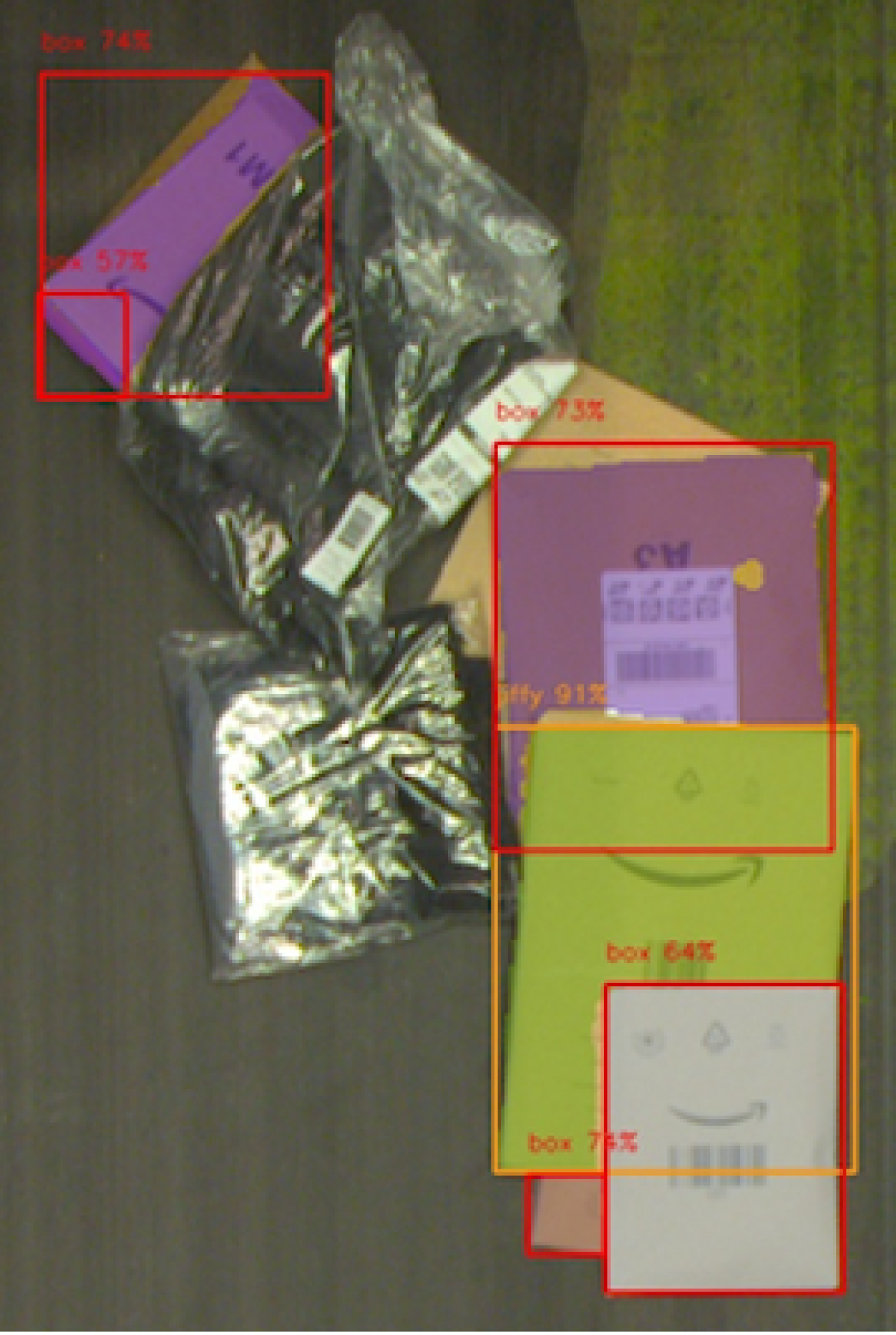

In the past, classical computer vision algorithms systematically segmented scenes into individual elements, a slow and computationally intensive approach. Supervised machine learning has made that process more efficient.
