-
IWSLT 2019 International Workshop on Spoken Language Translation2019Neural machine translation models have shown to achieve high quality when trained and fed with well structured and punctuated input texts. Unfortunately, the latter condition is not met in spoken language translation, where the input is generated by an automatic speech recognition (ASR) system. In this paper, we study how to adapt a strong NMT system to make it robust to typical ASR errors. As in our application
-
EMNLP 2019 Workshop on Noisy User-Generated Text2019Robustness to capitalization errors is a highly desirable characteristic of named entity recognizers, yet we find standard models for the task are surprisingly brittle to such noise. Existing methods to improve robustness to the noise completely discard given orthographic information, which significantly degrades their performance on well-formed text. We propose a simple alternative approach based on data
-
ACL 20192019Relation Extraction is the task of identifying entity mention spans in raw text and then identifying relations between pairs of the entity mentions. Recent approaches for this spanlevel task have been token-level models which have inherent limitations. They cannot easily define and implement span-level features, cannot model overlapping entity mentions and have cascading errors due to the use of sequential
-
EUSIPCO 20192019In this work, we describe limitations of the free-field propagation model for designing broadband beamformers for microphone arrays on a rigid surface. Towards this goal, we describe a general framework for quantifying the microphone array performance in a general wave-field by directly solving the acoustic wave equation. The model utilizes Finite-Element-Method (FEM) for evaluating the response of the
-
ACL 20192019We propose a novel neural topic model in the Wasserstein autoencoders (WAE) framework. Unlike existing variational autoencoder based models, we directly enforce Dirichlet prior on the latent document-topic vectors. We exploit the structure of the latent space and apply a suitable kernel in minimizing the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) to perform distribution matching. We discover that MMD performs much
Related content
-
October 17, 2019This year at EMNLP, we will cohost the Second Workshop on Fact Extraction and Verification — or FEVER — which will explore techniques for automatically assessing the veracity of factual assertions online.
-
October 11, 2019In the past few weeks, Amazon announced versions of Alexa in three new languages: Hindi, U.S. Spanish, and Brazilian Portuguese. Like all new-language launches, these addressed the problem of how to bootstrap the machine learning models that interpret customer requests, without the ability to learn from customer interactions.
-
October 01, 2019Amazon today announced the public release of a new data set that will help speech scientists address the difficult problem of separating speech signals in reverberant rooms with multiple speakers. In the field of automatic speech recognition, this problem is known as the “cocktail party” or “dinner party” problem; accordingly, we call our data set the Dinner Party Corpus, or DiPCo.
-
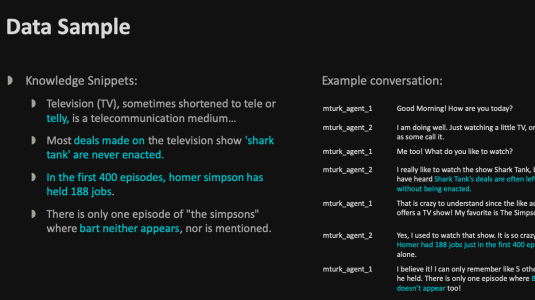
September 17, 2019Today I am happy to announce the public release of the Topical Chat Dataset, a text-based collection of more than 235,000 utterances (over 4,700,000 words) that will help support high-quality, repeatable research in the field of dialogue systems.
-
September 16, 2019During a conversation between a customer and a dialogue system like Alexa’s, the system must not only understand what the customer is saying currently but also remember the conversation history. Only by combining the history with the current utterance can the system truly understand the customer’s requirements.
-
September 10, 2019At next week’s Interspeech, the largest conference on the science and technology of spoken-language processing, Alexa researchers have 16 papers, which span the five core areas of Alexa functionality.