When Radhika Nagpal was starting graduate school in 1994, she and her future husband went snorkeling in the Caribbean. Nagpal, who grew up in a landlocked region of India, had never swum in the ocean before. It blew her away.
“The reef was super healthy and colorful, like being in a National Geographic television show,” she recalled. “As soon as I put my face in the water, this whole swarm of fish came towards me and then swerved to the right.”
The fish fascinated her. As she watched, large schools of fish would suddenly stop or switch direction as if they were guided by a single mind. A series of questions occurred to her. How did they communicate with one another? What rules — think of them as algorithms — produced such complex group behaviors? What environmental prompts triggered their actions? And most importantly, what made collectives so much smarter and more successful than their individual members?

Since then, Nagpal, a professor of computer science at Harvard University’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and an Amazon Scholar, has gone on to build swarming robots. Swarm robotics involves scores of individual mobile robots that mimic the collective behavior demonstrated by animals, e.g. how flocks of birds or schools of fish move together to achieve some end. The robots act as if they, too, were guided by a single mind, or, more precisely, a single computer. Yet they are not.
Instead, they follow a relatively simple set of behavioral rules. Without any external orders or directions, Nagpal’s swarms organize themselves to carry out surprisingly complex tasks, like spontaneously synchronizing their behavior, creating patterns, and even building a tower.
More recently, her lab developed swimming robots that performed some of the same behaviors as a school of fish, such as aggregation, dispersion, and searching. All without a leader.
Nagpal’s work demonstrates both how far we have come in creating self-organizing robot swarms that can perform tasks — and how far we still must go to emulate the complex tapestries woven by nature. It is a gap that Nagpal hopes to close by uncovering the secrets of swarm intelligence to make swarm robots far more useful.
Amorphous computing
The Caribbean fish sparked Nagpal’s imagination because she was already interested in distributed computing, where multiple computers collaborate to solve problems or transfer information without any single computer running the show. At MIT, where she had begun her PhD program, she was drawn to an offshoot of the field called amorphous computing. It investigates how limited, unreliable individuals — from cells to ants to fish — organize themselves to perform often complex tasks consistently without any hierarchies.
Amorphous computing was “hardware agnostic.” This meant that it sought rules that guided this behavior in both living organisms and computer systems. It asked, for example, how identical cells in an embryo form all the organs of an animal, how ants find the most direct route to food, or how fish coordinate their movements. By studying nature, these computer scientists hoped to build computer networks that operated on the same principles.
I got excited about how nature makes these complicated, distributed, mobile networks. Those multi-robot systems became a new direction of my research
After completing her doctoral work on self-folding materials inspired by how cells form tissues, Nagpal began teaching at Harvard. While there, she was visited by her friend James McLurkin, a pioneer in swarm robotics at MIT and iRobot.
“James is the one that got me into robot swarms by introducing me to all the things that ant and termite colonies do,” Nagpal said. “I got excited about how nature makes these complicated, distributed, mobile networks. James was developing that used similar principles to move around and work together. Those multi-robot systems became a new direction of my research.”
She was particularly taken by Namibian termites, which build large-scale nest mounds with multiple chambers and complex ventilation systems, often as high as 8 feet tall.
“As far as we know, there isn’t a blueprint or an a priori distribution between who’s doing the building and who is not. We know the queen does not set the agenda,” she explained. “These colonies start with hundreds of termites and expand their structure as they grow.”
The question fascinated her. “I have no idea how that works,” she said. “I mean, how do you create systems that are so adaptive?”
Finding the rules
Researchers have spent decades answering that question. One way, they found, is to act locally. Take, for example, a flock of geese at a pond. If one or two birds on the outside of the flock see a predator, they grow agitated and fly off, alerting the next nearest birds. The message percolates through flock. Once a certain number of birds have “voted” to fly off, the rest follow without any hesitation. They are not following a leader, only reacting only to the birds next to them.