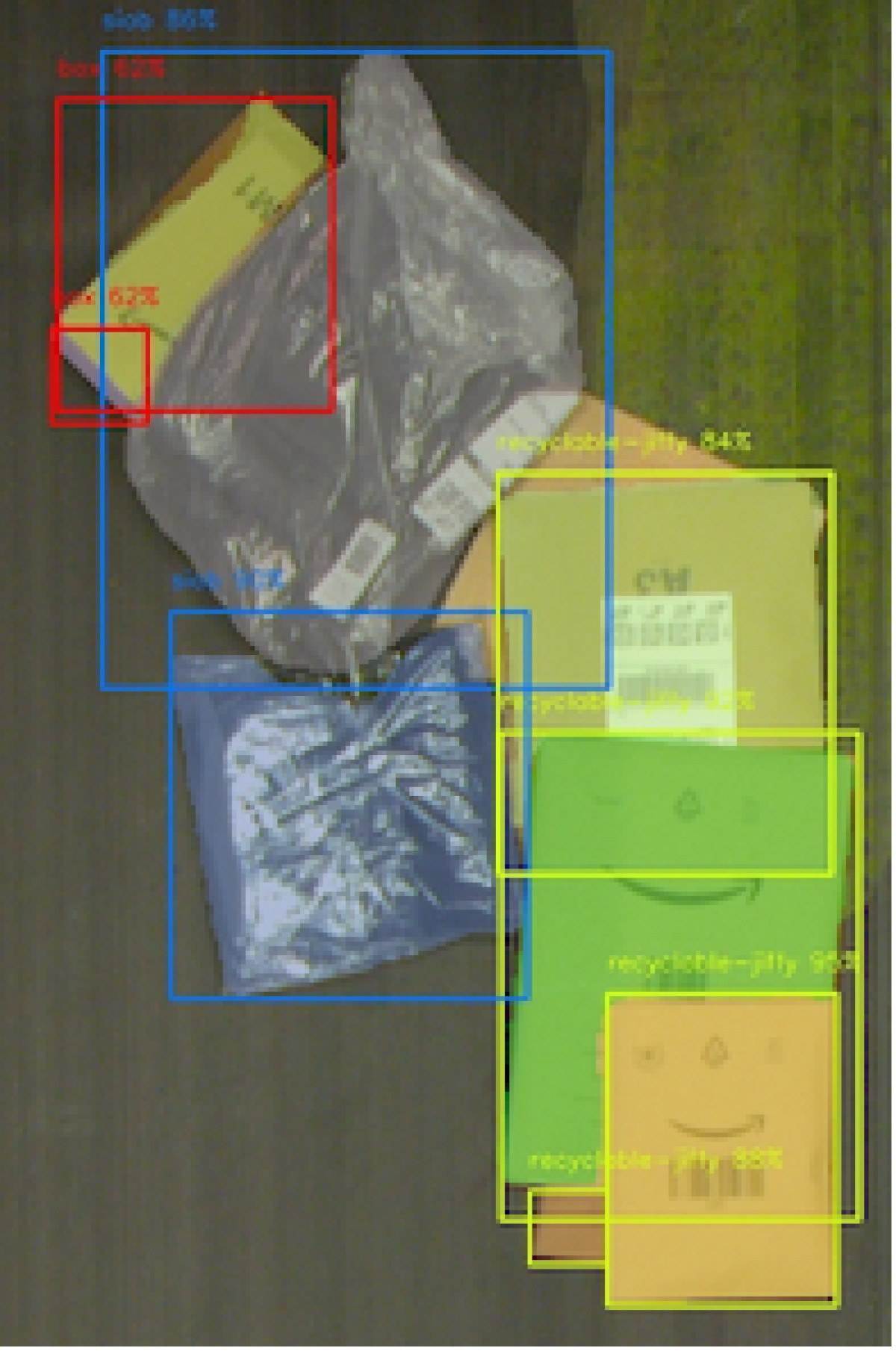
“We don’t explicitly say how the model should learn,” said Bhavana Chandrashekhar, a software development manager at Amazon Robotics & AI. “Instead, we give it an input image and say, ‘This is an object.’ Then it tries to identify the object in the image, and we grade how well it does that. Using only that supervised feedback, the model learns how to extract features from the images so it can classify the objects in them.”
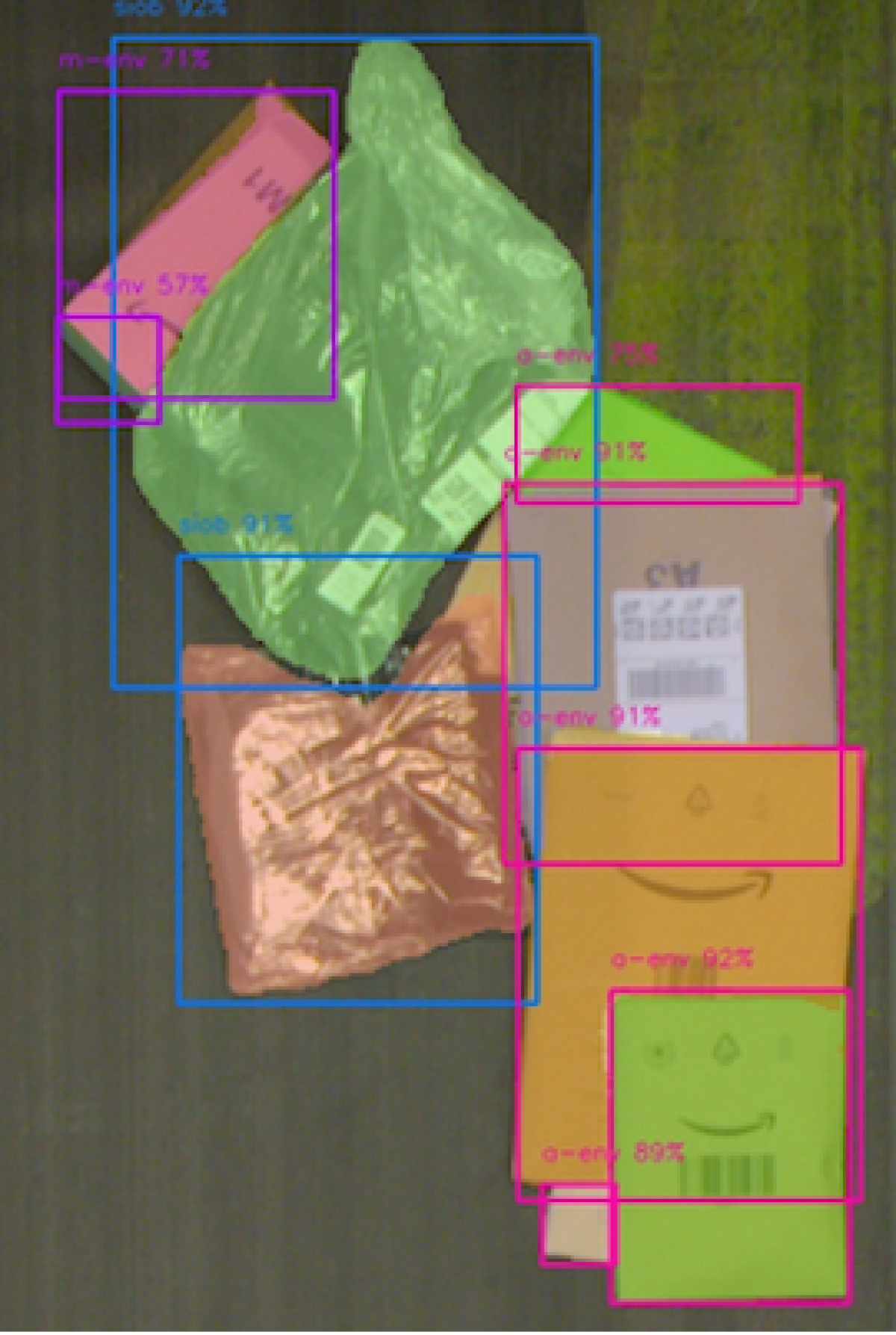
Robin’s perception system started with pre-trained models that could already identify object elements like edges and planes.