The same type of local behaviors could be used to make driverless vehicles safer. An autonomous vehicle, Nagpal explains, does not have to reason about all the other cars on the road, only the ones around it. By focusing on nearby vehicles, these distributed systems use less processing power without losing the ability to react to changes very quickly.
Such systems are highly scalable. “Instead of having to reason about everybody, your car only has to reason about its five neighbors,” Nagpal said. “I can make the system very large, but each individual’s reasoning space remains constant. That’s a traditional notion of scalable —the amount of processing per vehicle stays constant, but we’re allowed to increase the size of the system.”
Another key to swarm behavior involves embodied intelligence, the idea that brains interact with the world through bodies that can see, hear, touch, smell, and taste. This is a type of intelligence, too, Nagpal argues.
It’s almost like each individual fish acts like a distributed sensor. Instead of me doing all the work, somebody on the left can say, ‘Hey, I saw something.’ When the group divides the labor so that some of us look out for predators while the rest of us eat, it costs less in terms of energy and resources.
“When you think of an ant, there is not a concentrated set of neurons there,” she said, referring to the ant’s 20-microgram brain. “Instead, there is a huge amount of awareness in the body itself. I may wonder how an ant solves a problem, but I have to realize that somehow having a physical body full of sensors makes that easier. We do not really understand how to think about that still.”
Local actions, scalable behavior, and embodied intelligence are among the factors that make swarms successful. In fact, researchers have shown that the larger a school of fish, the more successful it is at evading predators, finding food, and not getting lost.
“It’s almost like each individual fish acts like a distributed sensor,” Nagpal said. “Instead of me doing all the work, somebody on the left can say, ‘Hey, I saw something.’ When the group divides the labor so that some of us look out for predators while the rest of us eat, it costs less in terms of energy and resources than trying to eat and look out for predators all by yourself.
“What’s really interesting about large insect colonies and fish schools is that they do really complicated things in a decentralized way, whereas people have a tendency to build hierarchies as soon as we have to work together,” she continued. “There is a cost to that, and if we try to do that with that with robots, we replicate the whole management structure and cost of a hierarchy.”
So Nagpal set out to build robots swarms that worked without top-down organization.
Animal behavior
A typical process in Nagpal’s group starts by identifying an interesting natural behavior and trying to discover the rules that generate those actions. Sometimes, they are surprisingly simple.
Take, for example, some behaviors exhibited by Nagpal’s colony of 1,000 interactive robots, each the size of quarter and each communicating with its nearest neighbors wirelessly. The robots will self-assemble into a simple line with a repeating color pattern based on only two rules: a motion rule that allows them to move around any stationary robots, and a pattern rule that tells them to take on the color of their two nearest neighbors.
Other combinations of simple rules spontaneously synchronize the blinking of robot lights, guide migrations, and get the robots to form the letter “K.”
Most impressively, Nagpal and her lab used a behavior found in termites, called stigmergy, to prompt self-organized robot swarms to build a tower. Stigmergy involves leaving a mark on the environment that triggers a specific behavior by another member of the group.
Stigmergy plays a role in how termites build their huge nests. One termite may sense that a spot would make a good place to build, so it puts down its equivalent of a mud brick. When a second termite comes along, the brick triggers it to place its brick there. As the number of bricks increase, the trigger grows stronger and other termites begin building pillars nearby. When they grow high enough, something triggers the termites to begin connecting them with roofs.
“The building environment has become a physical memory of what should happen next,” Nagpal said.
Nagpal used that type of structural memory to prompt her robotic swarm to build a ziggurat tower. The instructions included a motion rule about how to move through the tower and a pattern rule about where to place the blocks. She then built some small, block-carrying robots that built a smaller but no less impressive structure.
Her lab developed a compiler that could generate algorithms that would enable the robots to build specific types of structures — perhaps towers with minarets — by interacting with stigmergic physical memories. One day, algorithm-driven robots could move sandbags to shore up a levee in a hurricane or buttress a collapsed building. They could even monitor coral reefs, underwater infrastructure, and pipelines — if they could swim.