Next, it was taught to identify the type of packages found within the fulfillment center’s sortation area.
Machine learning models learn best when provided with an abundance of sample images. Yet, despite shipping millions of packages daily, Chandrashekhar’s team initially found it hard to find enough training data to capture the enormous variation of the boxes and packages continuously rolling down a conveyor.
“Everything comes in a jumble of sizes and shapes, some on top of the other, some in the shadows,” Chandrashekhar said. “During the holidays, you might see pictures of Minions or Billy Eilish mixed in with our usual brown and white packages. The taping might change.
“Sometimes, the differences between one package and another are hard to see, even for humans. You might have a white envelope on another white envelope, and both are crinkled so you can’t tell where one begins and the other ends,” she explained.
To teach Robin’s model to make sense of what it sees, researchers gathered thousands of images, drew lines around features like boxes, yellow, brown and white mailers, and labels, and added descriptions. The team then used these annotated images to continually retrain the robot.
The training continued in a simulated production environment, with the robot working on a live conveyor with test packages.
Whenever Robin failed to identify an object or make a pick, the researchers would annotate the errors and add them to the training deck. This on-going training regimen significantly improved the robot’s efficiency.
Continual learning
Robin’s success rate during these tests improved markedly, but the researchers pushed for near perfection. “We want to be really good at these random edge problems, which happen only a few times during testing, but occur more often in field when we’re running at larger scale,” Chandrashekhar said.
Because of Robin’s high accuracy rate in testing, researchers found it difficult to find enough of those mistakes to create a dataset for further training. “In the beginning, we had to imagine how the robot would make a mistake in order to create the type of data we could use to improve the model,” Chandrashekhar explained.
The Amazon team also monitored Robin’s confidence in its decisions. The perception model might, for example, indicate it was confident about spotting a package, but less confident about assigning it to a specific type of package. Chandrashekhar’s team developed a framework to ensure those low-confidence images were automatically sent for annotation by a human and then added back to the training deck.

“This is part of continual learning,” says Jeremy Wyatt, senior manager of applied science. “It’s incredibly powerful because every package becomes a learning opportunity. Every robot contributes experiences that helps the entire fleet get better.”
That continual learning led to big improvements. “In just six months, we halved the number of packages Robin’s perception system can’t pick and we reduced the errors the perception system makes by a factor of 10,” Wyatt notes.
Still, robots will make mistakes in production that have to be corrected. What happens in the moment if Robin drops a package or puts two mailers on one sortation robot? While most production robots are oblivious to mistakes, Robin is an exception. It monitors its performance for missteps.
Robin’s quality assurance system oversees how it handles packages. If it identifies a problem, it will try to fix it on its own, or call for human intervention if it cannot. “If Robin finds and corrects a mistake, it might lose some time,” Swan explained. “However, if that error wasn’t addressed at all, we might lose a day or two getting that product to the customer.”
Scaling Robin perception
Swan joined the Robin perception team when there were only a few dozen units in production. His goal: scale the perception system to thousands of robotic arms. To accomplish this, Swan’s team doesn’t just focus on catching and annotating errors for continual learning, it seeks the root cause of those errors.
They rely on Robin perception’s user interface, which lets engineers look through the robot’s eyes and trace how its vision system made the decision. They might, for example, find a Robin that picked up two packages because it could not distinguish one from the other, or another that failed to grab any package owing to a noisy depth signal. Auditing Robin’s decisions lets Amazon Robotics engineers fine-tune the robot’s behaviors.
This is complemented by the metrics derived from a fleet of machines sorting well over 1 million items every day. “Once you have that kind of data, then you can start to look for correlations,” Swan said. “Then you can say the latency in making a decision is related to this property of the machine or this property of the scene and that’s something we can focus on.”
Fleet metrics provide data about a greater range of scenes and problems than any one machine would ever see, from a broken light to an address label stuck on the conveyor belt. That data, used to retrain Robin every few days, gives it a much broader understanding of the world in which it works.
It also helps Amazon improve efficiency. Before Robin picks up a package, it must first segment a cluttered scene, decide which package it will grab, calculate how it will approach the package, and choose how many of its eight suction cups to use to pick it up. Choose too many and it might lift more than one package; too few, and it could drop its cargo.
That decision requires much more than computer vision. “Making decisions on what and where to grasp is accomplished with a combination of learning systems, optimization, geometric reasoning, and 3D understanding,” explained Nick Hudson, principal applied scientist with Amazon Robotics AI. “There are a lot of components which interact, and they all need to accommodate the variations seen across different sites and regions.”
“There is always a tradeoff between efficiency and good decisions,” Swan continued. “That was a major scaling challenge. We did a lot of experimentation offline with very cluttered scenes and other situations that slowed the robots down to improve our algorithms. When we liked them, we would run them on a small portion of the fleet. If they did well, we would roll them out to all the robots.”
Those rollouts were also made possible because the software was rewritten to support regular updates, said Sicong Zhao, a software development manager. “The software is modular. That way, we can upgrade one component without affecting the others. It also enables multiple groups to work on different improvements at the same time.” That modularity has enabled key parts of the perception system to be automatically retrained twice a week.
Nor was that a simple task. Robin had many tens of thousands of lines of code, so it took Zhao’s team months to understand how those lines interacted with one another well enough to modularize their components. The effort was worth it. It made Robin easier to upgrade and will ultimately enable automatic fleet updates as frequently as needed while mitigating operational disruptions.
Next-generation robot perception
Those continuous improvements are essential to deploy Robin at Amazon’s scale, Swan explained. The team’s goal is to update the fleet of Robin robots automatically several times weekly.
“We are increasing our usage of Robin,” Swan said. “To do that, we must continue to improve Robin’s ability to handle those random edge cases, so it never mis-sorts, has great motion planning, and moves at the fastest safe speed its arm can handle — all with time to spare.”
That means even more innovation. Take, for example, package recognition. Robin’s perception system needs to be able to spot a pile of packages and know to start with the top one to avoid upending the pile. “Robin has a sense of how to do that as well, but we need machine learning to accelerate the way Robin decides which one it is most likely to pick up successfully as we keep adding new types of packaging,” Zhao explained.
Chandrashekhar believes more powerful digital simulations, based on the physics of robot and package movement, will enable faster innovation. “This is very difficult when we’re talking about deformable packages, like a water bottle in a soft mailer,” she said. “But we’re getting a lot closer.”
Longer-term, she wants to see self-learning robots that teach themselves to make fewer mistakes and to recover from them faster. Self-learning will also make the robots easier to use. “Deploying a robot shouldn’t require a PhD,” Swan said.
We’ve only scratched the surface of what’s possible with robots.
“There is a unique opportunity to have this fleet adapt automatically,” agreed Hudson. “There are open questions on how to accomplish this, including whether individual robots should adapt on their own. The fleet already updates its object understanding using data collected worldwide. How can we also have the individual robots adapt to issues they are seeing locally – for instance if one of the suction cups is blocked or torn?”
Ultimately, though, Swan would like to use what Amazon Robotics researchers have learned to create new types of robots. “We’ve only scratched the surface of what’s possible with robots,” he said.




