Schooling robofish
From the start, Nagpal wanted to build her own school of robotic fish, but the hardware was simply too clunky to make them practical. That changed with the advent of smartphones, with their low-cost, low-power processors, sensors, and batteries.
In 2018, she got her chance when she received an Amazon Machine Learning Research Award. This allowed her to build Blueswarm, a group of robotic fish that performed tasks like those she observed in the Caribbean years ago.
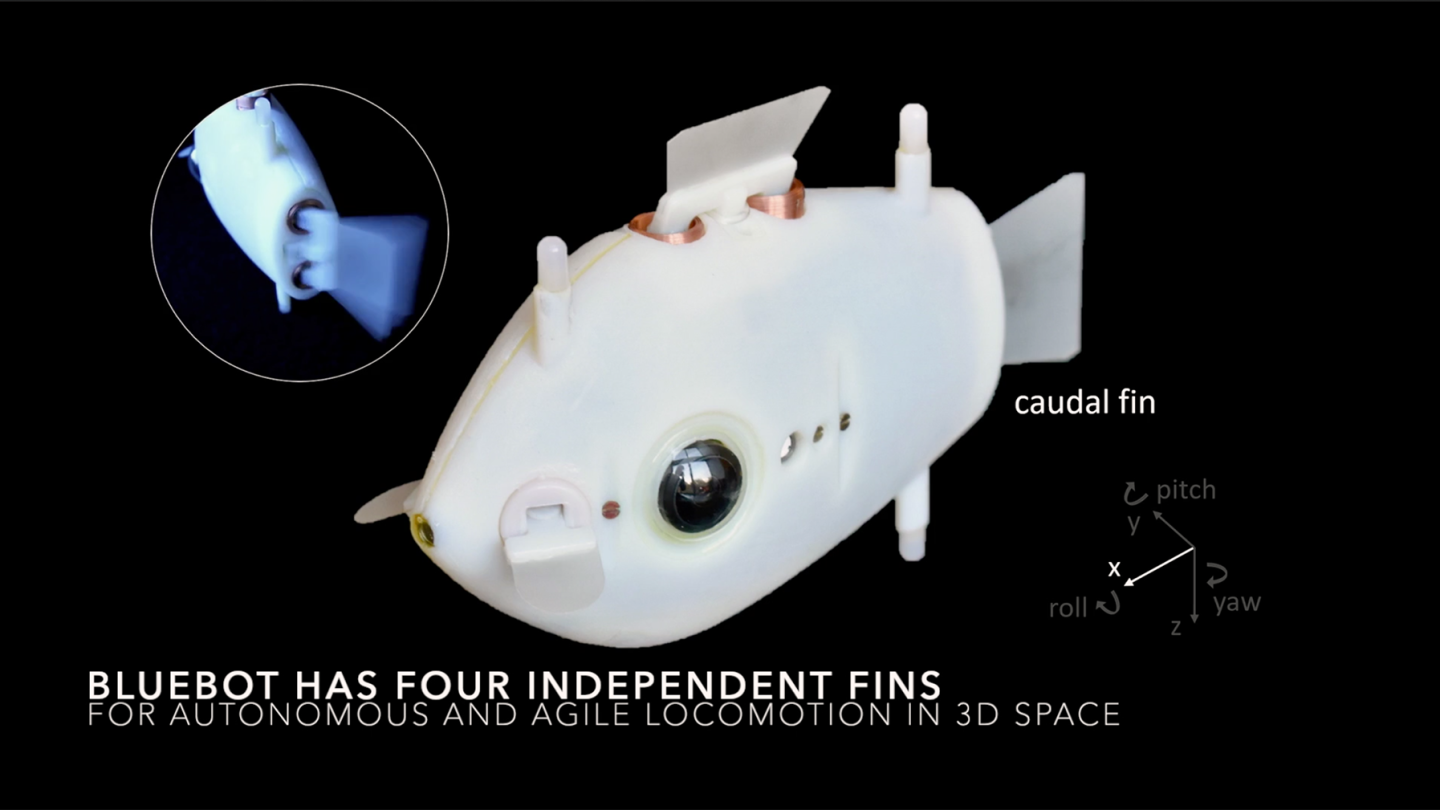
Each Bluebot is just four inches long, but it packs a small Raspberry Pi computer, two fish-eye cameras, and three blue LED lights. It also has a tail (caudal) fin for thrust, a dorsal fin to move up or down, and side fins (pectoral fins) to turn, stop, or swim backward.
Bluebots do not use Wi-Fi, GPS, or external cameras to communicate their positions without error. Instead, she wants to explore what behaviors are possible relying only on cameras and local perception of one’s mates.
Researchers, she explained, find it difficult to rely only upon local perception. It has been difficult to tackle fundamental questions, like how does a robot visually detect other members of the swarm, how they parse information, and what happens when one member moves in front of another. Limiting Bluebot sensing to local perception forces Nagpal and her team to think more deeply about what robots really need to know about their neighbors, especially when data is limited and imprecise.
Bluebots can mimic several fish school behaviors by tracking LED lights on the neighboring fishbots around them. Using 3D cameras and simple algorithms, they estimate distance between lights on neighboring fish. (The closer they appear, the further the fish.)
Nagpal’s seven Bluebots form a circle (called milling) by turning right if there is a robot in front of them. If there is no robot, they turn left. After a few moments, the school will be swimming in a circle, a formation fish use to trap prey.
They can also search for a target flashing red light. First, the school disperses within the tank. When a Bluebot finds the red LED, it begins to flash its lights. This signals the nearest Bluebots to aggregate, followed by the rest. If a single robot had to conduct a similar search by itself, it would take significantly longer.
These behaviors are impressive for robots, but represent a small subset of fish school behaviors. They also take place in a static fish tank populated by only one school of robot fish. To go further, Nagpal wants to improve their sensors and perhaps use machine learning to discover new rules that could be combined to produce the aquatic equivalent of a tower.
In the end, though, Nagpal does not want to build a better fish. Instead, she wants to apply the lessons she has learned to real-world robots. She is doing just that during a sabbatical working at Amazon, which operates the largest fleet of robots — more than 200,000 units — in the world.
Practical uses
Nagpal had little previous experience working in industry, but she jumped at the chance to work with Amazon.
“There are few others with hundreds of robots moving around safely in a facility space,” she said. “And the opportunity to work on algorithms in a deployed system was very exciting."
There are few others [like Amazon] with hundreds of robots moving around safely in a facility space. And the opportunity to work on algorithms in a deployed system was very exciting.
“The other factor is that Amazon’s robots do a mix of centralized and decentralized decision-making," she continued. "The robots plan their own paths, but they also use the cloud to know more. That lets us ask: Is it better to know everything about all your neighbors all the time? Or is it better to only know about the neighbors that are closer to you?”
Her current focus is on sortation centers, where robots help route packages to shipping stations sorted by ZIP codes. Not surprisingly, robots setting out from multiple points to dozens of different locations require a degree of coordination. Amazon’s robots are already aware of other robots. If they see one, they will choose an alternate route. But what path should they take, Nagpal asks. She wants to make sure those robots are making the most effective possible choices.
Cities already manage this. They limit access to some roads, change speed limits, and add one-way streets. Computer networks do it as well, rerouting traffic when packet delivery slows down.
Some of those concepts, such as one-way travel lanes, also work in sortation centers. They could act as stigmergic signals to guide robot behavior. She also believes there might be a way to create simple swarm behaviors that enable robots to react to advanced data about incoming packages.
Once her sabbatical is over, Nagpal plans to return to the lab. She wants to keep working on her Bluebots, improving their vision, and turning them loose in environments that look more like the coral reef she went snorkeling in 25 years ago.
She is also dreaming of swarms of bigger robots for use in construction or trash collection.
“Maybe we could do what Amazon is doing, but do it outside,” she said. “We could have swarms of robots that actually do some sort of practical task. At Amazon, that task is delivery. But given Boston’s snowstorms, I think shoveling the sidewalks would be nice.”